The TRUNCATE TABLE statement in SQL is a powerful command used to swiftly remove all rows from a table, leaving the table structure intact. This operation is often favored over the DELETE statement for its efficiency, especially when dealing with large datasets.
In this article, We will learn about SQL TRUNCATE TABLE in detail with the help of various examples and so on.
SQL TRUNCATE TABLE
- The
TRUNCATE TABLE statement in SQL is used to quickly remove all rows from a table, effectively emptying the table.
- Unlike the
DELETE statement, which removes rows one at a time and can be rolled back (depending on the database support for transactions).
TRUNCATE TABLE is usually more efficient because it deallocates the data pages used by the table, rather than performing individual row deletions.
Note: The TRUNCATE command can not be used to Truncate a Column or Database in SQL.
Syntax
TRUNCATE TABLE Syntax is:
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
Example of SQL TRUNCATE TABLE
Let's understand TRUNCATE in SQL with examples. Here we will look at different examples of the SQL TRUNCATE TABLE command.
First, we will create a demo SQL database and table, on which we will use the TRUNCATE TABLE command.
SQL CREATE DATABASE GEEKSFORGEEKS; USE GEEKSFORGEEKS; CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE( EMP_ID INT(4), NAME VARCHAR(20), AGE INT(3), DOB DATE, SALARY DECIMAL(7,2)); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES(121,'AJAY KUMAR',23,'1987-09-12',23456.32); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES(132,'BOBBY DEOL',34,'1989-02-19',84164.56); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES(246,'ELVISH SMITH',27,'1996-01-29',51876.97); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES(955,'GEORGE CLARKE',31,'1992-09-21',91451.64); INSERT INTO EMPLOYEE VALUES(729,'MONICA GELLER',28,'1985-11-18',98329.43);
The following table will be created.
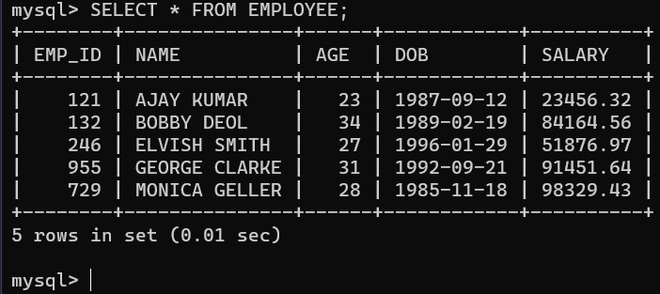 Records in the table
Records in the tableExample of TRUNCATE TABLE in SQL
In this example, we will Truncate the created table.
Query:
TRUNCATE TABLE EMPLOYEE;
Output:
 Truncating data
Truncating dataAfter truncating data of our table, the data of our table has been erased but the structure is preserved so now if we perform SELECT * FROM EMPLOYEE command on our table we will see everything is erased and an empty set is being returned.
 No data is returned
No data is returnedBut let's now check whether the structure of the table is deleted or it has been preserved so we again use the DESC command to see the structure of the table and we will see that the structure remains as it is.
 Structure is preserved
Structure is preservedSQL TRUNCATE vs DELETE
Here's a comparison of the TRUNCATE and DELETE statements in SQL presented in a tabular format:
| Feature | TRUNCATE TABLE | DELETE |
|---|
| Operation | Removes all rows from a table | Removes rows based on a WHERE clause or all rows if no condition is specified |
| WHERE Clause | Not supported | Supported |
| Transaction Logging | Minimal logging (usually faster) | Fully logged (can be slower) |
| Rollback (Transaction Support) | Generally cannot be rolled back in some DBMS | Can be rolled back if within a transaction |
| Triggers | Does not fire triggers | Fires triggers |
| Foreign Key Constraints | Cannot truncate a table referenced by a foreign key (without disabling the constraint) | Can delete rows in a table referenced by a foreign key |
| Identity Reset | Resets identity seed value (auto-increment counter) | Does not reset the identity seed value |
| Performance | Generally faster for large data volumes | Can be slower, especially for large data volumes |
| Usage | Typically used to quickly empty a table | Used to remove specific rows based on a condition |
| Space Reclamation | Releases the storage space used by the table rows | Does not automatically reclaim space, may require a VACUUM or similar command |
| Table Structure | Retains the table structure, constraints, and indexes | Retains the table structure, constraints, and indexes |
This table should help clarify the differences between TRUNCATE TABLE and DELETE
SQL TRUNCATE vs DROP
Here's a comparison of the SQL TRUNCATE TABLE and DROP TABLE commands in a tabular format:
| Feature | TRUNCATE TABLE | DROP TABLE |
|---|
| Operation | Removes all rows from a table, leaving the structure intact. | Deletes the entire table, including its structure. |
| Speed | Generally faster than DELETE since it deallocates data pages. | Fast operation since it removes both data and structure. |
| Transaction Log | Minimal logging; typically logs page deallocations only. | Fully logged; the entire table drop is recorded. |
| Table Structure | Retained; only the data is removed. | Deleted; table structure and data are both removed. |
| Auto-increment Counter | Resets the auto-increment counter to the seed value (if present). | No impact, as the entire table is removed. |
| Triggers | Triggers are not fired. | Not applicable, as the table no longer exists. |
| Foreign Key Constraints | Cannot truncate a table if it is referenced by a foreign key. | Cannot drop a table if other tables reference it unless the foreign key constraint is removed first. |
| Usage | Used when you need to remove all data from a table but keep the table itself. | Used when you want to completely remove the table from the database. |
| Recovery | Data cannot be recovered unless a backup is available (depends on the database system). | The table and its data cannot be recovered unless a backup is available. |
| Permissions Required | Requires ALTER permission on the table. | Requires DROP permission on the table. |
Important Points About SQL TRUNCATE TABLE
- TRUNCATE TABLE is used to empty a table by removing all rows, but it retains the table structure.
- TRUNCATE TABLE is ideal for quickly removing all data from a table without deleting the table structure, making it efficient for data cleanup operations
TRUNCATE TABLE is faster and uses fewer system and transaction logs compared to DELETE. - However,
TRUNCATE TABLE typically cannot be rolled back if executed within a transaction.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the TRUNCATE TABLE command is a highly efficient method for quickly removing all rows from a table while preserving its structure. It is particularly useful in scenarios where you need to clear a table without deleting it, offering a performance advantage over the DELETE statement due to minimal transaction logging.
Similar Reads
SQL Interview Questions Are you preparing for a SQL interview? SQL is a standard database language used for accessing and manipulating data in databases. It stands for Structured Query Language and was developed by IBM in the 1970's, SQL allows us to create, read, update, and delete data with simple yet effective commands.
15+ min read
SQL Tutorial Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard language used to interact with relational databases. Whether you want to create, delete, update or read data, SQL provides the structure and commands to perform these operations. SQL is widely supported across various database systems like MySQL, Oracl
8 min read
Non-linear Components In electrical circuits, Non-linear Components are electronic devices that need an external power source to operate actively. Non-Linear Components are those that are changed with respect to the voltage and current. Elements that do not follow ohm's law are called Non-linear Components. Non-linear Co
11 min read
SQL Commands | DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands SQL commands are crucial for managing databases effectively. These commands are divided into categories such as Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), Data Query Language (DQL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL). In this article, we will e
7 min read
SQL Joins (Inner, Left, Right and Full Join) SQL joins are fundamental tools for combining data from multiple tables in relational databases. Joins allow efficient data retrieval, which is essential for generating meaningful observations and solving complex business queries. Understanding SQL join types, such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JO
5 min read
Spring Boot Tutorial Spring Boot is a Java framework that makes it easier to create and run Java applications. It simplifies the configuration and setup process, allowing developers to focus more on writing code for their applications. This Spring Boot Tutorial is a comprehensive guide that covers both basic and advance
10 min read
Normal Forms in DBMS In the world of database management, Normal Forms are important for ensuring that data is structured logically, reducing redundancy, and maintaining data integrity. When working with databases, especially relational databases, it is critical to follow normalization techniques that help to eliminate
7 min read
Class Diagram | Unified Modeling Language (UML) A UML class diagram is a visual tool that represents the structure of a system by showing its classes, attributes, methods, and the relationships between them. It helps everyone involved in a project—like developers and designers—understand how the system is organized and how its components interact
12 min read
SQL Query Interview Questions SQL or Structured Query Language, is the standard language for managing and manipulating relational databases such as MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL. It serves as a powerful tool for efficiently handling data whether retrieving specific data points, performing complex analysis, or modifying database
15+ min read
3-Phase Inverter An inverter is a fundamental electrical device designed primarily for the conversion of direct current into alternating current . This versatile device , also known as a variable frequency drive , plays a vital role in a wide range of applications , including variable frequency drives and high power
13 min read