The SUM() function in SQL is one of the most commonly used aggregate functions. It allows us to calculate the total sum of a numeric column, making it essential for reporting and data analysis tasks. Whether we're working with sales data, financial figures, or any other numeric information, the SUM() function can help us quickly compute the sum of values based on specific conditions.
In this article, we will explain the SUM() function in detail, provide multiple examples, and highlight its use in various SQL queries to enhance our understanding.
What is the SQL SUM() Function?
The SUM() function in SQL is used to calculate the total of a numeric column or expression. This aggregate function sums the values in the specified column and returns a single result. It is commonly used in combination with other SQL clauses like WHERE, GROUP BY, and HAVING to refine the data set and calculate sums based on specific conditions.
Syntax
SELECT SUM(column_name)
FROM table_name
WHERE condition;
Key Terms
- column_name: The numeric column whose values you want to sum.
- table_name: The name of the table from which to retrieve the data.
- condition: (Optional) A condition to filter the rows before performing the aggregation.
Examples of SQL SUM() Function
In this section, we will demonstrate the usage of the SUM() function with examples using a sample table called Sales, which stores sales data such as the Product, Quantity, and Price. This simple dataset will help us understand how the SUM() function works in SQL to calculate totals, sums of distinct values, and more.
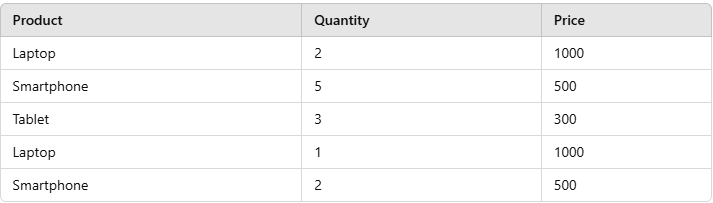 Sales Table
Sales TableExample 1: Using SUM() with One Column
In this example, we will use the SUM() function to calculate the total value of a specific column, such as total sales or total salary.
Query:
SELECT SUM(Salary) AS TotalSalary
FROM Employees;
Output
Explanation:
This query calculates the sum of the Salary column in the Employees table. This output shows the total salary paid to employees in the database.
Example 2: Using SUM() with an Expression
We can also use the SUM() function with an expression to calculate sums based on some logic or mathematical operations.
Query:
SELECT SUM(Price * Quantity) AS TotalRevenue
FROM Sales;
Output
Explanation:
This query multiplies Price and Quantity for each record in the Sales table and then calculates the sum of those values. This is useful for calculating the total revenue generated from sales.
Example 3: Using SUM() with GROUP BY
When we want to calculate the sum of values within groups, we can use the GROUP BY clause along with SUM(). This is particularly useful for grouping data by categories such as departments, products, or cities.
Query:
SELECT Department, SUM(Salary) AS DepartmentSalary
FROM Employees
GROUP BY Department;
Output
| Department | DepartmentSalary |
|---|
| HR | 200,000 |
| Sales | 300,000 |
| IT | 250,000 |
Explanation:
This query groups employees by their Department and then calculates the total salary for each department.
Example 4: Using SUM() with DISTINCT
If we want to sum only the distinct values in a column, we can use the DISTINCT keyword with the SUM() function.
Query:
SELECT SUM(DISTINCT Price) AS TotalDistinctPrice
FROM Products;
Output:
| TotalDistinctPrice |
|---|
| 500,000 |
Explanation:
This query sums only the unique values in the Price column of the Products table. Duplicate values are excluded from the sum.
Example 5: Using SUM() with HAVING
The HAVING clause can be used in combination with GROUP BY to filter groups based on the result of the SUM() function. This allows you to apply conditions to the grouped data after the aggregation.
Query:
SELECT Department, SUM(Salary) AS DepartmentSalary
FROM Employees
GROUP BY Department
HAVING SUM(Salary) > 200,000;
Output
| Department | DepartmentSalary |
|---|
| Sales | 300,000 |
| IT | 250,000 |
Explanation:
This query calculates the total salary per department and then filters the result to include only those departments where the total salary is greater than 200,000.
Best Practices for Using the SQL SUM() Function
- Use with Indexes: When summing a large dataset, it’s important to have indexes on the columns you’re filtering by, such as dates or categories. This will improve the performance of your query.
- Use GROUP BY to Categorize Data: The SUM() function works perfectly with GROUP BY. It helps you summarize data efficiently by different categories like departments or regions.
- Avoid Summing Non-Numeric Values: Ensure that the column you are summing contains only numeric values. Summing non-numeric values can result in errors.
- Consider Using Aliases: Always use aliases for SUM() results for better readability and clarity in your output.
Conclusion
The SQL SUM() function is a powerful tool for aggregating numeric data. Whether we need to calculate the total salary, revenue, or count items, the SUM() function simplifies these tasks and helps us derive valuable insights from our database. By using it with different clauses like DISTINCT, GROUP BY, and HAVING, we can tailor our queries to specific conditions, making our analysis more efficient. The SUM() function is especially useful for generating summary reports and analyzing financial, sales, or inventory data.
Explore
SQL Tutorial
6 min read
Basics
Queries & Operations
SQL Joins & Functions
Data Constraints & Aggregate Functions
Advanced SQL Topics
Database Design & Security
My Profile