Ruby | Decision Making (if, if-else, if-else-if, ternary) | Set - 1
Last Updated : 15 Feb, 2023
Decision Making in programming is similar to decision making in real life. In programming too, a certain block of code needs to be executed when some condition is fulfilled. A programming language uses control statements to control the flow of execution of the program based on certain conditions. These are used to cause the flow of execution to advance and branch based on changes to the state of a program. Similarly, in Ruby, the if-else statement is used to test the specified condition.
Decision-Making Statements in Ruby:
if statement
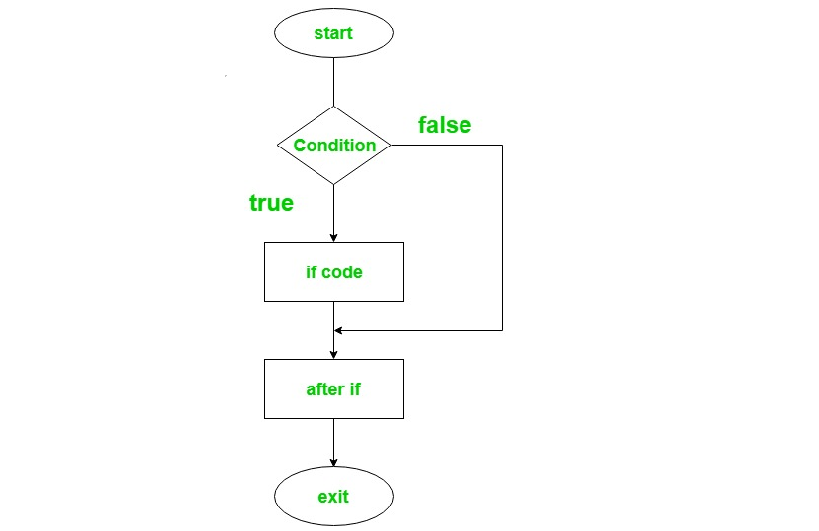
If statement in Ruby is used to decide whether a certain statement or block of statements will be executed or not i.e if a certain condition is true then a block of statement is executed otherwise not.
Syntax:
if (condition) # statements to be executed end
Flowchart:
Example:
Ruby # Ruby program to illustrate if statement a = 20 # if condition to check whether # your age is enough for voting if a >= 18 puts "You are eligible to vote." end
Output:
You are eligible to vote.
if - else Statement
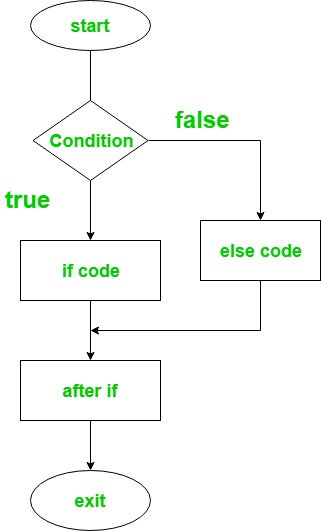
In this 'if' statement used to execute block of code when the condition is true and 'else' statement is used to execute a block of code when the condition is false.
Syntax:
if(condition) # code if the condition is true else # code if the condition is false end
Flowchart:
Example:
Ruby # Ruby program to illustrate # if - else statement a = 15 # if condition to check # whether age is enough for voting if a >= 18 puts "You are eligible to vote." else puts "You are not eligible to vote." end
Output:
You are not eligible to vote.
If – elsif - else ladder Statement
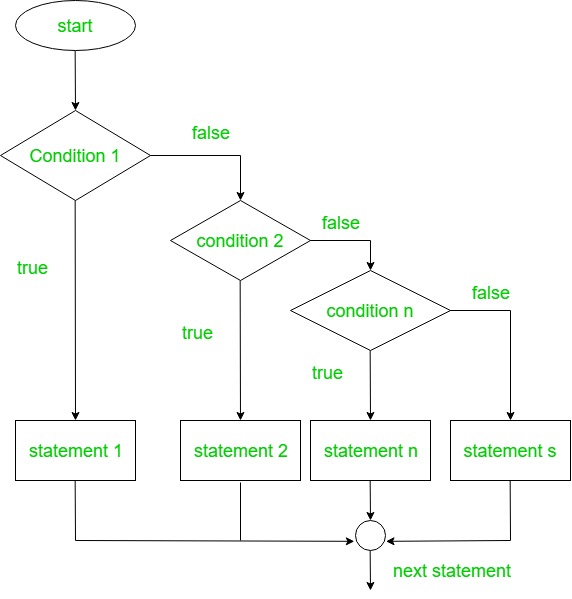
Here, a user can decide among multiple options. 'if' statements are executed from the top down. As soon as one of the conditions controlling the 'if' is true, the statement associated with that 'if' is executed, and the rest of the ladder is bypassed. If none of the conditions is true, then the final else statement will be executed.
Syntax:
if(condition1) # code to be executed if condition1is true elsif(condition2) # code to be executed if condition2 is true else(condition3) # code to be executed if condition3 is true end
Flowchart:
Example:
Ruby # Ruby program to illustrate the # if - else - if statement a = 78 if a < 50 puts "Student is failed" elsif a >= 50 && a <= 60 puts "Student gets D grade" elsif a >= 70 && a <= 80 puts "Student gets B grade" elsif a >= 80 && a <= 90 puts "Student gets A grade" elsif a >= 90 && a <= 100 puts "Student gets A+ grade" end
Output:
Student gets B grade
Ternary Statement
In Ruby ternary statement is also termed as the shortened if statement. It will first evaluate the expression for true or false value and then execute one of the statements. If the expression is true, then the true statement is executed else false statement will get executed.
Syntax:
test-expression ? if-true-expression : if-false-expression
Example:
Ruby # Ruby program to illustrate the # Ternary statement # variable var = 5; # ternary statement a = (var > 2) ? true : false ; puts a
Output:
true