Implementation of React.memo() and useMemo() in React
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
React.memo allows functional component to have same optimization as Pure Component provides for class-based components. useMemo is for memoizing function's calls inside functional component.
What is React.memo() ?
React.memo() is a higher-order component (HOC) provided by React that memoizes functional components. It means that it caches the result of the component’s rendering based on its props, and re-renders only when the props have changed.
Syntax of React.memo():
const MemoizedComponent = React.memo(FunctionalComponent);
What is useMemo() ?
useMemo() is a React Hook used to memoize the result of expensive computations within functional components. It memorizes the value returned by a provided function and re-calculates it only when the dependencies change.
Syntax of useMemo():
const memoizedValue = useMemo(() => computeExpensiveValue(dep1, dep2), [dep1, dep2]);
Features:
- Efficient Rendering: Utilize React.memo() to prevent unnecessary re-renders of components, ensuring optimal performance, especially with complex UIs.
- Memoization of Filtered Data: Employ useMemo() to memoize the filtered data based on user input, reducing redundant computations and enhancing responsiveness.
- Dynamic Filtering: Implement dynamic filtering functionality, allowing users to search and filter through large datasets with minimal performance impact.
- Real-time Updates: Ensure that the list component updates in real-time as users interact with the filter input, providing a seamless and responsive user experience.
- Scalability: Design the solution to handle large datasets efficiently, ensuring that performance remains consistent even as the volume of data grows.
- Easy Integration: The optimized list component can be easily integrated into various React applications, providing developers with a reusable and performant solution for managing lists.
Steps to Create a React App:
Step 1: Create a new React.js project and install the required dependencies:-
npx create-react-app my-react-app.
Step 2: Navigate to the root directory of your project using the following command.
cd my-react-app
Exaplanation:
- main.jsx: This will be the main component. It manages the state of the todo list and renders TodoList.
- App.jsx: This component receives the list of todos as props and renders individual TodoItem components.
- TodoItem.jsx: This component renders a single todo item and handles deletion.
- In a Todo List application, React.memo() can be applied to functional components like TodoItem to memoize their rendering process, preventing unnecessary re-renders when their props haven't changed.
- useMemo() can be used to memoize the filtered list of todos based on a filter input, recalculating it only when the todos list or filter input changes.
Example: Below is an example of both React.memo() and useMemo().
JavaScript import React, { useState, useMemo } from 'react'; const TodoList = React.memo(({ todos, onDelete }) => { console.log('Rendering TodoList'); if (todos.length === 0) { return <p className="message"> Todo list is empty. </p>; } return ( <ul className="todo-list"> {todos.map((todo, index) => ( <li key={index}> {todo} <button className="buttons" onClick={() => onDelete(index)}> Delete </button> </li> ))} </ul> ); }); const TodoApp = () => { const [filter, setFilter] = useState(''); const [newTodo, setNewTodo] = useState(''); const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]); // Memoize the filtered todos based on the filter value const filteredTodos = useMemo(() => { console.log('Filtering todos'); return todos.filter(todo => todo.toLowerCase().includes(filter.toLowerCase())); }, [todos, filter]); const handleAddTodo = () => { if (newTodo !== '') { setTodos(prevTodos => [...prevTodos, newTodo]); setNewTodo(''); } }; const handleDeleteTodo = (index) => { setTodos(prevTodos => prevTodos.filter((_, i) => i !== index)); }; return ( <div className="container"> <div className="input-container"> <h1 className="heading">TODO-LIST</h1> <input type="text" placeholder="Add a todo" value={newTodo} onChange={(e) => setNewTodo(e.target.value)} /> <button className="buttons" onClick={handleAddTodo}> Add </button> </div> <div className="input-container"> <input type="text" placeholder="Filter todos" value={filter} onChange={(e) => setFilter(e.target.value)} /> </div> { filteredTodos.length === 0 && todos.length !== 0 && ( <p className="message"> No matching todos found. </p> )} <TodoList todos={filteredTodos} onDelete={handleDeleteTodo} /> </div> ); }; export default TodoApp; Output:
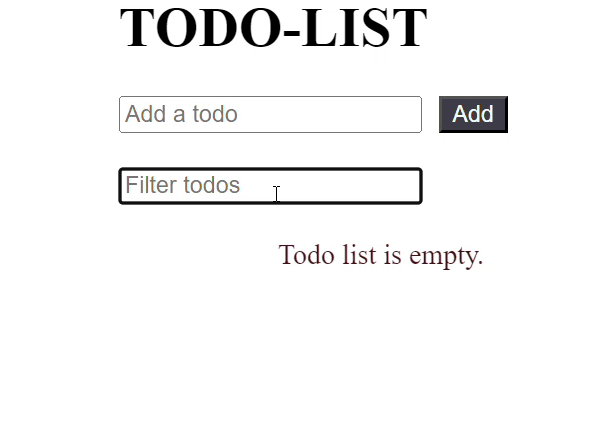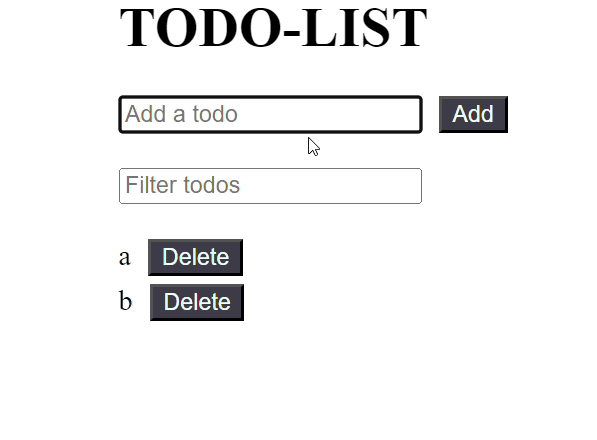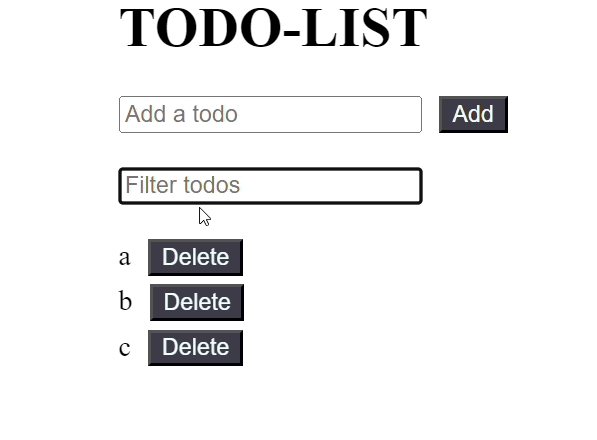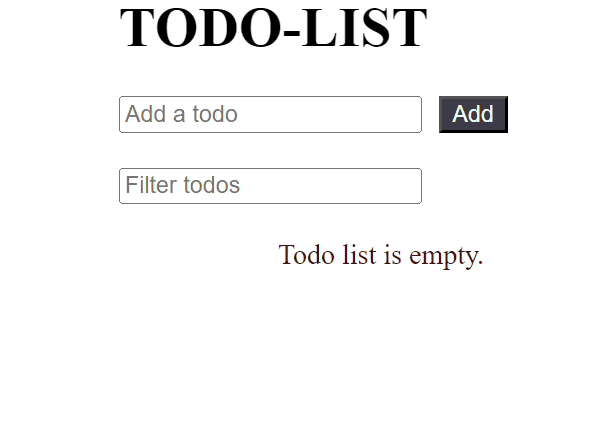 Output
Output