Queue is a linear data structure that stores items in a First In First Out (FIFO) manner. The item that is added first will be removed first. Queues are widely used in real-life scenarios, like ticket booking, or CPU task scheduling, where first-come, first-served rule is followed.
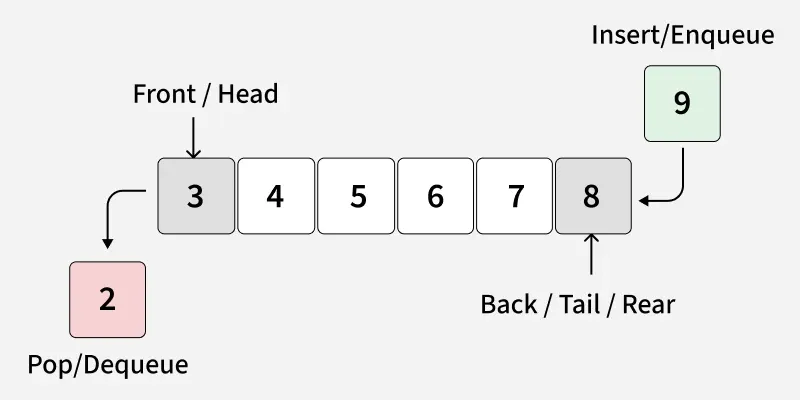
There are various ways to implement a queue in Python by following ways:
1. Using list - Inefficient
Lists can be used as queues, but removing elements from front requires shifting all other elements, making it O(n).
Python q = [] q.append('a') q.append('b') q.append('c') print("Initial queue:", q) print("Elements dequeued from queue:") print(q.pop(0)) print(q.pop(0)) print(q.pop(0)) print("Queue after removing elements:", q) OutputInitial queue: ['a', 'b', 'c'] Elements dequeued from queue: a b c Queue after removing elements: []
Explanation: We added elements using append() and removed from the front using pop(0). After removing all elements, queue is empty.
2. Using collections.deque - Efficient
deque (double-ended queue) is preferred over a list for queues because both append() and popleft() run in O(1) time.
Python from collections import deque q = deque() q.append('a') q.append('b') q.append('c') print("Initial queue:", q) print("Elements dequeued from the queue:") print(q.popleft()) print(q.popleft()) print(q.popleft()) print("Queue after removing elements:", q) OutputInitial queue: deque(['a', 'b', 'c']) Elements dequeued from the queue: a b c Queue after removing elements: deque([])
Explanation: popleft() efficiently removes the first element without shifting, making deque ideal for queues.
3. Using queue.Queue - Efficient and Thread Safe
Python’s queue module provides a thread-safe FIFO queue. You can specify a maxsize. Key Methods are:
- put(item) / put_nowait(item) – Add an element.
- get() / get_nowait() – Remove an element.
- empty() – Check if the queue is empty.
- full() – Check if the queue is full.
- qsize() – Get current size of the queue.
Python from queue import Queue q = Queue(maxsize=3) print("Initial size:", q.qsize()) q.put('a') q.put('b') q.put('c') print("Is full:", q.full()) print("Elements dequeued from the queue:") print(q.get()) print(q.get()) print(q.get()) print("Is empty:", q.empty()) q.put(1) print("Is empty:", q.empty()) print("Is full:", q.full()) OutputInitial size: 0 Is full: True Elements dequeued from the queue: a b c Is empty: True Is empty: False Is full: False
Explanation: queue.Queue class handles thread-safe operations. You can check fullness or emptiness before adding or removing elements.
To practice problems related to Queue, refer to this article Queue Data Structure
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice
My Profile