Build a REST API using Flask - Python
Last Updated : 22 Nov, 2025
REST (Representational State Transfer) is an approach used to build web services that interact using standard HTTP methods such as GET, POST, PUT and DELETE. APIs built using REST follow predictable rules, making them suitable for data exchange between applications.
In this article, we will build a REST API using Python’s Flask framework through two methods:
- Using Flask
- Using Flask-RESTful
Before starting this, let us install the necessary libraries.
Installation
Install all required packages in one command:
pip install flask flask-restful
This installs both Flask and Flask-RESTful, preparing the environment for building APIs using both methods.
Using Flask
This method use Flask framework only. Here, API is created using regular functions called “routes.” Flask checks the URL the user visits and executes the matching function. One route sends a simple message, and another route receives a number from the URL and returns its square.
Python from flask import Flask, jsonify app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/', methods=['GET']) def home(): return jsonify({'data': 'hello world'}) @app.route('/home/<int:num>', methods=['GET']) def disp(num): return jsonify({'data': num ** 2}) if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True) Explanation:
- app = Flask(name) creates the main application object where routes are defined.
- Home Route ('/') returns a simple JSON message when opened in a browser.
- Square Route ('/home/<int:num>') receives a number through the URL and returns its square.
- app.run(debug=True) starts the server and reloads automatically while developing.
Output
Open your browser and visit - http://127.0.0.1:5000/. You will see a JSON message returned as below:
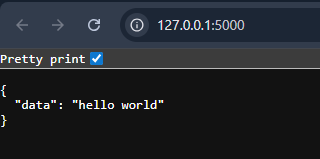 Browser output showing the home route response
Browser output showing the home route responseNow, In the browser, visit: http://127.0.0.1:5000/home/22. The API reads the number 22 and returns its square.
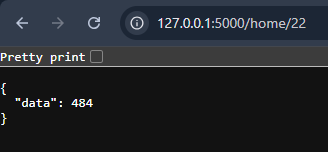 Browser output showing square of the number received from the URL.
Browser output showing square of the number received from the URL.This shows how passing values through the URL works in a REST API.
Using Flask-RESTful
This method uses the Flask-RESTful extension, which organizes APIs using classes called resources. Each resource represents an endpoint and contains methods such as get(), which run when a GET request is made. One resource returns a message, and another resource calculates the square of a number.
Python from flask import Flask, jsonify from flask_restful import Resource, Api app = Flask(__name__) api = Api(app) class Hello(Resource): def get(self): return jsonify({'message': 'hello world'}) class Square(Resource): def get(self, num): return jsonify({'square': num ** 2}) api.add_resource(Hello, '/') api.add_resource(Square, '/square/<int:num>') if __name__ == '__main__': app.run(debug=True) Explanation:
- Resource represents an API endpoint using a class.
- Hello Resource (/) returns a JSON message when accessed.
- Square Resource (/square/<int:num>) accepts a number in the URL and returns its square.
- api.add_resource() connects each class to a specific route.
Output
Open your browser and visit: http://127.0.0.1:5000/
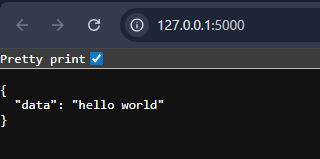 Browser output showing message returned from Hello Resource
Browser output showing message returned from Hello ResourceNow, In the browser, visit: http://127.0.0.1:5000/square/3
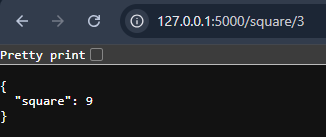 Browser output showing the square returned by Square Resource
Browser output showing the square returned by Square ResourceThis shows how Flask-RESTful handles different routes cleanly using class-based resources.
Explore
Python Fundamentals
Python Data Structures
Advanced Python
Data Science with Python
Web Development with Python
Python Practice
My Profile