Sleeping Barber problem in Process Synchronization
Last Updated : 03 Sep, 2025
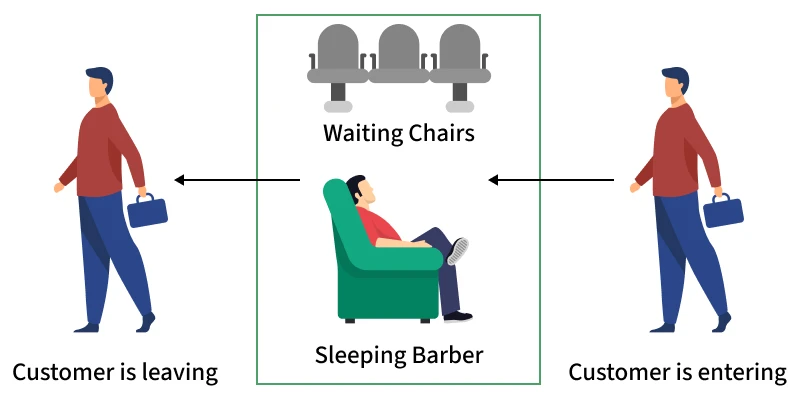
The Sleeping Barber Problem is a classic process synchronization problem that demonstrates how to manage concurrent processes. It models a barbershop scenario with a barber chair and a waiting room, where synchronization mechanisms like semaphores are used to manage access. The rules ensure that only one customer occupies the barber chair at a time, the barber works whenever a customer is present, and sleeps when no customers are waiting.
Problem statement
1. One barber, one barber chair, and N waiting chairs.
2. If no customer, the barber sleeps in his chair.
3. A customer who arrives:
- Wakes the barber if he is sleeping.
- Waits if there are free chairs.
- Leaves if no chairs are available.
The challenge is to safely synchronize customers and the barber so that:
- Only one customer is in the barber’s chair at a time.
- Customers either wait or leave when seats are full.
- The barber works when customers are available and sleeps otherwise.
 Sleeping Barber Problem
Sleeping Barber ProblemSynchronization Solution
We use three semaphores:
- Customers counts waiting customers.
- Barber signals when the barber is ready.
- Mutex ensures mutual exclusion when accessing chairs.
Algorithm
Customer
- Tries to sit (if free seats > 0).
- If seated increments waiting count and signals the barber.
- If no seat leaves.
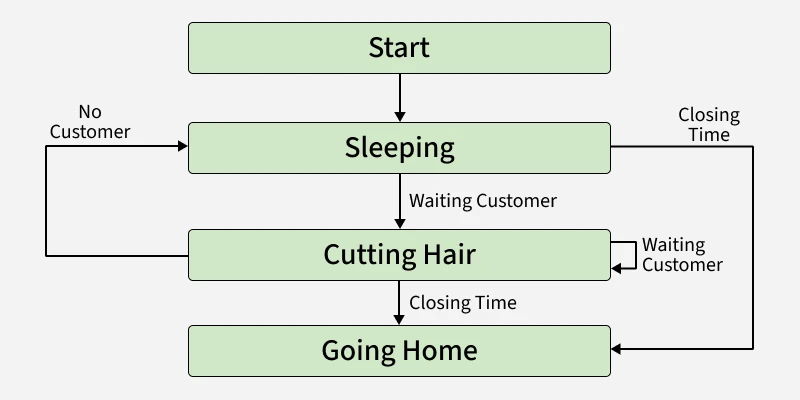
Barber
- Sleeps if no customers.
- Wakes up when signaled.
- Serves one customer at a time.
 Sleeping Barber Problem flowchart
Sleeping Barber Problem flowchartPseudocode
Semaphore Customers = 0;
Semaphore Barber = 0;
Mutex Seats = 1;
int FreeSeats = N;
Barber {
while(true) {
down(Customers); // wait for customer
down(Seats);
FreeSeats++; // one waiting chair becomes free
up(Barber); // barber ready
up(Seats);
// cut hair
}
}
Customer {
while(true) {
down(Seats);
if(FreeSeats > 0) {
FreeSeats--; // take a seat
up(Customers); // notify barber
up(Seats);
down(Barber); // wait for barber
// get haircut
} else {
up(Seats); // leave if no seat
}
}
}
Explanation:
- Customers counts waiting customers, Barber signals barber availability, Seats (mutex) protects chair count, and FreeSeats = N tracks empty chairs.
- Barber loop: Waits (down(Customers)) until a customer arrives. Locks seats, frees one chair (FreeSeats++), signals the barber is ready (up(Barber)), unlocks seats, and cuts hair.
- Customer loop: Locks seats. If a chair is free (FreeSeats > 0), takes it (FreeSeats--), notifies barber (up(Customers)), unlocks seats, then waits for barber (down(Barber)) to get haircut. If no seat is free, unlocks seats and leaves.
Here's the code implementation of the Sleeping Barber Problem using semaphores:
C++ #include <iostream> #include <thread> #include <vector> #include <mutex> #include <condition_variable> #include <random> #include <chrono> std::mutex mtx; std::condition_variable cv; std::vector<int> waiting; const int NUM_CHAIRS = 3; void barber() { while (true) { std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mtx); std::cout << "Barber is sleeping..." << std::endl; cv.wait(lock, []{ return !waiting.empty(); }); int cust = waiting.front(); waiting.erase(waiting.begin()); std::cout << "Barber cutting hair of customer " << cust << std::endl; lock.unlock(); std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(rand() % 3 + 1)); std::cout << "Barber finished with customer " << cust << std::endl; lock.lock(); cv.notify_one(); } } void customer(int i) { std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(rand() % 4 + 1)); std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(mtx); if (waiting.size() < NUM_CHAIRS) { waiting.push_back(i); std::cout << "Customer " << i << " waiting" << std::endl; lock.unlock(); cv.notify_one(); lock.lock(); cv.wait(lock, []{ return waiting.front() != i; }); std::cout << "Customer " << i << " got haircut" << std::endl; } else { std::cout << "Customer " << i << " left (no seat)" << std::endl; } } int main() { std::thread t1(barber); for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { std::thread t(customer, i); t.detach(); } t1.join(); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <time.h> pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_cond_t cv = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; int waiting[3]; int waiting_count = 0; const int NUM_CHAIRS = 3; void* barber(void* arg) { while (1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); while (waiting_count == 0) { pthread_cond_wait(&cv, &mtx); } int cust = waiting[0]; for (int i = 0; i < waiting_count - 1; ++i) { waiting[i] = waiting[i + 1]; } waiting_count--; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); printf("Barber cutting hair of customer %d\n", cust); sleep(rand() % 3 + 1); printf("Barber finished with customer %d\n", cust); pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); pthread_cond_signal(&cv); } return NULL; } void* customer(void* arg) { int i = *((int*)arg); sleep(rand() % 4 + 1); pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx); if (waiting_count < NUM_CHAIRS) { waiting[waiting_count++] = i; printf("Customer %d waiting\n", i); pthread_cond_signal(&cv); while (waiting[0] != i) { pthread_cond_wait(&cv, &mtx); } printf("Customer %d got haircut\n", i); } else { printf("Customer %d left (no seat)\n", i); } pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx); return NULL; } int main() { pthread_t t1, t[5]; pthread_create(&t1, NULL, barber, NULL); for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { int* arg = malloc(sizeof(int)); *arg = i; pthread_create(&t[i], NULL, customer, arg); } for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { pthread_join(t[i], NULL); } pthread_join(t1, NULL); return 0; } import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; import java.util.Random; public class BarberShop { private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private final Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); private final int[] waiting = new int[3]; private int waitingCount = 0; private static final int NUM_CHAIRS = 3; private Random random = new Random(); public void barber() { while (true) { lock.lock(); try { while (waitingCount == 0) { try { condition.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } int cust = waiting[0]; for (int i = 0; i < waitingCount - 1; ++i) { waiting[i] = waiting[i + 1]; } waitingCount--; System.out.println("Barber cutting hair of customer " + cust); } finally { lock.unlock(); } try { Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(3) + 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("Barber finished with customer " + cust); lock.lock(); try { condition.signal(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } } public void customer(int i) { try { Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(4) + 1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } lock.lock(); try { if (waitingCount < NUM_CHAIRS) { waiting[waitingCount++] = i; System.out.println("Customer " + i + " waiting"); condition.signal(); while (waiting[0] != i) { try { condition.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("Customer " + i + " got haircut"); } else { System.out.println("Customer " + i + " left (no seat)"); } } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { BarberShop barberShop = new BarberShop(); Thread barberThread = new Thread(() -> barberShop.barber()); barberThread.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { new Thread(() -> barberShop.customer(i)).start(); } try { barberThread.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } import threading import random import time mtx = threading.Lock() cv = threading.Condition(mtx) waiting = [] NUM_CHAIRS = 3 def barber(): while True: with cv: while not waiting: cv.wait() cust = waiting.pop(0) print(f'Barber cutting hair of customer {cust}') time.sleep(random.randint(1, 3)) print(f'Barber finished with customer {cust}') with cv: cv.notify() def customer(i): time.sleep(random.randint(1, 4)) with cv: if len(waiting) < NUM_CHAIRS: waiting.append(i) print(f'Customer {i} waiting') cv.notify() while waiting[0] != i: cv.wait() print(f'Customer {i} got haircut') else: print(f'Customer {i} left (no seat)') if __name__ == '__main__': t1 = threading.Thread(target=barber) t1.start() for i in range(5): threading.Thread(target=customer, args=(i,)).start() t1.join()
Explore
OS Basics
Process Management
Memory Management
I/O Management
Important Links
My Profile