Python - Coefficient of Determination-R2 score
Last Updated : 20 Aug, 2025
The Coefficient of determination, also called R² score, is used to evaluate the performance of a linear regression model. It is the amount of the variation in the output dependent attribute that is predictable from the input independent variable(s). It is used to check how well-observed results are reproduced by the model, depending on the ratio of the total deviation of results described by the model.
Mathematical Formula:
R^2= 1- \frac{SS_{res}}{SS_{tot}}
Where,
- SS_{res} is the sum of squares of the residual errors
- SS_{tot} is the total sum of the errors
Interpretation of R2 score
Assume R2 = 0.68. It can be inferred that 68% of the changeability of the dependent output attribute can be explained by the model, while the remaining 32 % of the variability is still unaccounted for. R2 indicates the proportion of data points that lie within the line created by the regression equation. A higher value of R2 is desirable as it indicates better results.
Examples
Case 1 (Model gives accurate results):
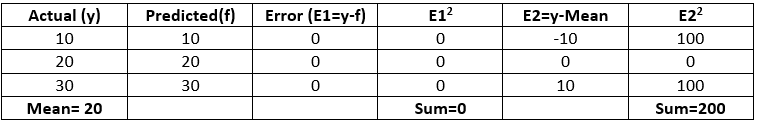
R^2 = 1 - \frac{0}{200} = 1
Case 2 (Model gives same results always):
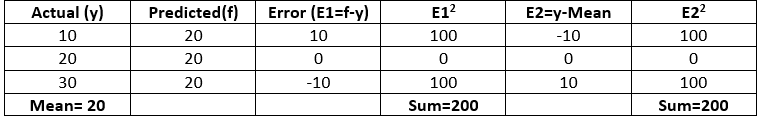
R^2 = 1 - \frac{200}{200} = 0
Case 3 (Model gives ambiguous results):

R^2 = 1 - \frac{600}{200} = -2
We can import r2_score from sklearn.metrics in Python to compute R2 score.
Python Implementation
Step 1: Import r2_score from sklearn.metrics
Python from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
Step 2: Calculate R2 score for all the above cases.
Python ### Assume y is the actual value and f is the predicted values y =[10, 20, 30] f =[10, 20, 30] r2 = r2_score(y, f) print('r2 score for perfect model is', r2) Output:
r2 score for perfect model is 1.0
Python ### Assume y is the actual value and f is the predicted values y =[10, 20, 30] f =[20, 20, 20] r2 = r2_score(y, f) print('r2 score for a model which predicts mean value always is', r2) Output:
r2 score for a model which predicts mean value always is 0.0
Code 3:
Python ### Assume y is the actual value and f is the predicted values y = [10, 20, 30] f = [30, 10, 20] r2 = r2_score(y, f) print('r2 score for a worse model is', r2) Output:
r2 score for a worse model is -2.0
Conclusion
- The best possible score is 1 which is obtained when the predicted values are the same as the actual values.
- R2 score of baseline model is 0.
- During the worse cases, R2 score can even be negative.
Explore
Machine Learning Basics
Python for Machine Learning
Feature Engineering
Supervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning
Model Evaluation and Tuning
Advanced Techniques
Machine Learning Practice
My Profile