Types of Statements in JDBC
Last Updated : 15 Sep, 2025
In Java, the Statement interface in JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) is used to create and execute SQL queries in Java applications. JDBC provides three types of statements to interact with the database:
- Statement -> For executing static SQL queries.
- PreparedStatement -> For executing parameterized queries.
- CallableStatement -> For executing stored procedures.
1. Statement
A Statement object is used for general-purpose access to databases and is useful for executing static SQL statements at runtime.
Syntax:
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
Execution Methods
- execute(String sql): Executes any SQL (SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). Returns true if a ResultSet is returned.
- executeUpdate(String sql): Executes DML (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE). Returns number of rows affected.
- executeQuery(String sql): Executes SELECT queries. Returns a ResultSet.
Example:
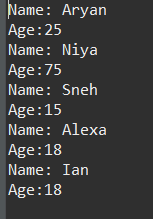
Java import java.sql.*; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Load the driver Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // Establish the connection Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/world", "root", "12345"); // Create a statement Statement st = con.createStatement(); // Execute a query String sql = "SELECT * FROM people"; ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(sql); // Process the results while (rs.next()) { System.out.println("Name: " + rs.getString("name") + ", Age: " + rs.getInt("age")); } // Close resources rs.close(); st.close(); con.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } Output: Name and age are as shown for random inputs.
2. Prepared Statement
A PreparedStatement is a precompiled SQL statement. It supports parameters (?) which can be set dynamically, making it faster and safer than Statement.
Syntax:
String query = "INSERT INTO people(name, age) VALUES (?, ?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = con.prepareStatement(query);
Execution Methods
- execute(): This returns a boolean value and executes a static SQL statement that is present in the prepared statement object.
- executeQuery(): This returns a ResultSet from the current prepared statement.
- executeUpdate(): This returns the number of rows affected by the DML statements such as INSERT, DELETE and more that is present in the current Prepared Statement.
Example: Java Program illustrating Prepared Statement in JDBC
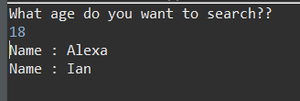
Java import java.sql.*; import java.util.Scanner; class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // try block to check for exceptions try { // Loading drivers using forName() method Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // Scanner class to take input from user Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println( "What age do you want to search?? "); // Reading age an primitive datatype from user using nextInt() method int age = sc.nextInt(); // Registering drivers using DriverManager Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection( "jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345"); // Create a statement PreparedStatement ps = con.prepareStatement( "select name from world.people where age = ?"); // Execute the query ps.setInt(1, age); ResultSet res = ps.executeQuery(); // Condition check using next() method to check for element while (res.next()) { // Print and display elements(Names) System.out.println("Name : " + res.getString(1)); } } // Catch block to handle database exceptions catch (SQLException e) { // Display the DB exception if any System.out.println(e); } // Catch block to handle class exceptions catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } Output:
3. Callable Statement
A CallableStatement is used to execute stored procedures in the database. Stored procedures are precompiled SQL logic stored on the server, often used for complex operations.
Syntax:
CallableStatement cstmt = con.prepareCall("{call ProcedureName(?, ?)}");
Execution Methods
- execute(): Executes the stored procedure and returns a boolean indicating whether the result is a ResultSet (true) or an update count (false).
- executeQuery(): Executes a stored procedure that returns a ResultSet.
- executeUpdate(): Executes a stored procedure that performs an update and returns the number of rows affected.
Example: Java Program illustrating Callable Statement in JDBC
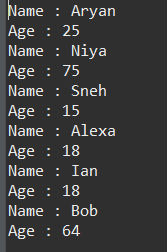
Java import java.sql.*; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { // Try block to check if any exceptions occur try { // Load and register the driver Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); // Establish a connection Connection con = DriverManager .getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///world", "root", "12345"); // Create a CallableStatement CallableStatement cs = con.prepareCall("{call GetPeopleInfo()}"); // Execute the stored procedure ResultSet res = cs.executeQuery(); // Process the results while (res.next()) { // Print and display elements (Name and Age) System.out.println("Name : " + res.getString("name")); System.out.println("Age : " + res.getInt("age")); } // Close resources res.close(); cs.close(); con.close(); } // Catch block for SQL exceptions catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } // Catch block for ClassNotFoundException catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } Output:
Difference Between Statement, PreparedStatement and CallableStatement
| Feature/Aspect | Statement | PreparedStatement | CallableStatement |
|---|
| Purpose | Used for executing simple/static SQL queries | Used for executing parameterized SQL queries | Used for executing stored procedures |
| SQL Reusability | SQL query written directly inside executeQuery() or executeUpdate() | SQL query is precompiled and stored; can be executed multiple times with different parameters | Calls stored procedures that may contain multiple SQL statements |
| Parameters Support | Not supported (values must be hard-coded in query) | Supported using ? placeholders | Supported using ? placeholders for IN, OUT and INOUT parameters |
| Performance | Slower for repeated queries (query compiled each time) | Faster for repeated queries (query compiled once and reused) | Efficient when using stored procedures, since logic is precompiled in DB |
| Security (SQL Injection) | Vulnerable to SQL injection if user input is concatenated directly into query | Prevents SQL injection (parameters are bound safely) | Prevents SQL injection (parameters are bound safely) |
| Return Type | Returns single/multiple ResultSet or update count | Returns single/multiple ResultSet or update count | Returns single/multiple ResultSet, update count and can handle output parameters |
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java
My Profile