In Java, the final keyword makes a variable's reference constant, not its contents. When an array is declared as final, you cannot reassign it to point to a new array. However, you can still modify the elements within the array.
What Does Final Mean for Arrays?
If an array is final, it means we can not make it point to a new array, but we can change the elements inside it.
Sample Example: final int[] arr = {10, 20, 30};
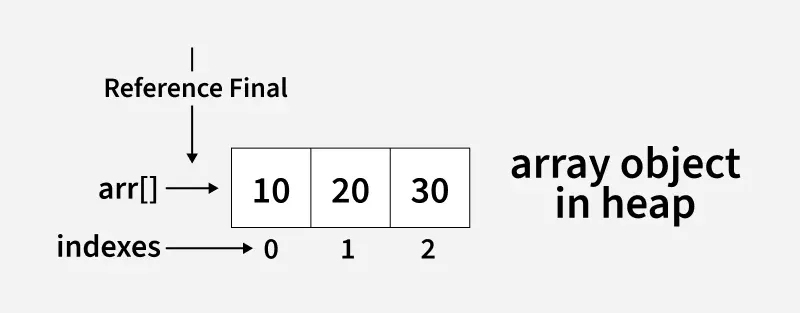 Array object in heap
Array object in heap
Modifying elements inside the array is allowed
arr[2] = 99;
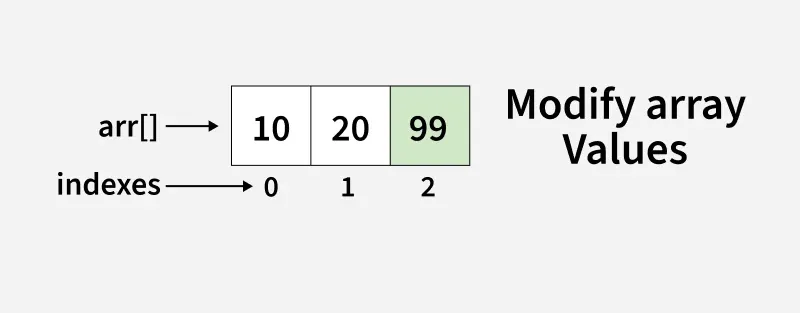 Modify array values
Modify array valuesReassigning the array reference is NOT allowed
arr = new int[]{600, 700, 800}; // Compilation error
Explanation: Here we have declared an array arr as final, which means we can not point arr to a different array, but we can change the value inside the array.
Examples of Final Arrays in Java
Let's now see some examples for better understanding.
Example 1: Modifying Elements of a Final Array
Java import java.util.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { final int[] arr = {10,20,30}; arr[2] = 99; for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } } Explanation: The above example shows that we can change the values inside the final array but we can not replace the whole array.
Example 2: Modifying Object State Referenced by a Final Variable
Java class Geeks { int p = 20; public static void main(String args[]) { final Geeks t = new Geeks(); t.p = 30; System.out.println(t.p); } } Explanation: The above example shows that we can change values inside a final object, but can not replace the object itself.
Example 3: Compilation Error When Reassigning Final Reference
Here is Java program to illustrate final arrays where compilation error is thrown
Java // Main class class Geeks { int p = 20; // Main driver method public static void main(String args[]) { // Creating objects of above class final Geeks t1 = new Geeks(); Geeks t2 = new Geeks(); // Assigning values into other objects t1 = t2; System.out.println(t1.p); } } Output:
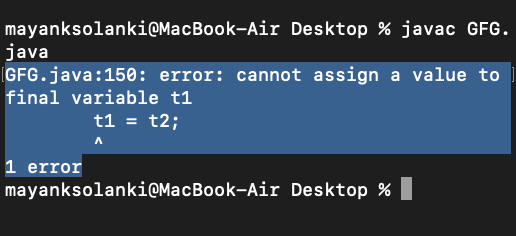
Note: We cannot assign a value to final variable t1.
Explanation: Above program compiles without any error and program 2 fails in compilation. Let us discuss why the error occurred. So a final array means that the array variable which is actually a reference to an object, cannot be changed to refer to anything else, but the members of the array can be modified. Let us propose an example below justifying the same.
Example 4: Final Array Reference and Reassignment.
Here is Java Program to Illustrate Reassignment Error in Final Array
Java // Main class class Geeks { // Main driver method public static void main(String args[]) { // Declaring a final array final int arr1[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // Declaring normal integer array int arr2[] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }; // Assigning values to each other arr2 = arr1; arr1 = arr2; // Now iterating over normal integer array for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) // Printing the elements of above array System.out.println(arr2[i]); } } Output:
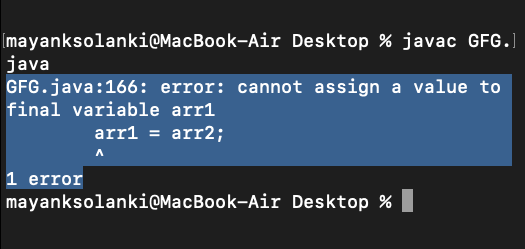
Explanation: In the above example, we are trying to change a final array that why we are getting an error.
Example 5: Modifying Elements in a Final Array and Attempting Reassignment
Here is demonstrating how to change value inside a final array
Java // Import Arrays class for toString() method import java.util.Arrays; public class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { final int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; // Assigning new element into the array numbers[0] = 10; System.out.println( "Array after modifying first element: " + Arrays.toString(numbers)); } } Output:
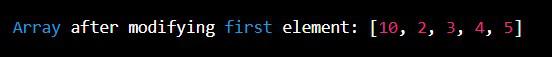 Output
Output Explanation: The above example shows that we can change the values inside a final array but we can not assign a new array to it.
What we can and cannot do with final arrays and objects in Java:
Operation | Allowed or Not | Explanation |
|---|
Modify element in final array | Yes | Array contents are mutable. |
|---|
Reassign final array to new array | No | The reference is final and it cannot point to a new object. |
|---|
Modify object state in final variable | Yes | Object fields can be updated. |
|---|
Reassign final object reference | No | Final variables cannot point to new instances. |
|---|
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java
My Profile