Decision Making in Java - Conditional Statements
Last Updated : 06 Oct, 2025
Decision-making in programming is similar to real-life decision-making. We often want certain blocks of code to execute only when specific conditions are met. In Java, this is achieved using decision-making statements that control the flow of execution.
In Java, the following decision-making statements are available:
Java if Statement
The if statement is the simplest decision-making statement. It executes a block of code only if a given condition is true.
Java class Geeks { public static void main(String args[]) { int i = 10; if (i < 15) { System.out.println("Condition is True"); } } } Note: If curly braces {} are omitted, only the next line after if is considered part of the block.
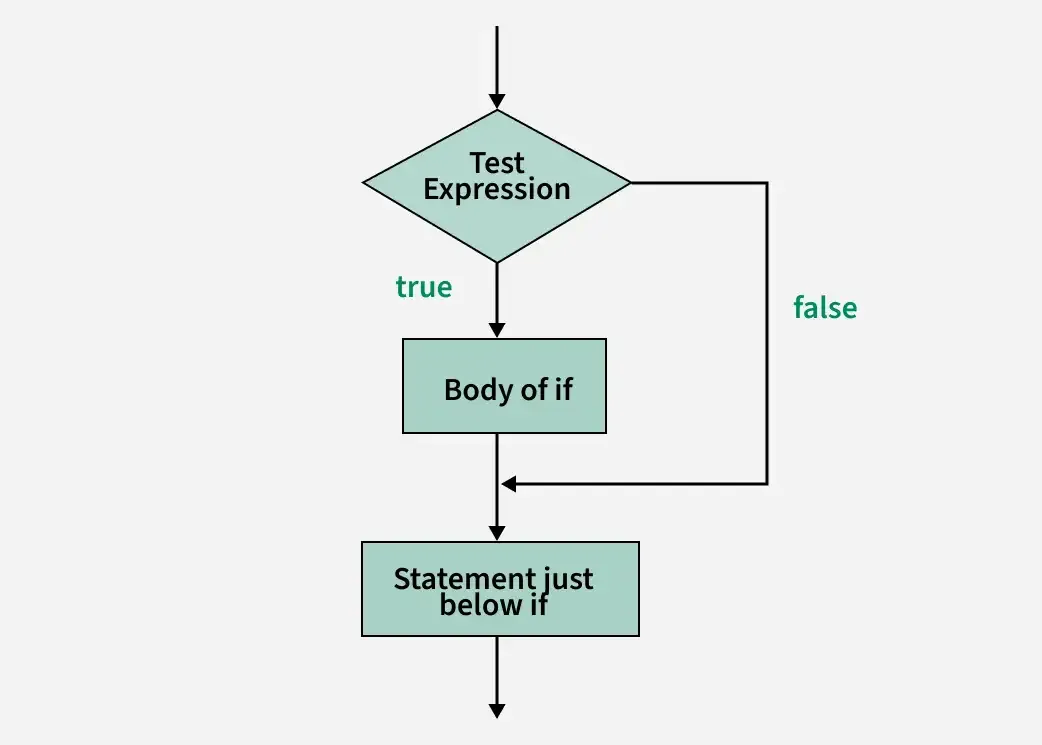
if Statement Execution Flow
The below diagram demonstrates the flow chart of an "if Statement execution flow" in programming.
 Java if
Java ifJava if-else Statement
The if-else statement allows you to execute one block if the condition is true and another block if it is false.
Java import java.util.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String args[]) { int i = 10; if (i < 15) System.out.println("i is smaller than 15"); else System.out.println("i is greater than 15"); } } Outputi is smaller than 15
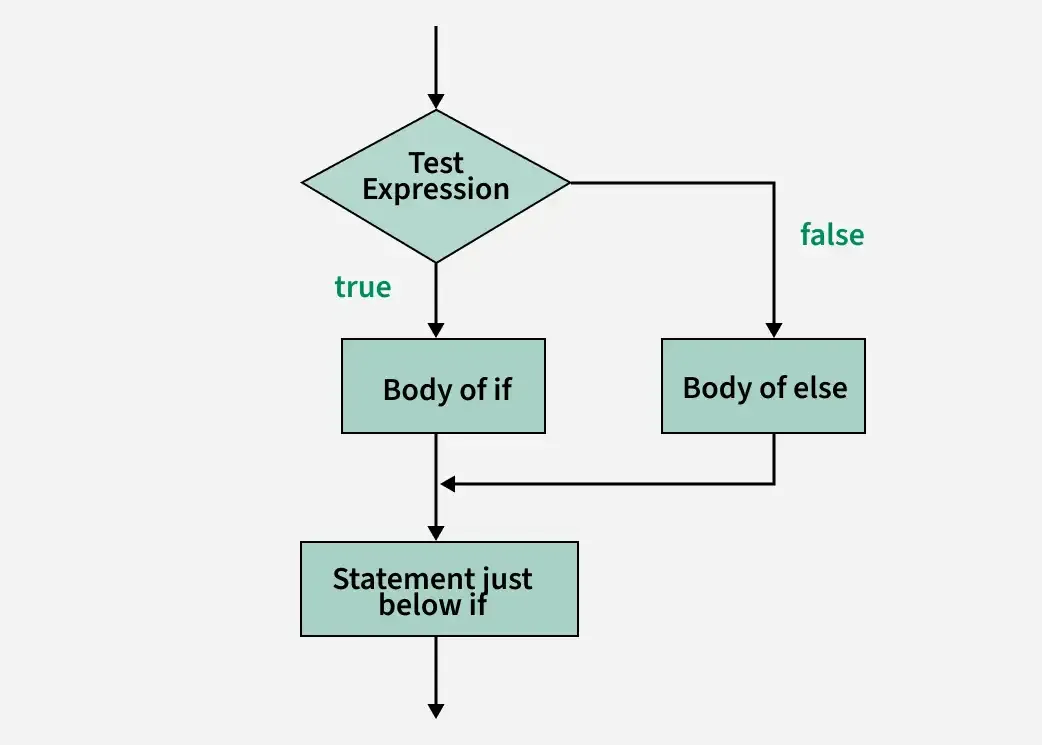
if-else Statement Execution flow
The below diagram demonstrates the flow chart of an "if-else Statement execution flow" in programming
 if-else
if-elseJava nested-if Statement
A nested-if is an if statement inside another if statement. It is useful when a second condition depends on the first.
Java class Geeks { public static void main(String args[]) { int i = 10; // Outer if statement if (i < 15) { System.out.println("i is smaller than 15"); // Nested if statement if (i == 10) { System.out.println("i is exactly 10"); } } } } Outputi is smaller than 15 i is exactly 10
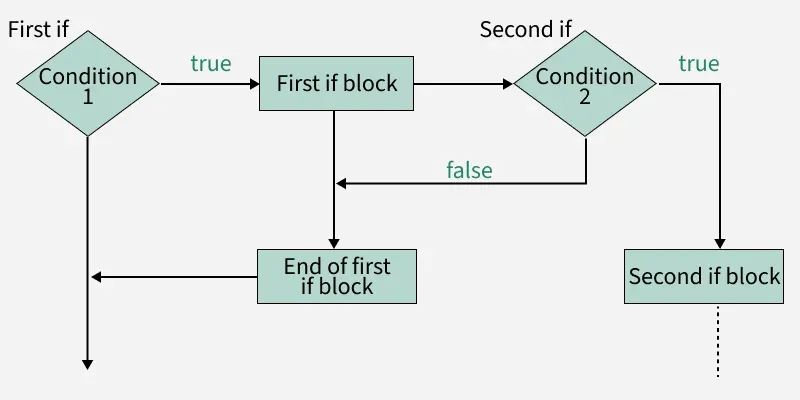
nested-if Statement Execution Flow
The below diagram demonstrates the flow chart of an "nested-if Statement execution flow" in programming.
 Nested-if
Nested-ifJava if-else-if ladder
The if-else-if ladder allows multiple independent conditions to be checked in order. As soon as one condition is true, its block executes, and the rest are skipped.
Java import java.util.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String args[]) { int i = 20; if (i == 10) System.out.println("i is 10"); else if (i == 15) System.out.println("i is 15"); else if (i == 20) System.out.println("i is 20"); else System.out.println("i is not present"); } } if-else-if ladder Execution Flow
The below diagram demonstrates the flow chart of an "if-else-if ladder execution flow" in programming
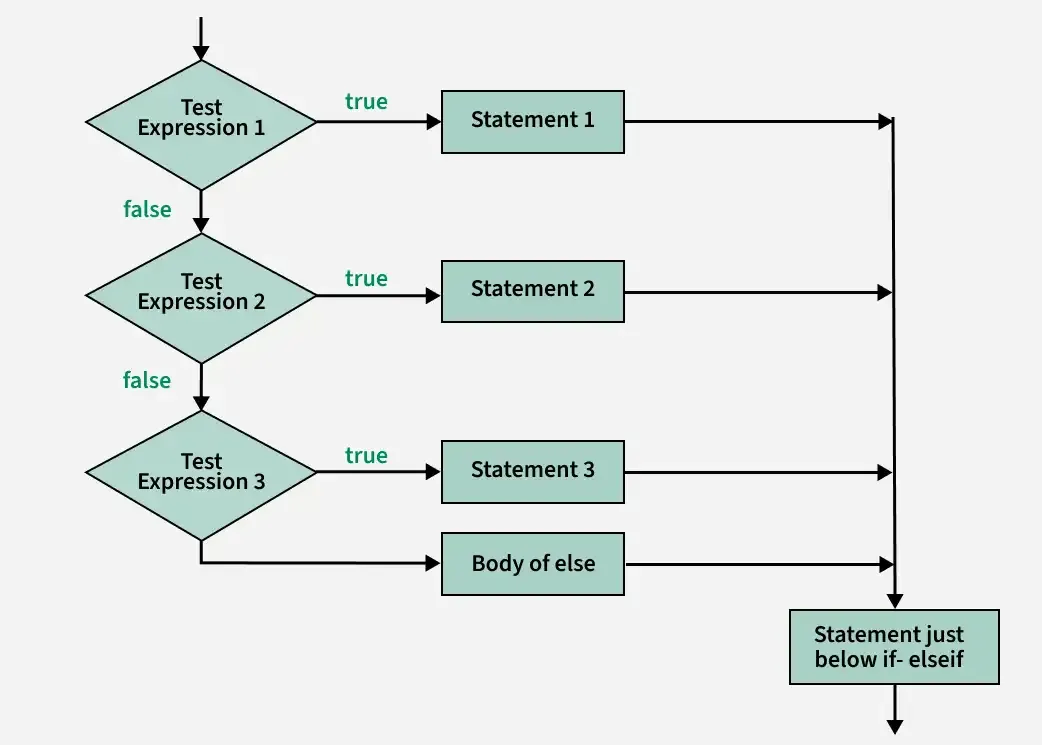 if-else-if ladder
if-else-if ladderJava Switch Case
The switch statement is a multiway branch statement. It provides an easy way to dispatch execution to different parts of code based on the value of the expression.
Java import java.io.*; class Geeks { public static void main(String[] args) { int num = 20; switch (num) { case 5: System.out.println("It is 5"); break; case 10: System.out.println("It is 10"); break; case 15: System.out.println("It is 15"); break; case 20: System.out.println("It is 20"); break; default: System.out.println("Not present"); } } } switch Statements Execution Flow
The below diagram demonstrates the flow chart of a "switch Statements execution flow" in programming.
 switch statement
switch statementNote:
- The expression can be of type byte, short, int char, or an enumeration. Beginning with JDK7, the expression can also be of type String.
- Duplicate case values are not allowed.
- The default statement is optional.
- The break statement is used inside the switch to terminate a statement sequence.
- The break statements are necessary without the break keyword, statements in switch blocks fall through.
Ternary Operator (? :) in Java
The ternary operator in Java is a conditional operator that provides a shorthand way to write simple if-else statements
Syntax:
condition ? expression_if_true : expression_if_false;
Java class Geeks { public static void main(String args[]) { int a = 10, b = 20; int max = (a > b) ? a : b; System.out.println("Maximum is " + max); } } Explanation: This program uses the ternary operator ( ? : ) to find the maximum of two numbers. It checks the condition a > b; if true, it assigns a to the variable max, otherwise it assigns b. Finally, it prints the maximum value.
if-else vs switch-case
The table below demonstrates the difference between if-else and switch-case.
Features | if-else | switch-case |
|---|
Use Case | Suitable for condition-based checks | Best for exact value matching |
|---|
Readability | More readable for a few conditions | More readable and efficient for many cases |
|---|
Performance | Slower for many checks due to multiple conditions | Faster and optimized for handling many cases |
|---|
Flexibility | Supports ranges and complex conditions | Only supports exact matches of values |
|---|
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java
My Profile