Insert a Node at Front/Beginning of a Linked List
Last Updated : 26 Jul, 2024
Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node at the beginning/start/front of the linked list.
Example:
Input: LinkedList = 2->3->4->5, NewNode = 1
Output: 1 2 3 4 5
Input: LinkedList = 2->10, NewNode = 1
Output: 1 2 10
Approach:
To insert a new node at the front, we create a new node and point its next reference to the current head of the linked list. Then, we update the head to be this new node. This operation is efficient because it only requires adjusting a few pointers.
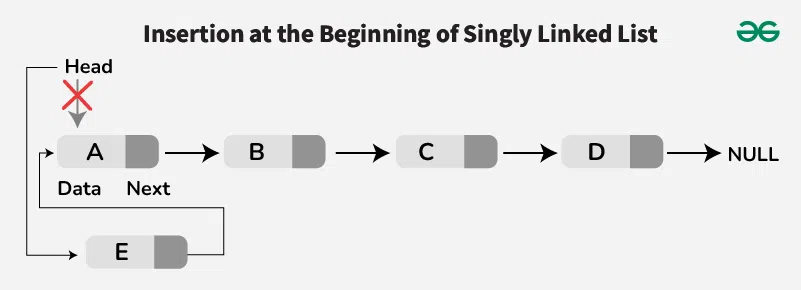 Insertion at Front/Beginning of Linked List
Insertion at Front/Beginning of Linked ListAlgorithm:
- Make the first node of Linked List linked to the new node
- Remove the head from the original first node of Linked List
- Make the new node as the Head of the Linked List.
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++ // C++ Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Define a node in the linked list struct Node { int data; // Data stored in the node Node* next; // Pointer to the next node in the list // Constructor to initialize the node Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = nullptr; // Set next to null } }; // Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the // list Node* insertAtFront(Node* head, int new_data) { // Create a new node with the given data Node* new_node = new Node(new_data); // Make the next of the new node point to the current // head new_node->next = head; // Return the new node as the new head of the list return new_node; } // Function to print the contents of the linked list void printList(Node* head) { // Start from the head of the list Node* curr = head; // Traverse the list while (curr != nullptr) { // Print the current node's data cout << " " << curr->data; // Move to the next node curr = curr->next; } // Print a newline at the end cout << endl; } // Driver code to test the functions int main() { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 Node* head = new Node(2); head->next = new Node(3); head->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next = new Node(5); // Print the original list cout << "Original Linked List:"; printList(head); // Insert a new node at the front of the list cout << "After inserting Nodes at the front:"; int data = 1; head = insertAtFront(head, data); // Print the updated list printList(head); return 0; } // C Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Define a node in the linked list struct Node { int data; // Data stored in the node struct Node* next; // Pointer to the next node in the list }; // Function to create a new node with the given data struct Node* createNode(int new_data) { // Allocate memory for a new node struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Initialize the node's data new_node->data = new_data; // Set the next pointer to NULL new_node->next = NULL; // Return the newly created node return new_node; } // Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the // list struct Node* insertAtFront(struct Node* head, int new_data) { // Create a new node with the given data struct Node* new_node = createNode(new_data); // Make the next of the new node point to the current // head new_node->next = head; // Return the new node as the new head of the list return new_node; } // Function to print the contents of the linked list void printList(struct Node* head) { // Start from the head of the list struct Node* curr = head; // Traverse the list while (curr != NULL) { // Print the current node's data printf(" %d", curr->data); // Move to the next node curr = curr->next; } // Print a newline at the end printf("\n"); } // Driver code to test the functions int main() { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 struct Node* head = createNode(2); head->next = createNode(3); head->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next = createNode(5); // Print the original list printf("Original Linked List:"); printList(head); // Insert a new node at the front of the list printf("After inserting Nodes at the front:"); int data = 1; head = insertAtFront(head, data); // Print the updated list printList(head); return 0; } // Java Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List class Node { int data; // Data stored in the node Node next; // Pointer to the next node in the list // Constructor to initialize the node Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } public class GFG { // Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the list public static Node insertAtFront(Node head, int new_data) { // Create a new node with the given data Node new_node = new Node(new_data); // Make the next of the new node point to the current head new_node.next = head; // Return the new node as the new head of the list return new_node; } // Function to print the contents of the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { // Start from the head of the list Node curr = head; // Traverse the list while (curr != null) { // Print the current node's data System.out.print(" " + curr.data); // Move to the next node curr = curr.next; } // Print a newline at the end System.out.println(); } // Driver code to test the functions public static void main(String[] args) { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 Node head = new Node(2); head.next = new Node(3); head.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next = new Node(5); // Print the original list System.out.println("Original Linked List:"); printList(head); // Insert a new node at the front of the list System.out.println("After inserting Nodes at the front:"); int data = 1; head = insertAtFront(head, data); // Print the updated list printList(head); } } # Python Program to insert the node at the beginning of # Linked List class Node: def __init__(self, new_data): # Initialize the node's data self.data = new_data # Set the next pointer to None self.next = None def insert_at_front(head, new_data): # Create a new node with the given data new_node = Node(new_data) # Make the next of the new node point to the current head new_node.next = head # Return the new node as the new head of the list return new_node def print_list(head): # Start from the head of the list curr = head # Traverse the list while curr is not None: # Print the current node's data print(f" {curr.data}", end="") # Move to the next node curr = curr.next # Print a newline at the end print() # Driver code to test the functions if __name__ == "__main__": # Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 head = Node(2) head.next = Node(3) head.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next = Node(5) # Print the original list print("Original Linked List:", end="") print_list(head) # Insert a new node at the front of the list print("After inserting Nodes at the front:", end="") data = 1 head = insert_at_front(head, data) # Print the updated list print_list(head) // JavaScript Program to insert the node at the beginning of // Linked List class Node { constructor(newData) { // Initialize the node's data this.data = newData; // Set the next pointer to null this.next = null; } } // Function to insert a new node at the beginning of the // list function insertAtFront(head, newData) { // Create a new node with the given data const newNode = new Node(newData); // Make the next of the new node point to the current // head newNode.next = head; // Return the new node as the new head of the list return newNode; } // Function to print the contents of the linked list function printList(head) { // Start from the head of the list let curr = head; let result = ""; // Traverse the list while (curr !== null) { // Append the current node's data to result result += " " + curr.data; // Move to the next node curr = curr.next; } // Print the result console.log(result); } // Driver code to test the functions function main() { // Create the linked list 2->3->4->5 let head = new Node(2); head.next = new Node(3); head.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next = new Node(5); // Print the original list console.log("Original Linked List:"); printList(head); // Insert a new node at the front of the list console.log("After inserting Nodes at the front:"); const data = 1; head = insertAtFront(head, data); // Print the updated list printList(head); } main(); // Execute the driver code OutputOriginal Linked List: 2 3 4 5 After inserting Nodes at the front: 1 2 3 4 5
Time Complexity: O(1), We have a pointer to the head and we can directly attach a node and update the head pointer. So, the Time complexity of inserting a node at the head position is O(1).
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Similar Reads
Insert a Node after a given Node in Linked List Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node after a given node of the linked list. If the given node is not present in the linked list, print "Node not found".Examples:Input: LinkedList = 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5, newData = 1, key = 2Output: LinkedList = 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5I
11 min read
Insert Node at the End of a Linked List Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node at the end of the linked list.Examples:Input: LinkedList = 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5, NewNode = 1Output: LinkedList = 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 1Input: LinkedList = NULL, NewNode = 1Output: LinkedList = 1Approach:Â Inserting at the end invol
9 min read
Insert a Node after a given node in Doubly Linked List Given a Doubly Linked List, the task is to insert a new node after a given node in the linked list.Examples: Input: Linked List = 1 <-> 2 <-> 4, newData = 3, key = 2Output: Linked List = 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4Explanation: New node 3 is inserted after key, that is node 2.In
11 min read
Insert a node in Linked List before a given node Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node with a specified value into a linked list before a node with a given key.ExamplesInput: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 , newData = 6, key = 2Output: 1 -> 6 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Explanation: After inserting node with value 6
15+ min read
Insert a Node at the end of Doubly Linked List Given a Doubly Linked List, the task is to insert a new node at the end of the linked list.Examples: Input: Linked List = 1 <-> 2 <-> 3, NewNode = 4Output: Linked List = 1 <-> 2 <-> 3 <-> 4Input: Linked List = NULL, NewNode = 1Output: Linked List = 1Approach: Inserting
9 min read
Insertion at the beginning in circular linked list A circular linked list is a special type of data structure where each node points to the next, and the last node connects back to the first, forming a loop. This design allows for continuous traversal without stopping. Inserting a node at the beginning of a circular linked list is an important opera
7 min read