Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem (Introduction and Implementation)
Last Updated : 26 Apr, 2025
You are the head of a company with n agents and n tasks. Every agent incurs a different cost to complete each task, as given by the cost[][] matrix, where cost[i][j] represents the cost for the ith agent to perform the jth task. Your objective is to assign exactly one agent to each task—and one task to each agent—in such a way that the total cost of all assignments is minimized.
Example:
Input: n = 3
cost[][] = [ [2500, 4000, 3500],
[4000, 6000, 3500],
[2000, 4000, 2500] ]
Output: 9500
Explanation: The optimal assignment is to assign job 2 to the 1st worker, job 3 to the 2nd worker and job 1 to the 3rd worker.
Hence, the optimal cost is 4000 + 3500 + 2000 = 9500.
This example can also be understood in the following way:
You work as a manager for a chip manufacturer, and you currently have 3 people on the road meeting clients. Your salespeople are in Jaipur, Pune and Bangalore, and you want them to fly to three other cities: Delhi, Mumbai and Kerala. The table below shows the cost of airline tickets in INR between the cities: 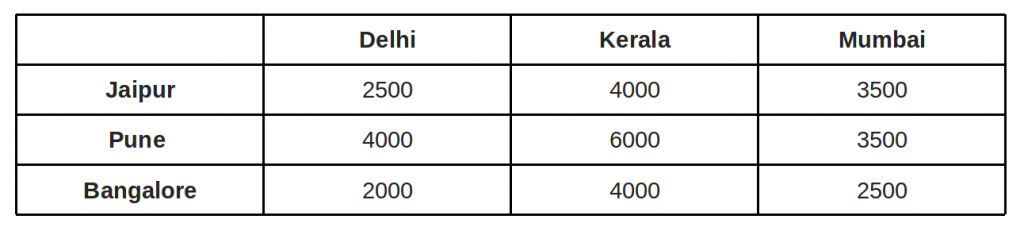 The question: where would you send each of your salespeople in order to minimize fair? Possible assignment: Cost = 11000 INR
The question: where would you send each of your salespeople in order to minimize fair? Possible assignment: Cost = 11000 INR  Other Possible assignment: Cost = 9500 INR and this is the best of the 3! possible assignments.
Other Possible assignment: Cost = 9500 INR and this is the best of the 3! possible assignments. 
Approach:
The Hungarian algorithm (also known as the Munkres assignment algorithm) is designed to find an optimal assignment between n agents and n tasks with a worst-case time complexity of O(n³). Its key insight is that if you add or subtract a constant from all elements in any row or column of the cost matrix, the set of optimal assignments does not change. By leveraging this property, the algorithm reduces the original cost matrix to one containing zeros, thereby simplifying the assignment process to one where each agent can be assigned a task at zero penalty.
Follow the below given step-by-step approach:
- Row Reduction: For each row in the matrix, identify the smallest element and subtract it from every element in that row.
- Column Reduction: For each column in the matrix, identify the smallest element and subtract it from every element in that column.
- Zero Coverage: Cover all zeros in the resulting matrix using the minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
- Optimality Check:
- If the number of covering lines equals n, then an optimal assignment is possible, and the algorithm terminates.
- If the number of covering lines is less than n, proceed to the next step.
- Adjust the Matrix:
- Determine the smallest entry that is not covered by any line.
- Subtract this entry from every uncovered row.
- Add the same entry to every column that is covered by a line.
- Return to step 3 with the modified matrix.
- This process is repeated until an optimal assignment is identified.
Consider few examples to understand the approach:
Let the 2D array be:
cost[][] = [ [2500, 4000, 3500],
[4000, 6000, 3500],
[2000, 4000, 2500] ]
Step 1: Subtract minimum of every row. Thus, 2500, 3500 and 2000 are subtracted from rows 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
cost[][] = [ [0, 1500, 1000],
[500, 2500, 0],
[0, 2000, 500] ]
Step 2: Subtract minimum of every column. Thus 0, 1500 and 0 are subtracted from columns 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
cost[][] = [ [0, 0, 1000],
[500, 1000, 0],
[0, 500, 500] ]
Step 3: Cover all zeroes with minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.

Step 4: Since we need 3 lines to cover all zeroes, the optimal assignment is found.
cost[][] = [ [2500, 4000, 3500],
[4000, 6000, 3500],
[2000, 4000, 2500] ]
So the optimal cost is 4000 + 3500 + 2000 = 9500
In the above example, the first check for optimality did give us solution, but what if we the number covering lines is less than n. The below given example consider this case:
Let the 2D array be:
cost[][] = [ [1500, 4000, 4500],
[2000, 6000, 3500],
[2000, 4000, 2500] ]
Step 1: Subtract minimum of every row. Thus, 1500, 2000 and 2000 are subtracted from rows 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
cost[][] = [ [0, 2500, 3000],
[0, 4000, 1500],
[0, 2000, 500] ]
Step 2: Subtract minimum of every column. Thus 0, 2000 and 500 are subtracted from columns 1, 2 and 3 respectively.
cost[][] = [ [0, 500, 2500],
[0, 2000, 1000],
[0, 0, 0] ]
Step 3: Cover all zeroes with minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
Step 4: Since we need only 2 lines to cover all zeroes, the optimal assignment is not found.
Step 5: We subtract the smallest uncovered entry from all uncovered rows. Smallest entry is 500.
cost[][] = [ [-500, 0, 2000],
[-500, 1500, 500],
[0, 0, 0] ]
Step 6: Then we add the smallest entry to all covered columns, we get
cost[][] = [ [0, 0, 2000],
[0, 1500, 500],
[500, 0, 0] ]
Now we return to Step 3: Here we cover again using lines. and go to Step 4. Since we need 3 lines to cover, we found the optimal solution.
cost[][] = [ [1500, 4000, 4500],
[2000, 6000, 3500],
[2000, 4000, 2500] ]
So the optimal cost is 4000 + 2000 + 2500 = 8500
Below is given the implementation:
C++ #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; void labelIt(vector<vector<int>> &cost, vector<int> &lx) { int n = cost.size(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) lx[i] = max(lx[i], cost[i][j]); } void addTree(int x, int prevX, vector<bool> &inTreeX, vector<int> &prev, vector<int> &slack, vector<int> &slackX, vector<int> &lx, vector<int> &ly, vector<vector<int>> &cost) { inTreeX[x] = true; prev[x] = prevX; for(int y = 0; y < slack.size(); y++) { if (lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] < slack[y]) { slack[y] = lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y]; slackX[y] = x; } } } void updateLabels(vector<bool> &inTreeX, vector<bool> &inTreeY, vector<int> &slack, vector<int> &lx, vector<int> &ly) { int n = slack.size(); int delta = INT_MAX; for(int y = 0; y < n; y++) if(!inTreeY[y]) delta = min(delta, slack[y]); for(int x = 0; x < n; x++) if(inTreeX[x]) lx[x] -= delta; for(int y = 0; y < n; y++) if(inTreeY[y]) ly[y] += delta; for(int y = 0; y < n; y++) if(!inTreeY[y]) slack[y] -= delta; } void augment(vector<vector<int>> &cost, int &match, vector<bool> &inTreeX, vector<bool> &inTreeY, vector<int> &prev, vector<int> &xy, vector<int> &yx, vector<int> &slack, vector<int> &slackX, vector<int> &lx, vector<int> &ly) { // augmenting path algorithm int n = cost.size(); // check if we have found a perfect matching if(match == n) return; int x, y, root; queue<int> q; // find root of tree for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(xy[i] == -1) { q.push(root = i); prev[i] = -2; inTreeX[i] = true; break; } } // initialize slack for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { slack[i] = lx[root] + ly[i] - cost[root][i]; slackX[i] = root; } // BFS to find augmenting path while(true) { // building tree with BFS cycle while(!q.empty()) { // current vertex x = q.front(); q.pop(); //iterate through all edges in equality graph for(y = 0; y < n; y++) { if(lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] == 0 && !inTreeY[y]) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if(yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is // matched with y, to the queue q.push(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], x, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; // else improve labeling updateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly); for(y = 0; y < n; y++) { if(!inTreeY[y] && slack[y] == 0) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if(yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is matched with y, to the queue if(!inTreeX[yx[y]]) { q.push(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], slackX[y], inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; } if(y < n) { // augmenting path found match++; // update xy and yx for(int cx = x, cy = y, ty; cx != -2; cx = prev[cx], cy = ty) { ty = xy[cx]; xy[cx] = cy; yx[cy] = cx; } // reset inTreeX and inTreeY fill(inTreeX.begin(), inTreeX.end(), false); fill(inTreeY.begin(), inTreeY.end(), false); // recall function, go to step 1 of the algorithm augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); } } int findMinCost(vector<vector<int>> &cost) { int n = cost.size(); // convert cost matrix to profit matrix // by multiplying each element by -1 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) cost[i][j] = -1 * cost[i][j]; // to store the results int result = 0; // number of vertices in current matching int match = 0; vector<int> xy(n, -1), yx(n, -1), lx(n, 0); vector<int> ly(n, 0), slack(n), slackX(n), prev(n); vector<bool> inTreeX(n, false), inTreeY(n, false); labelIt(cost, lx); augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { result += cost[i][xy[i]]; } return -1 * result; } int main() { vector<vector<int>> cost = { {2500, 4000, 3500}, {4000, 6000, 3500}, {2000, 4000, 2500} }; cout << findMinCost(cost); return 0; } import java.util.*; public class GfG { public static void labelIt(int[][] cost, int[] lx) { int n = cost.length; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) lx[i] = Math.max(lx[i], cost[i][j]); } public static void addTree(int x, int prevX, boolean[] inTreeX, int[] prev, int[] slack, int[] slackX, int[] lx, int[] ly, int[][] cost) { inTreeX[x] = true; prev[x] = prevX; for(int y = 0; y < slack.length; y++) { if (lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] < slack[y]) { slack[y] = lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y]; slackX[y] = x; } } } public static void updateLabels(boolean[] inTreeX, boolean[] inTreeY, int[] slack, int[] lx, int[] ly) { int n = slack.length; int delta = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for(int y = 0; y < n; y++) if(!inTreeY[y]) delta = Math.min(delta, slack[y]); for(int x = 0; x < n; x++) if(inTreeX[x]) lx[x] -= delta; for(int y = 0; y < n; y++) if(inTreeY[y]) ly[y] += delta; for(int y = 0; y < n; y++) if(!inTreeY[y]) slack[y] -= delta; } public static void augment(int[][] cost, int[] match, boolean[] inTreeX, boolean[] inTreeY, int[] prev, int[] xy, int[] yx, int[] slack, int[] slackX, int[] lx, int[] ly) { // augmenting path algorithm int n = cost.length; // check if we have found a perfect matching if(match[0] == n) return; int x = 0, y = 0, root = 0; Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>(); // find root of tree for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(xy[i] == -1) { q.add(root = i); prev[i] = -2; inTreeX[i] = true; break; } } // initialize slack for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { slack[i] = lx[root] + ly[i] - cost[root][i]; slackX[i] = root; } // BFS to find augmenting path while(true) { // building tree with BFS cycle while(!q.isEmpty()) { // current vertex x = q.poll(); //iterate through all edges in equality graph for(y = 0; y < n; y++) { if(lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] == 0 && !inTreeY[y]) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if(yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is // matched with y, to the queue q.add(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], x, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; // else improve labeling updateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly); for(y = 0; y < n; y++) { if(!inTreeY[y] && slack[y] == 0) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if(yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is matched with y, to the queue if(!inTreeX[yx[y]]) { q.add(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], slackX[y], inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; } if(y < n) { // augmenting path found match[0]++; // update xy and yx for(int cx = x, cy = y, ty; cx != -2; cx = prev[cx], cy = ty) { ty = xy[cx]; xy[cx] = cy; yx[cy] = cx; } // reset inTreeX and inTreeY Arrays.fill(inTreeX, false); Arrays.fill(inTreeY, false); // recall function, go to step 1 of the algorithm augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); } } public static int findMinCost(int[][] cost) { int n = cost.length; // convert cost matrix to profit matrix // by multiplying each element by -1 for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) cost[i][j] = -1 * cost[i][j]; // to store the results int result = 0; // number of vertices in current matching int[] match = new int[]{0}; int[] xy = new int[n]; int[] yx = new int[n]; int[] lx = new int[n]; int[] ly = new int[n]; int[] slack = new int[n]; int[] slackX = new int[n]; int[] prev = new int[n]; Arrays.fill(xy, -1); Arrays.fill(yx, -1); boolean[] inTreeX = new boolean[n]; boolean[] inTreeY = new boolean[n]; labelIt(cost, lx); augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { result += cost[i][xy[i]]; } return -1 * result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] cost = { {2500, 4000, 3500}, {4000, 6000, 3500}, {2000, 4000, 2500} }; System.out.println(findMinCost(cost)); } } from collections import deque import sys def labelIt(cost, lx): n = len(cost) for i in range(n): for j in range(n): lx[i] = max(lx[i], cost[i][j]) def addTree(x, prevX, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost): inTreeX[x] = True prev[x] = prevX for y in range(len(slack)): if lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] < slack[y]: slack[y] = lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] slackX[y] = x def updateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly): n = len(slack) delta = sys.maxsize for y in range(n): if not inTreeY[y]: delta = min(delta, slack[y]) for x in range(n): if inTreeX[x]: lx[x] -= delta for y in range(n): if inTreeY[y]: ly[y] += delta for y in range(n): if not inTreeY[y]: slack[y] -= delta def augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly): # augmenting path algorithm n = len(cost) # check if we have found a perfect matching if match[0] == n: return x = y = root = 0 q = deque() # find root of tree for i in range(n): if xy[i] == -1: root = i q.append(root) prev[i] = -2 inTreeX[i] = True break # initialize slack for i in range(n): slack[i] = lx[root] + ly[i] - cost[root][i] slackX[i] = root # BFS to find augmenting path while True: # building tree with BFS cycle while q: x = q.popleft() #iterate through all edges in equality graph for y in range(n): if lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] == 0 and not inTreeY[y]: # if y is an exposed vertex in Y # found, so augmenting path exists if yx[y] == -1: x = slackX[y] break else: # else just add y to inTreeY inTreeY[y] = True # add vertex yx[y], which is # matched with y, to the queue q.append(yx[y]) # add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], x, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost) if y < n: break # augmenting path found if y < n: break # else improve labeling updateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly) for y in range(n): if not inTreeY[y] and slack[y] == 0: if yx[y] == -1: x = slackX[y] break else: inTreeY[y] = True if not inTreeX[yx[y]]: q.append(yx[y]) addTree(yx[y], slackX[y], inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost) if y < n: break if y < n: # augmenting path found match[0] += 1 # update xy and yx cx = x cy = y while cx != -2: ty = xy[cx] xy[cx] = cy yx[cy] = cx cx = prev[cx] cy = ty # reset inTreeX and inTreeY for i in range(n): inTreeX[i] = False inTreeY[i] = False # recall function, go to step 1 of the algorithm augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly) def findMinCost(cost): n = len(cost) # convert cost matrix to profit matrix # by multiplying each element by -1 for i in range(n): for j in range(n): cost[i][j] = -1 * cost[i][j] # to store the results result = 0 # number of vertices in current matching match = [0] xy = [-1] * n yx = [-1] * n lx = [0] * n ly = [0] * n slack = [0] * n slackX = [0] * n prev = [0] * n inTreeX = [False] * n inTreeY = [False] * n labelIt(cost, lx) augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly) for i in range(n): result += cost[i][xy[i]] return -1 * result if __name__ == "__main__": cost = [ [2500, 4000, 3500], [4000, 6000, 3500], [2000, 4000, 2500] ] print(findMinCost(cost))
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class GfG { public static void LabelIt(int[][] cost, int[] lx) { int n = cost.Length; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) lx[i] = Math.Max(lx[i], cost[i][j]); } public static void AddTree(int x, int prevX, bool[] inTreeX, int[] prev, int[] slack, int[] slackX, int[] lx, int[] ly, int[][] cost) { inTreeX[x] = true; prev[x] = prevX; for (int y = 0; y < slack.Length; y++) { if (lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] < slack[y]) { slack[y] = lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y]; slackX[y] = x; } } } public static void UpdateLabels(bool[] inTreeX, bool[] inTreeY, int[] slack, int[] lx, int[] ly) { int n = slack.Length; int delta = int.MaxValue; for (int y = 0; y < n; y++) if (!inTreeY[y]) delta = Math.Min(delta, slack[y]); for (int x = 0; x < n; x++) if (inTreeX[x]) lx[x] -= delta; for (int y = 0; y < n; y++) if (inTreeY[y]) ly[y] += delta; for (int y = 0; y < n; y++) if (!inTreeY[y]) slack[y] -= delta; } public static void Augment(int[][] cost, int[] match, bool[] inTreeX, bool[] inTreeY, int[] prev, int[] xy, int[] yx, int[] slack, int[] slackX, int[] lx, int[] ly) { // augmenting path algorithm int n = cost.Length; // check if we have found a perfect matching if (match[0] == n) return; int x = 0, y = 0, root = 0; Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>(); // find root of tree for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (xy[i] == -1) { q.Enqueue(root = i); prev[i] = -2; inTreeX[i] = true; break; } } // initialize slack for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { slack[i] = lx[root] + ly[i] - cost[root][i]; slackX[i] = root; } // BFS to find augmenting path while (true) { // building tree with BFS cycle while (q.Count != 0) { // current vertex x = q.Dequeue(); //iterate through all edges in equality graph for (y = 0; y < n; y++) { if (lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] == 0 && !inTreeY[y]) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if (yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is // matched with y, to the queue q.Enqueue(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree AddTree(yx[y], x, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } // augmenting path found if (y < n) break; } // augmenting path found if (y < n) break; // else improve labeling UpdateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly); for (y = 0; y < n; y++) { if (!inTreeY[y] && slack[y] == 0) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if (yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is matched with y, to the queue if (!inTreeX[yx[y]]) { q.Enqueue(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree AddTree(yx[y], slackX[y], inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } } // augmenting path found if (y < n) break; } if (y < n) { // augmenting path found match[0]++; // update xy and yx for (int cx = x, cy = y, ty; cx != -2; cx = prev[cx], cy = ty) { ty = xy[cx]; xy[cx] = cy; yx[cy] = cx; } // reset inTreeX and inTreeY for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { inTreeX[i] = false; inTreeY[i] = false; } // recall function, go to step 1 of the algorithm Augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); } } public static int FindMinCost(int[][] cost) { int n = cost.Length; // convert cost matrix to profit matrix // by multiplying each element by -1 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) cost[i][j] = -1 * cost[i][j]; // to store the results int result = 0; // number of vertices in current matching int[] match = new int[]{0}; int[] xy = new int[n]; int[] yx = new int[n]; int[] lx = new int[n]; int[] ly = new int[n]; int[] slack = new int[n]; int[] slackX = new int[n]; int[] prev = new int[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { xy[i] = -1; yx[i] = -1; } bool[] inTreeX = new bool[n]; bool[] inTreeY = new bool[n]; LabelIt(cost, lx); Augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { result += cost[i][xy[i]]; } return -1 * result; } public static void Main(String[] args) { int[][] cost = new int[][] { new int[] {2500, 4000, 3500}, new int[] {4000, 6000, 3500}, new int[] {2000, 4000, 2500} }; Console.WriteLine(FindMinCost(cost)); } } function labelIt(cost, lx) { let n = cost.length; for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) lx[i] = Math.max(lx[i], cost[i][j]); } function addTree(x, prevX, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost) { inTreeX[x] = true; prev[x] = prevX; for(let y = 0; y < slack.length; y++) { if (lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] < slack[y]) { slack[y] = lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y]; slackX[y] = x; } } } function updateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly) { let n = slack.length; let delta = Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER; for(let y = 0; y < n; y++) if(!inTreeY[y]) delta = Math.min(delta, slack[y]); for(let x = 0; x < n; x++) if(inTreeX[x]) lx[x] -= delta; for(let y = 0; y < n; y++) if(inTreeY[y]) ly[y] += delta; for(let y = 0; y < n; y++) if(!inTreeY[y]) slack[y] -= delta; } function augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly) { // augmenting path algorithm let n = cost.length; // check if we have found a perfect matching if(match[0] == n) return; let x, y, root; let q = []; // find root of tree for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) { if(xy[i] == -1) { q.push(root = i); prev[i] = -2; inTreeX[i] = true; break; } } // initialize slack for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) { slack[i] = lx[root] + ly[i] - cost[root][i]; slackX[i] = root; } // BFS to find augmenting path while(true) { // building tree with BFS cycle while(q.length > 0) { // current vertex x = q.shift(); //iterate through all edges in equality graph for(y = 0; y < n; y++) { if(lx[x] + ly[y] - cost[x][y] == 0 && !inTreeY[y]) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if(yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is // matched with y, to the queue q.push(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], x, inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; // else improve labeling updateLabels(inTreeX, inTreeY, slack, lx, ly); for(y = 0; y < n; y++) { if(!inTreeY[y] && slack[y] == 0) { // if y is an exposed vertex in Y // found, so augmenting path exists if(yx[y] == -1) { x = slackX[y]; break; } // else just add y to inTreeY else { inTreeY[y] = true; // add vertex yx[y], which is matched with y, to the queue if(!inTreeX[yx[y]]) { q.push(yx[y]); // add edges (x, y) and (y, yx[y]) to the tree addTree(yx[y], slackX[y], inTreeX, prev, slack, slackX, lx, ly, cost); } } } } // augmenting path found if(y < n) break; } if(y < n) { // augmenting path found match[0]++; // update xy and yx for(let cx = x, cy = y, ty; cx != -2; cx = prev[cx], cy = ty) { ty = xy[cx]; xy[cx] = cy; yx[cy] = cx; } // reset inTreeX and inTreeY for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) { inTreeX[i] = false; inTreeY[i] = false; } // recall function, go to step 1 of the algorithm augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); } } function findMinCost(cost) { let n = cost.length; // convert cost matrix to profit matrix // by multiplying each element by -1 for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) for(let j = 0; j < n; j++) cost[i][j] = -1 * cost[i][j]; // to store the results let result = 0; // number of vertices in current matching let match = [0]; let xy = new Array(n).fill(-1); let yx = new Array(n).fill(-1); let lx = new Array(n).fill(0); let ly = new Array(n).fill(0); let slack = new Array(n); let slackX = new Array(n); let prev = new Array(n); let inTreeX = new Array(n).fill(false); let inTreeY = new Array(n).fill(false); labelIt(cost, lx); augment(cost, match, inTreeX, inTreeY, prev, xy, yx, slack, slackX, lx, ly); for(let i = 0; i < n; i++) { result += cost[i][xy[i]]; } return -1 * result; } let cost = [ [2500, 4000, 3500], [4000, 6000, 3500], [2000, 4000, 2500] ]; console.log(findMinCost(cost)); Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3).
Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional arrays of size n to store the labels, matches, and auxiliary information needed for the algorithm.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile