Difference between Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
Last Updated : 15 Jul, 2025
Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM) are two fundamental techniques used in analog communication systems to transmit information, such as audio signals, over radio waves. While both serve the purpose of modulating a carrier signal to encode data, they differ in their modulation techniques and the properties of the signals they produce. This article explores the differences between AM and FM, along with their advantages, disadvantages, and applications.
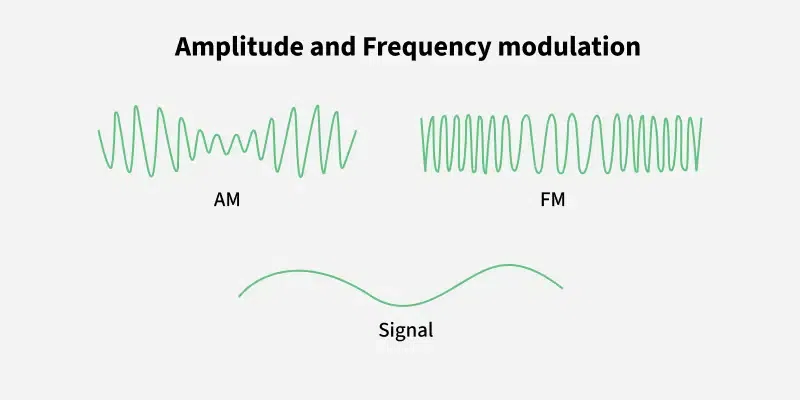 Amplitude and Frequency Modulation
Amplitude and Frequency ModulationWhat is Amplitude Modulation?
Amplitude modulation is a modulation in which the amplitude of the carrier wave changes according to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal, keeping phase and frequency constant. The amplitude of the carrier wave is modified in order to send the data or information. It can transmit over long distances, and has a large range. Its modulation index varies from 0 to 1. In amplitude modulation, the frequency and phase remain the same.
Advantages of Amplitude Modulation
- Simplicity: AM is easy to implement and does not require complex equipment.
- Wider Coverage Area: AM signals can travel long distances, especially at lower frequencies (e.g., AM radio stations).
- Low Bandwidth Requirement: AM uses less bandwidth compared to FM or Phase Modulation (PM).
- Ease of Demodulation: AM signals can be demodulated using simple circuits
Disadvantages of Amplitude Modulation
- Prone to Noise: AM signals are highly susceptible to noise and interference, such as static from electrical devices.
- Lower Sound Quality: AM generally provides lower-quality sound, particularly for music or high-frequency content.
- Inefficient Power Usage: A significant portion of the transmitted power does not carry useful information.
- Limited Data Capacity: AM signals have a lower data-carrying capability compared to other modulation techniques
Applications of Amplitude Modulation
- AM modulation is commonly used to broadcast radio signals, particularly for AM radio stations.
- AM is extensively utilized in shortwave radio communication, especially for multinational broadcasts.
- AM is utilized in aviation communication systems, including air traffic control and aircraft-to-aircraft communication.
What is Frequency Modulation?
Frequency Modulation is a modulation in which the frequency of the carrier wave changes according to the instantaneous amplitude of the modulating signal keeping phase and amplitude as constant. The frequency of the carrier wave is modified in order to send the data or information. It cannot transmit over long distances, have a smaller range. Its modulation index is always greater than one. In frequency modulation amplitude and phase remain the same.
Advantages of Frequency Modulation (FM)
- Better Sound Quality: FM provides much better sound quality than AM, making it ideal for music and high-quality audio broadcasts.
- Noise Immunity: FM is more resistant to noise and interference, so the signal remains clearer even in noisy environments, like in cars.
- Higher Bandwidth Efficiency: FM allows for a wider bandwidth, which can carry more information.
- Efficient Power Usage: FM uses the power more effectively, as the carrier signal doesn't carry the entire load of the transmission.
Disadvantages of Frequency Modulation (FM)
- Limited Range: FM signals don’t travel as far as AM signals, so they are better suited for local broadcasts (like FM radio stations).
- More Complex Equipment: FM transmitters and receivers are more complex than AM, requiring more advanced equipment.
- Uses More Bandwidth: FM requires more space on the radio spectrum than AM, which means fewer channels can be used in the same frequency range.
- Power Consumption: FM transmitters require more power to maintain signal quality, which can increase energy consumption.
Applications of Frequency Modulation
- FM modulation is commonly utilized in commercial radio broadcasting, particularly among FM radio stations.
- FM modulation is used in mobile communication systems, including analog FM-based mobile networks and digital systems.
- FM modulation is widely utilized in wireless microphone systems designed for live events, broadcasting, and recording.
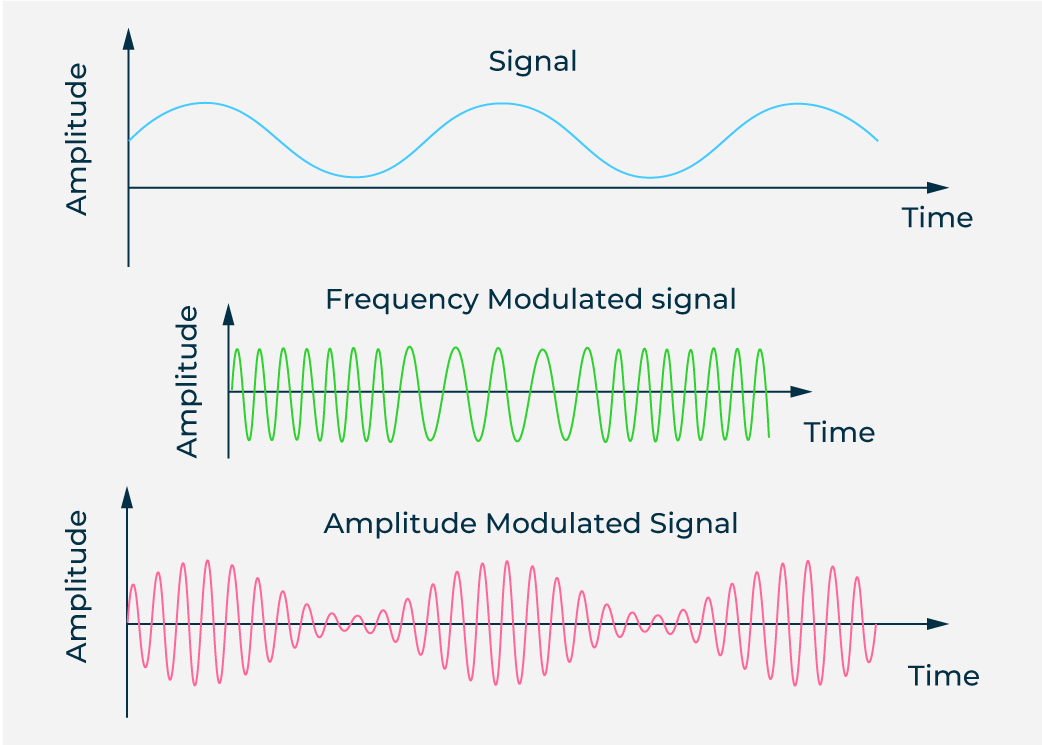 Difference between amplitude modulation and frequency modulation
Difference between amplitude modulation and frequency modulationDifference between Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation
| Amplitude Modulation | Frequency Modulation |
|---|
| In amplitude modulation, the frequency and phase remain the same. | In frequency modulation amplitude and phase remain the same. |
| Its modulation index varies from 0 to 1. | Its modulation index is always greater than one. |
| It has only two sidebands. | It has an infinite number of sidebands. |
| It has simple circuit. | It has complex circuit. |
| The amplitude of the carrier wave is modified in order to send the data or information. | The frequency of the carrier wave is modified in order to send the data or information. |
| It requires low bandwidth in the range of 10 kHz. | It requires high bandwidth in the range of 200 kHz. |
| In AM received signal is of low quality. | In FM received signal is of high quality. |
| It works in a frequency range of 535 to 1705 Kilohertz (KHz). | It works in a frequency range of 88 to 108 Megahertz (MHz). |
| It operates in the medium frequency (MF) and high frequency (HF). | It operates in the very high frequency. |
Less efficient power usage. Most power is in the carrier. | More power is needed for FM transmission. |
Highly susceptible to noise and interference. | Less susceptible to noise; better resistance. |
| It has poor sound quality. | It has better sound quality. |
Conclusion
Both Amplitude Modulation (AM) and Frequency Modulation (FM) are important in analog communication, with unique strengths and limitations. AM is simple, cost-effective, and suitable for long-distance communication, making it ideal for talk radio and aviation communication.
However, it suffers from poor sound quality and high noise susceptibility. FM, on the other hand, provides better sound quality and noise resistance, making it perfect for music and high-quality broadcasts, though it is limited to shorter distances and requires more complex equipment. Choosing between AM and FM depends on the specific requirements, such as range, sound quality, and equipment complexity.
Also, Check
Explore
Electronic Devices & Components
Digital Circuits & Logic
Analog & Circuit Behavior
Solid-State Devices
Communication Systems
Signal Processing
My Profile