ZigZag Tree Traversal of a Binary Tree
Last Updated : 08 Oct, 2025
Given the root of a binary tree, perform a zigzag (spiral) level order traversal. For odd-numbered levels, traverse the nodes from left to right and for even-numbered levels, traverse the nodes from right to left.
Examples:
Input:
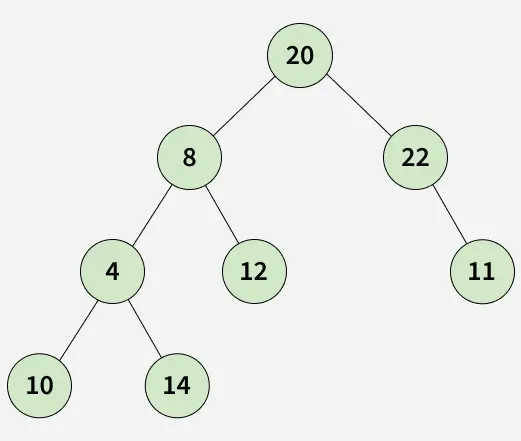
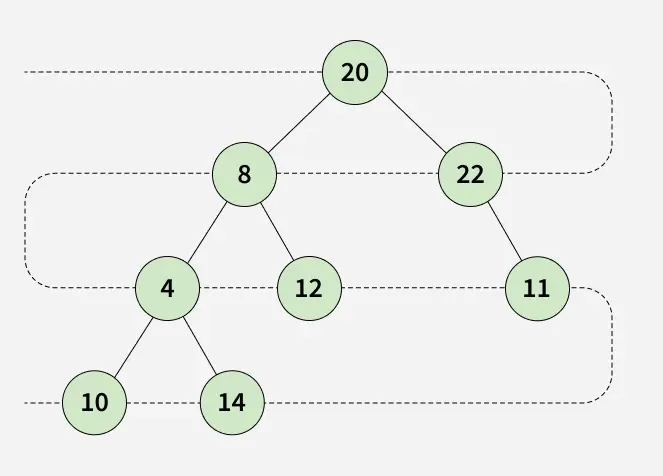
Output: [20, 22, 8, 4, 12, 11, 14, 10]
Explanation:
[Naive Approach] - Using Recursion
The idea is to first calculate the height of the tree, and then recursively traverse each level to perform a level order traversal according to the current level’s direction.
The traversal alternates directions at each level to achieve a zigzag pattern:
- At the first level, nodes are visited from left to right.
- At the next level, nodes are visited from right to left.
- This pattern continues for all levels by flipping the direction after each level.
C++ #include <vector> #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; // Finding the Tree Height int treeHeight(Node *root){ if(!root) return 0; int lHeight = treeHeight(root->left); int rHeight = treeHeight(root->right); return max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function which prints from left to // right traversal at a certain level void leftToRightTrav(Node* root, int level, vector<int>&res) { if (root == nullptr) return; if (level == 1) { res.push_back(root->data); } else { leftToRightTrav(root->left, level-1, res); leftToRightTrav(root->right, level-1, res); } } // Function which prints from right to // left traversal at a certain level void rightToLeftTrav(Node* root, int level, vector<int>&res) { if (root == nullptr) return; if (level == 1) { res.push_back(root->data); } else { rightToLeftTrav(root->right, level-1, res); rightToLeftTrav(root->left, level-1, res); } } vector<int> zigZagTraversal(Node* root) { vector<int> res; bool leftToRight = true; int height = treeHeight(root); for(int i = 1; i <= height; i++){ if (leftToRight) leftToRightTrav(root, i, res); else rightToLeftTrav(root, i, res); // Flip the value of leftToRight leftToRight = !leftToRight; } return res; } int main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node* root = new Node(20); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(22); root->right->right = new Node(11); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(12); root->left->right->left = new Node(10); root->left->right->right = new Node(14); vector<int> res = zigZagTraversal(root); for (int i=0; i<res.size(); i++) { cout << res[i] << " "; } return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdbool.h> // Node Structure struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; }; // Finding the Tree Height int treeHeight(struct Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; int lHeight = treeHeight(root->left); int rHeight = treeHeight(root->right); return (lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight : rHeight) + 1; } // Function to traverse from left to right traversal at a certain level void leftToRightTrav(struct Node* root, int level, int* res, int* index) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) { res[(*index)++] = root->data; } else { leftToRightTrav(root->left, level - 1, res, index); leftToRightTrav(root->right, level - 1, res, index); } } // Function to traverse from right to left traversal at a certain level void rightToLeftTrav(struct Node* root, int level, int* res, int* index) { if (root == NULL) return; if (level == 1) { res[(*index)++] = root->data; } else { rightToLeftTrav(root->right, level - 1, res, index); rightToLeftTrav(root->left, level - 1, res, index); } } // Function to traverse the tree in zigzag order void zigZagTraversal(struct Node* root, int* res, int* size) { bool leftToRight = true; int height = treeHeight(root); int index = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) { if (leftToRight) leftToRightTrav(root, i, res, &index); else rightToLeftTrav(root, i, res, &index); leftToRight = !leftToRight; } // Set the size of the result *size = index; } struct Node* createNode(int val) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = val; node->left = node->right = NULL; return node; } int main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 struct Node* root = createNode(20); root->left = createNode(8); root->right = createNode(22); root->right->right = createNode(11); root->left->left = createNode(4); root->left->right = createNode(12); root->left->right->left = createNode(10); root->left->right->right = createNode(14); // Array to hold zigzag traversal results int res[200]; int size = 0; zigZagTraversal(root, res, &size); for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { printf("%d ", res[i]); } printf("\n"); return 0; } import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; // Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Finding the Tree Height static int treeHeight(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; int lHeight = treeHeight(root.left); int rHeight = treeHeight(root.right); return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function which prints from left to // right traversal at a certain level static void leftToRightTrav(Node root, int level, ArrayList<Integer> res) { if (root == null) return; if (level == 1) { res.add(root.data); } else { leftToRightTrav(root.left, level - 1, res); leftToRightTrav(root.right, level - 1, res); } } // Function which prints from right to // left traversal at a certain level static void rightToLeftTrav(Node root, int level, ArrayList<Integer> res) { if (root == null) return; if (level == 1) { res.add(root.data); } else { rightToLeftTrav(root.right, level - 1, res); rightToLeftTrav(root.left, level - 1, res); } } // Finding the zigZagTraversal static ArrayList<Integer> zigZagTraversal(Node root) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); boolean leftToRight = true; int height = treeHeight(root); for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) { if (leftToRight) leftToRightTrav(root, i, res); else rightToLeftTrav(root, i, res); // Flip the value of leftToRight leftToRight = !leftToRight; } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); ArrayList<Integer> res = zigZagTraversal(root); for (int i : res) { System.out.print(i + " "); } System.out.println(); } } # Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Finding the Tree Height def treeHeight(root): if root is None: return 0 lHeight = treeHeight(root.left) rHeight = treeHeight(root.right) return max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1 # Function which prints from left to # right traversal at a certain level def leftToRightTrav(root, level, res): if root is None: return if level == 1: res.append(root.data) else: leftToRightTrav(root.left, level - 1, res) leftToRightTrav(root.right, level - 1, res) # Function which prints from right to # left traversal at a certain level def rightToLeftTrav(root, level, res): if root is None: return if level == 1: res.append(root.data) else: rightToLeftTrav(root.right, level - 1, res) rightToLeftTrav(root.left, level - 1, res) # Finding the zigZagTraversal def zigZagTraversal(root): res = [] leftToRight = True height = treeHeight(root) for i in range(1, height + 1): if leftToRight: leftToRightTrav(root, i, res) else: rightToLeftTrav(root, i, res) # Flip the value of leftToRight leftToRight = not leftToRight return res if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a input binary tree # 20 # / \ # 8 22 # / \ \ # 4 12 11 # / \ # 10 14 root = Node(20) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(22) root.right.right = Node(11) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(12) root.left.right.left = Node(10) root.left.right.right = Node(14) res = zigZagTraversal(root) for i in res: print(i, end=" ") print()
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Finding the Tree Height static int treeHeight(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; int lHeight = treeHeight(root.left); int rHeight = treeHeight(root.right); return Math.Max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function which prints from left to // right traversal at a certain level static void leftToRightTrav(Node root, int level, List<int> res) { if (root == null) return; if (level == 1) { res.Add(root.data); } else { leftToRightTrav(root.left, level - 1, res); leftToRightTrav(root.right, level - 1, res); } } // Function which prints from right to // left traversal at a certain level static void rightToLeftTrav(Node root, int level, List<int> res) { if (root == null) return; if (level == 1) { res.Add(root.data); } else { rightToLeftTrav(root.right, level - 1, res); rightToLeftTrav(root.left, level - 1, res); } } // Finding the zigZagTraversal static List<int> zigZagTraversal(Node root) { List<int> res = new List<int>(); bool leftToRight = true; int height = treeHeight(root); for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) { if (leftToRight) leftToRightTrav(root, i, res); else rightToLeftTrav(root, i, res); // Flip the value of leftToRight leftToRight = !leftToRight; } return res; } static void Main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); List<int> res = zigZagTraversal(root); foreach (int i in res) { Console.Write(i + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); } } // Node Structure class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Finding the Tree Height function treeHeight(root) { if (root === null) return 0; let lHeight = treeHeight(root.left); let rHeight = treeHeight(root.right); return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function which prints from left to // right traversal at a certain level function leftToRightTrav(root, level, res) { if (root === null) return; if (level === 1) { res.push(root.data); } else { leftToRightTrav(root.left, level - 1, res); leftToRightTrav(root.right, level - 1, res); } } // Function which prints from right to // left traversal at a certain level function rightToLeftTrav(root, level, res) { if (root === null) return; if (level === 1) { res.push(root.data); } else { rightToLeftTrav(root.right, level - 1, res); rightToLeftTrav(root.left, level - 1, res); } } function zigZagTraversal(root) { let res = []; let leftToRight = true; let height = treeHeight(root); for (let i = 1; i <= height; i++) { if (leftToRight) { leftToRightTrav(root, i, res); } else { rightToLeftTrav(root, i, res); } // Flip the value of leftToRight leftToRight = !leftToRight; } return res; } // Driver code // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 let root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); let res = zigZagTraversal(root); res.forEach(i => console.log(i)); Output20 22 8 4 12 11 14 10
Time Complexity: O(n*h), where n is the number of nodes and h is the height of the tree. For each height from 1 to n, we are recursively traversing the tree from root in order to get nodes at a certain height.
Auxiliary Space: O(h)
[Expected Approach - 1] - Using Two Stacks - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to perform a zigzag (spiral) level order traversal of a binary tree using two stacks instead of recursion.
- s1 stores nodes of the current level, and s2 stores nodes of the next level.
- Nodes in s1 are processed from top to bottom, and their children are pushed onto s2 in left → right order.
- Nodes in s2 are then processed from top to bottom, and their children are pushed onto s1 in right → left order.
- By alternating the order of pushing children between the two stacks at each level, the traversal naturally alternates direction, achieving the zigzag pattern.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; // Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; vector<int> zigZagTraversal(Node* root) { vector<int> res; if (root == nullptr) return res; // Current level stack<Node*> s1; // Next level stack<Node*> s2; s1.push(root); while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) { // Print nodes of current level from s1 // and push nodes of next level to s2 while (!s1.empty()) { Node* curr = s1.top(); s1.pop(); res.push_back(curr->data); if (curr->left) s2.push(curr->left); if (curr->right) s2.push(curr->right); } // Print nodes of current level from s2 // and push nodes of next level to s1 while (!s2.empty()) { Node* curr = s2.top(); s2.pop(); res.push_back(curr->data); if (curr->right) s1.push(curr->right); if (curr->left) s1.push(curr->left); } } return res; } int main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node* root = new Node(20); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(22); root->right->right = new Node(11); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(12); root->left->right->left = new Node(10); root->left->right->right = new Node(14); vector<int> res = zigZagTraversal(root); for (auto val: res) cout << val << " "; cout << endl; return 0; } import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; // Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GFG { static ArrayList<Integer> zigZagTraversal(Node root) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return res; // Current level Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<>(); // Next level Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<>(); s1.push(root); while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty()) { // Print nodes of current level from s1 // and push nodes of next level to s2 while (!s1.empty()) { Node curr = s1.pop(); res.add(curr.data); if (curr.left != null) s2.push(curr.left); if (curr.right != null) s2.push(curr.right); } // Print nodes of current level from s2 // and push nodes of next level to s1 while (!s2.empty()) { Node curr = s2.pop(); res.add(curr.data); if (curr.right != null) s1.push(curr.right); if (curr.left != null) s1.push(curr.left); } } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); ArrayList<Integer> res = zigZagTraversal(root); for (int val : res) System.out.print(val + " "); System.out.println(); } } # Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None def zigZagTraversal(root): res = [] if root is None: return res # Current level s1 = [] # Next level s2 = [] s1.append(root) while s1 or s2: # Print nodes of current level from s1 # and push nodes of next level to s2 while s1: curr = s1.pop() res.append(curr.data) if curr.left: s2.append(curr.left) if curr.right: s2.append(curr.right) # Print nodes of current level from s2 # and push nodes of next level to s1 while s2: curr = s2.pop() res.append(curr.data) if curr.right: s1.append(curr.right) if curr.left: s1.append(curr.left) return res if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a input binary tree # 20 # / \ # 8 22 # / \ \ # 4 12 11 # / \ # 10 14 root = Node(20) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(22) root.right.right = Node(11) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(12) root.left.right.left = Node(10) root.left.right.right = Node(14) res = zigZagTraversal(root) for val in res: print(val, end=" ") print()
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GFG { static List<int> zigZagTraversal(Node root) { List<int> res = new List<int>(); if (root == null) return res; // Current level Stack<Node> s1 = new Stack<Node>(); // Next level Stack<Node> s2 = new Stack<Node>(); s1.Push(root); while (s1.Count > 0 || s2.Count > 0) { // Print nodes of current level from s1 // and push nodes of next level to s2 while (s1.Count > 0) { Node curr = s1.Pop(); res.Add(curr.data); if (curr.left != null) s2.Push(curr.left); if (curr.right != null) s2.Push(curr.right); } // Print nodes of current level from s2 // and push nodes of next level to s1 while (s2.Count > 0) { Node curr = s2.Pop(); res.Add(curr.data); if (curr.right != null) s1.Push(curr.right); if (curr.left != null) s1.Push(curr.left); } } return res; } static void Main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); List<int> res = zigZagTraversal(root); foreach (int val in res) Console.Write(val + " "); Console.WriteLine(); } } // Node Structure class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function zigZagTraversal(root) { let res = []; if (root == null) return res; // Current level let s1 = []; // Next level let s2 = []; s1.push(root); while (s1.length > 0 || s2.length > 0) { // Print nodes of current level from s1 // and push nodes of next level to s2 while (s1.length > 0) { let curr = s1.pop(); res.push(curr.data); if (curr.left) s2.push(curr.left); if (curr.right) s2.push(curr.right); } // Print nodes of current level from s2 // and push nodes of next level to s1 while (s2.length > 0) { let curr = s2.pop(); res.push(curr.data); if (curr.right) s1.push(curr.right); if (curr.left) s1.push(curr.left); } } return res; } // Driver code // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 let root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); let res = zigZagTraversal(root); console.log(res.join(" ")); Output20 22 8 4 12 11 14 10
[Expected Approach - 2] - Using Deque - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use a deque to store nodes level by level and alternate the direction of traversal at each level.
- For a level traversed left to right, nodes are popped from the front, and their children are added to the back in left → right order.
- For a level traversed right to left, nodes are popped from the back, and their children are added to the front in right → left order.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <vector> // Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; vector<int> zigZagTraversal(Node* root) { vector<int> res; if (!root) return res; deque<Node*> dq; dq.push_back(root); bool reverse = false; while (!dq.empty()) { int n = dq.size(); while (n--) { // Push right to the front // first if reverse is true if (reverse) { Node* curr = dq.back(); dq.pop_back(); res.push_back(curr->data); if (curr->right) dq.push_front(curr->right); if (curr->left) dq.push_front(curr->left); } // Else push left to the back first else { Node* curr = dq.front(); dq.pop_front(); res.push_back(curr->data); if (curr->left) dq.push_back(curr->left); if (curr->right) dq.push_back(curr->right); } } reverse = !reverse; } return res; } int main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node* root = new Node(20); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(22); root->right->right = new Node(11); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(12); root->left->right->left = new Node(10); root->left->right->right = new Node(14); vector<int> res = zigZagTraversal(root); for (auto val: res) cout << val << " "; cout << endl; return 0; } import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; // Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GFG { static ArrayList<Integer> zigZagTraversal(Node root) { ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return res; Deque<Node> dq = new LinkedList<>(); dq.addLast(root); boolean reverse = false; while (!dq.isEmpty()) { int n = dq.size(); while (n-- > 0) { // Push right to the front // first if reverse is true if (reverse) { Node curr = dq.removeLast(); res.add(curr.data); if (curr.right != null) dq.addFirst(curr.right); if (curr.left != null) dq.addFirst(curr.left); } // Else push left to the back first else { Node curr = dq.removeFirst(); res.add(curr.data); if (curr.left != null) dq.addLast(curr.left); if (curr.right != null) dq.addLast(curr.right); } } reverse = !reverse; } return res; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); ArrayList<Integer> res = zigZagTraversal(root); for (int val : res) System.out.print(val + " "); System.out.println(); } } from collections import deque # Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None def zigZagTraversal(root): res = [] if not root: return res dq = deque() dq.append(root) reverse = False while dq: n = len(dq) for _ in range(n): # Push right to the front # first if reverse is true if reverse: curr = dq.pop() res.append(curr.data) if curr.right: dq.appendleft(curr.right) if curr.left: dq.appendleft(curr.left) # Else push left to the back first else: curr = dq.popleft() res.append(curr.data) if curr.left: dq.append(curr.left) if curr.right: dq.append(curr.right) reverse = not reverse return res if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a input binary tree # 20 # / \ # 8 22 # / \ \ # 4 12 11 # / \ # 10 14 root = Node(20) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(22) root.right.right = Node(11) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(12) root.left.right.left = Node(10) root.left.right.right = Node(14) res = zigZagTraversal(root) for val in res: print(val, end=" ") print()
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GFG { static List<int> zigZagTraversal(Node root) { List<int> res = new List<int>(); if (root == null) return res; LinkedList<Node> dq = new LinkedList<Node>(); dq.AddLast(root); bool reverse = false; while (dq.Count > 0) { int n = dq.Count; while (n-- > 0) { // Push right to the front // first if reverse is true if (reverse) { Node curr = dq.Last.Value; dq.RemoveLast(); res.Add(curr.data); if (curr.right != null) dq.AddFirst(curr.right); if (curr.left != null) dq.AddFirst(curr.left); } // Else push left to the back first else { Node curr = dq.First.Value; dq.RemoveFirst(); res.Add(curr.data); if (curr.left != null) dq.AddLast(curr.left); if (curr.right != null) dq.AddLast(curr.right); } } reverse = !reverse; } return res; } static void Main() { // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 Node root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); List<int> res = zigZagTraversal(root); foreach (int val in res) Console.Write(val + " "); Console.WriteLine(); } } // Node Structure class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } class Deque { constructor() { this.front = []; this.back = []; } pushFront(val) { this.front.push(val); } pushBack(val) { this.back.push(val); } popFront() { if (this.front.length === 0) this._balance('front'); return this.front.pop(); } popBack() { if (this.back.length === 0) this._balance('back'); return this.back.pop(); } length() { return this.front.length + this.back.length; } _balance(side) { if (side === 'front') { while (this.back.length) this.front.push(this.back.pop()); } else { while (this.front.length) this.back.push(this.front.pop()); } } } function zigZagTraversal(root) { if (!root) return []; let res = []; let dq = new Deque(); dq.pushBack(root); let reverse = false; while (dq.length() > 0) { let n = dq.length(); for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { // Push right to the front // first if reverse is true if (reverse) { let curr = dq.popBack(); res.push(curr.data); if (curr.right) dq.pushFront(curr.right); if (curr.left) dq.pushFront(curr.left); } // Else push left to the back first else { let curr = dq.popFront(); res.push(curr.data); if (curr.left) dq.pushBack(curr.left); if (curr.right) dq.pushBack(curr.right); } } reverse = !reverse; } return res; } // Driver code // Create a input binary tree // 20 // / \ // 8 22 // / \ \ // 4 12 11 // / \ // 10 14 let root = new Node(20); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(22); root.right.right = new Node(11); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(12); root.left.right.left = new Node(10); root.left.right.right = new Node(14); let res = zigZagTraversal(root); console.log(res.join(" ")); Output20 22 8 4 12 11 14 10
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile