Intersection point of two Linked Lists
Last Updated : 29 Aug, 2025
Given the head of two singly linked lists that merge at some point to form a Y-shaped structure. The two lists may have different lengths and contain distinct nodes initially, but from the intersection point onward, they share the same sequence of nodes. Find the node at which the two linked lists first intersect.
Example:
Input:
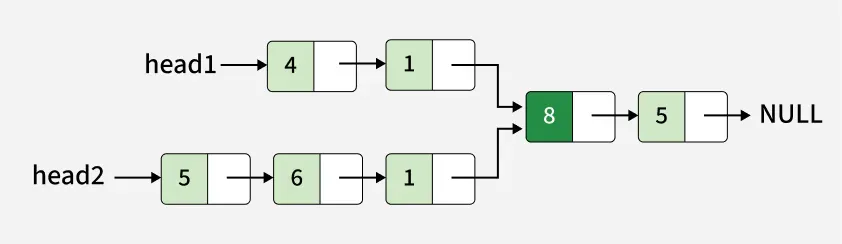
Output: 8
Explanation: 8 is the first common node where both linked lists start sharing the same sequence of nodes.
[Naive Approach] Using two nested loops - O(m × n) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is to take each node of the first linked list and compare it with every node of the second list. The first common node that appears in both lists will be the intersection point.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; Node *intersectPoint(Node *head1, Node *head2) { // Iterate over second list and for each node // Search it in first list while (head2 != nullptr) { Node *temp = head1; while (temp) { // If both Nodes are same if (temp == head2) return head2; temp = temp->next; } head2 = head2->next; } // intersection is not present between the lists return nullptr; } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head1 = new Node(10); head1->next = new Node(15); head1->next->next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head2 = new Node(3); head2->next = new Node(6); head2->next->next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; Node *intersectionPoint = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (intersectionPoint == nullptr) cout << "-1"; else cout << intersectionPoint->data << endl; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* createNode(int data) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } struct Node* intersectPoint(struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { // iterate over second list and for each node // Search it in first list while (head2 != NULL) { struct Node* temp = head1; while (temp != NULL) { // if both Nodes are same if (temp == head2) return head2; temp = temp->next; } head2 = head2->next; } // intersection is not present between the lists return NULL; } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 struct Node* head1 = createNode(10); head1->next = createNode(15); head1->next->next = createNode(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 struct Node* head2 = createNode(3); head2->next = createNode(6); head2->next->next = createNode(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; struct Node* intersectionPoint = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (intersectionPoint == NULL) printf("-1\n"); else printf("%d\n", intersectionPoint->data); return 0; } class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { // iterate over second list and for each node // Search it in first list while (head2 != null) { Node temp = head1; while (temp != null) { // if both Nodes are same if (temp == head2) return head2; temp = temp.next; } head2 = head2.next; } // intersection is not present between the lists return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node intersectionPoint = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (intersectionPoint == null) System.out.println("-1"); else System.out.println(intersectionPoint.data); } } class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None def intersectPoint(head1, head2): # iterate over second list and for each node # Search it in first list while head2 is not None: temp = head1 while temp is not None: # If both Nodes are same if temp == head2: return head2 temp = temp.next head2 = head2.next # intersection is not present between the lists return None if __name__ == "__main__": # creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 head1 = Node(10) head1.next = Node(15) head1.next.next = Node(30) # creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 head2 = Node(3) head2.next = Node(6) head2.next.next = Node(9) # 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next intersectionPoint = intersectPoint(head1, head2) if intersectionPoint is None: print("-1") else: print(intersectionPoint.data) using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { // Iterate over second list and for each node // Search it in first list while (head2 != null) { Node temp = head1; while (temp != null) { // If both Nodes are same if (temp == head2) return head2; temp = temp.next; } head2 = head2.next; } // intersection is not present between the lists return null; } static void Main(string[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node intersectionPoint = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (intersectionPoint == null) Console.WriteLine("-1"); else Console.WriteLine(intersectionPoint.data); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } function intersectPoint(head1, head2) { // Iterate over second list and for each node // Search it in first list while (head2 !== null) { let temp = head1; while (temp !== null) { // If both Nodes are same if (temp === head2) return head2; temp = temp.next; } head2 = head2.next; } // Intersection is not present between the lists return null; } // Driver Code // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 let head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 let head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; const intersectionPoint = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (intersectionPoint === null) console.log("-1"); else console.log(intersectionPoint.data); [Better Approach] Using Hashing - O(m + n) Time and O(m) Space
The idea is to use hashing to store all the nodes of the first list in a hash set and then iterate over second list checking if the node is present in the set. If we find a node which is present in the hash set, we return the node.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <unordered_set> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; Node *intersectPoint(Node *head1, Node *head2) { unordered_set<Node *> visNodes; // traverse the first list and store all // nodes in a set Node *curr1 = head1; while (curr1 != nullptr) { visNodes.insert(curr1); curr1 = curr1->next; } // traverse the second list and check if any // node is in the set Node *curr2 = head2; while (curr2 != nullptr) { if (visNodes.find(curr2) != visNodes.end()) { // Intersection point found return curr2; } curr2 = curr2->next; } return nullptr; } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head1 = new Node(10); head1->next = new Node(15); head1->next->next = new Node(30); // creation of second list // 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head2 = new Node(3); head2->next = new Node(6); head2->next->next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; Node *interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == nullptr) cout << "-1"; else cout << interPt->data << endl; } import java.util.HashSet; class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { HashSet<Node> visNodes = new HashSet<>(); // Traverse the first list and store all nodes in a set Node curr1 = head1; while (curr1 != null) { visNodes.add(curr1); curr1 = curr1.next; } // Traverse the second list and check if any node is // in the set Node curr2 = head2; while (curr2 != null) { if (visNodes.contains(curr2)) { // Intersection point found return curr2; } curr2 = curr2.next; } return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) System.out.println("-1"); else System.out.println(interPt.data); } } class Node: def __init__(self, new_data): self.data = new_data self.next = None def intersectPoint(head1, head2): visNodes = set() # Traverse the first list and store all nodes in a set curr1 = head1 while curr1 is not None: visNodes.add(curr1) curr1 = curr1.next # Traverse the second list and check if any node is in the set curr2 = head2 while curr2 is not None: if curr2 in visNodes: return curr2 # Intersection point found curr2 = curr2.next return None if __name__ == "__main__": # creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 head1 = Node(10) head1.next = Node(15) head1.next.next = Node(30) # creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 head2 = Node(3) head2.next = Node(6) head2.next.next = Node(9) # 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2) if interPt is None: print("-1") else: print(interPt.data) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { HashSet<Node> visNodes = new HashSet<Node>(); // Traverse the first list and store all nodes in a set Node curr1 = head1; while (curr1 != null) { visNodes.Add(curr1); curr1 = curr1.next; } // Traverse the second list and check if any node is // in the set Node curr2 = head2; while (curr2 != null) { // Intersection point found if (visNodes.Contains(curr2)) return curr2; curr2 = curr2.next; } return null; } static void Main(string[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) Console.WriteLine("-1"); else Console.WriteLine(interPt.data); } } class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } function intersectPoint(head1, head2) { const visNodes = new Set(); // traverse the first list and store // all nodes in a set let curr1 = head1; while (curr1 !== null) { visNodes.add(curr1); curr1 = curr1.next; } // traverse the second list and check // if any node is in // the set let curr2 = head2; while (curr2 !== null) { // intersection point found if (visNodes.has(curr2)) { return curr2; } curr2 = curr2.next; } return null; } // Driver Code // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 let head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list // 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 let head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; const interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt === null) console.log("-1"); else console.log(interPt.data); [Expected Approach - 1] Using difference in node counts - O(m + n) Time and O(1) Space
The two lists share the same tail after the intersection; only their starting parts differ in length. To align them, we should skip the extra nodes in the longer list so both pointers stand at the same distance from the intersection.
Count the nodes in both lists and find the difference (d). Advance the pointer of the longer list by d steps, then move both pointers together until they meet. The meeting point is the intersection.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // function to get the count of nodes in a linked list int getCount(Node *head) { int cnt = 0; Node *curr = head; while (curr != nullptr) { cnt++; curr = curr->next; } return cnt; } // function to get the intersection point of two // linked lists where head1 has d more nodes than head2 Node* getIntersectionByDiff(int diff, Node *head1, Node *head2) { Node *curr1 = head1; Node *curr2 = head2; // move the pointer forward by d nodes for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) { if (curr1 == nullptr) return nullptr; curr1 = curr1->next; } // move both pointers until they intersect while (curr1 != nullptr && curr2 != nullptr) { if (curr1 == curr2) return curr1; curr1 = curr1->next; curr2 = curr2->next; } return nullptr; } // function to get the intersection point of two linked lists Node* intersectPoint(Node *head1, Node *head2) { // count the number of nodes in both linked lists int len1 = getCount(head1); int len2 = getCount(head2); int diff = 0; // if the first list is longer if (len1 > len2) { diff = len1 - len2; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2); } else { diff = len2 - len1; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head2, head1); } } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head1 = new Node(10); head1->next = new Node(15); head1->next->next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head2 = new Node(3); head2->next = new Node(6); head2->next->next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; Node *interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == nullptr) cout << "-1"; else cout << interPt->data << endl; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* createNode(int data) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } // Function to get the count of nodes in a linked list int getCount(struct Node* head) { int cnt = 0; struct Node* curr = head; while (curr != NULL) { cnt++; curr = curr->next; } return cnt; } // Function to get the intersection point of two // linked lists where head1 has d more nodes than head2 struct Node* getIntersectionByDiff(int diff, struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { struct Node* curr1 = head1; struct Node* curr2 = head2; // Move the pointer forward by d nodes for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) { if (curr1 == NULL) return NULL; curr1 = curr1->next; } // Move both pointers until they intersect while (curr1 != NULL && curr2 != NULL) { if (curr1 == curr2) return curr1; curr1 = curr1->next; curr2 = curr2->next; } return NULL; } // Function to get the intersection point of two linked lists struct Node* intersectPoint(struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { // Count the number of nodes in both linked lists int len1 = getCount(head1); int len2 = getCount(head2); int diff = 0; // If the first list is longer if (len1 > len2) { diff = len1 - len2; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2); } else { diff = len2 - len1; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head2, head1); } } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 struct Node* head1 = createNode(10); head1->next = createNode(15); head1->next->next = createNode(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 struct Node* head2 = createNode(3); head2->next = createNode(6); head2->next->next = createNode(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; struct Node* interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == NULL) printf("-1\n"); else printf("%d\n", interPt->data); return 0; } class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to get the count of nodes in a linked list static int getCount(Node head) { int cnt = 0; Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { cnt++; curr = curr.next; } return cnt; } // Function to get the intersection point of two // linked lists where head1 has d more nodes than head2 static Node getIntersectionByDiff(int diff, Node head1, Node head2) { Node curr1 = head1; Node curr2 = head2; // Move the pointer forward by d nodes for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) { if (curr1 == null) return null; curr1 = curr1.next; } // Move both pointers until they intersect while (curr1 != null && curr2 != null) { if (curr1 == curr2) return curr1; curr1 = curr1.next; curr2 = curr2.next; } return null; } // Function to get the intersection point of two linked lists static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { // Count the number of nodes in both linked lists int len1 = getCount(head1); int len2 = getCount(head2); int diff = 0; // If the first list is longer if (len1 > len2) { diff = len1 - len2; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2); } else { diff = len2 - len1; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head2, head1); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) System.out.println("-1"); else System.out.println(interPt.data); } } class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None # Function to get the count of nodes in a linked list def getCount(head): cnt = 0 curr = head while curr: cnt += 1 curr = curr.next return cnt # Function to get the intersection point of two # linked lists where head1 has d more nodes than head2 def getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2): curr1 = head1 curr2 = head2 # Move the pointer forward by d nodes for _ in range(diff): if not curr1: return None curr1 = curr1.next # Move both pointers until they intersect while curr1 and curr2: if curr1 == curr2: return curr1 curr1 = curr1.next curr2 = curr2.next return None # Function to get the intersection point of two linked lists def intersectPoint(head1, head2): # Count the number of nodes in both linked lists len1 = getCount(head1) len2 = getCount(head2) diff = 0 # If the first list is longer if len1 > len2: diff = len1 - len2 return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2) else: diff = len2 - len1 return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head2, head1) if __name__ == "__main__": # creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 head1 = Node(10) head1.next = Node(15) head1.next.next = Node(30) # creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 head2 = Node(3) head2.next = Node(6) head2.next.next = Node(9) # 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2) if not interPt: print("-1") else: print(interPt.data) using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to get the count of nodes in a linked list static int getCount(Node head) { int cnt = 0; Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { cnt++; curr = curr.next; } return cnt; } // Function to get the intersection point of two // linked lists where head1 has d more nodes than head2 static Node getIntersectionByDiff(int diff, Node head1, Node head2) { Node curr1 = head1; Node curr2 = head2; // Move the pointer forward by d nodes for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) { if (curr1 == null) return null; curr1 = curr1.next; } // Move both pointers until they intersect while (curr1 != null && curr2 != null) { if (curr1 == curr2) return curr1; curr1 = curr1.next; curr2 = curr2.next; } return null; } // Function to get the intersection point of two linked lists static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { // Count the number of nodes in both linked lists int len1 = getCount(head1); int len2 = getCount(head2); int diff = 0; // If the first list is longer if (len1 > len2) { diff = len1 - len2; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2); } else { diff = len2 - len1; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head2, head1); } } static void Main(string[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) Console.WriteLine("-1"); else Console.WriteLine(interPt.data); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Function to get the count of nodes in a linked list function getCount(head) { let cnt = 0; let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { cnt++; curr = curr.next; } return cnt; } // Function to get the intersection point of two // linked lists where head1 has d more nodes than head2 function getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2) { let curr1 = head1; let curr2 = head2; // Move the pointer forward by d nodes for (let i = 0; i < diff; i++) { if (curr1 === null) return null; curr1 = curr1.next; } // Move both pointers until they intersect while (curr1 !== null && curr2 !== null) { if (curr1 === curr2) return curr1; curr1 = curr1.next; curr2 = curr2.next; } return null; } // Function to get the intersection point of two linked lists function intersectPoint(head1, head2) { // Count the number of nodes in both linked lists let len1 = getCount(head1); let len2 = getCount(head2); let diff = 0; // If the first list is longer if (len1 > len2) { diff = len1 - len2; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head1, head2); } else { diff = len2 - len1; return getIntersectionByDiff(diff, head2, head1); } } // Driver Code // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 let head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 let head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; let interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt === null) console.log("-1"); else console.log(interPt.data); [Expected Approach - 2] Using Two Pointer Technique - O(m + n) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is to traverse the two given linked lists simultaneously, using two pointers. When one pointer reaches the end of its list, it is reassigned to the head of the other list. This process continues until the two pointers meet, which indicates that they have reached the intersection point.
Why this works:
- Suppose the lengths of the two lists are m and n, and they share a common tail of length c.
- The unique parts before the intersection are m - c and n - c.
- By switching lists, each pointer travels (m - c) + c + (n - c) = m + n - c steps before reaching the intersection.
- Since both pointers cover exactly m + n - c steps, they must arrive at the intersection at the same time.
Step by Step Approach:
- Initialize two pointers ptr1 and ptr2 at head1 and head2 respectively.
- Traverse through the lists, one node at a time.
=> When ptr1 reaches the end of a list, then redirect it to head2.
=> Similarly, when ptr2 reaches the end of a list, redirect it to the head1.
=> Once both of them go through reassigning, they will be at equal distance from the collision point.
=> If at any node ptr1 meets ptr2, then it is the intersection node. - After the second iteration if there is no intersection node, returns NULL.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; Node *intersectPoint(Node *head1, Node *head2) { Node *ptr1 = head1; Node *ptr2 = head2; if (ptr1 == nullptr || ptr2 == nullptr) return nullptr; // traverse through the lists until both pointers meet while (ptr1 != ptr2) { // move to the next node in each list and if the one // pointer reaches NULL, start from the other linked list ptr1 = ptr1 ? ptr1->next : head2; ptr2 = ptr2 ? ptr2->next : head1; } return ptr1; } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head1 = new Node(10); head1->next = new Node(15); head1->next->next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head2 = new Node(3); head2->next = new Node(6); head2->next->next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; Node *interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == nullptr) cout << "-1"; else cout << interPt->data << endl; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* createNode(int data) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } struct Node* intersectPoint(struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { struct Node* ptr1 = head1; struct Node* ptr2 = head2; if (ptr1 == NULL || ptr2 == NULL) return NULL; // Traverse through the lists until both pointers meet while (ptr1 != ptr2) { ptr1 = ptr1 ? ptr1->next : head2; ptr2 = ptr2 ? ptr2->next : head1; } return ptr1; } int main() { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 struct Node* head1 = createNode(10); head1->next = createNode(15); head1->next->next = createNode(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 struct Node* head2 = createNode(3); head2->next = createNode(6); head2->next->next = createNode(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2->next->next->next = head1->next; struct Node* interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == NULL) printf("-1\n"); else printf("%d\n", interPt->data); return 0; } class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2){ Node ptr1 = head1; Node ptr2 = head2; if (ptr1 == null || ptr2 == null) return null; // traverse through the lists until both // pointers meet while (ptr1 != ptr2) { // move to the next node in each list and if the one // pointer reaches NULL, start from the other linked list ptr1 = (ptr1 != null) ? ptr1.next : head2; ptr2 = (ptr2 != null) ? ptr2.next : head1; } return ptr1; } public static void main(String[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) System.out.println("-1"); else System.out.println(interPt.data); } } class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None def intersectPoint(head1, head2): ptr1 = head1 ptr2 = head2 if not ptr1 or not ptr2: return None # traverse through the lists until both pointers meet while ptr1 != ptr2: # move to the next node in each list and if the one # pointer reaches None, start from the other linked list ptr1 = ptr1.next if ptr1 else head2 ptr2 = ptr2.next if ptr2 else head1 return ptr1 if __name__ == "__main__": # creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 head1 = Node(10) head1.next = Node(15) head1.next.next = Node(30) # creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 head2 = Node(3) head2.next = Node(6) head2.next.next = Node(9) # 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2) if not interPt: print("-1") else: print(interPt.data) using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { Node ptr1 = head1; Node ptr2 = head2; if (ptr1 == null || ptr2 == null) return null; // traverse through the lists until both pointers meet while (ptr1 != ptr2) { // move to the next node in each list and if the one // pointer reaches null, start from the other linked list ptr1 = (ptr1 != null) ? ptr1.next : head2; ptr2 = (ptr2 != null) ? ptr2.next : head1; } return ptr1; } public static void Main(string[] args) { // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) Console.WriteLine("-1"); else Console.WriteLine(interPt.data); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } function intersectPoint(head1, head2) { let ptr1 = head1; let ptr2 = head2; if (!ptr1 || !ptr2) return null; // traverse through the lists until both // pointers meet while (ptr1 !== ptr2) { // move to the next node in each list and if the one // pointer reaches null, start from the other linked list ptr1 = ptr1 ? ptr1.next : head2; ptr2 = ptr2 ? ptr2.next : head1; } return ptr1; } // Driver Code // creation of first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 let head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // creation of second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 let head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // 15 is the intersection point head2.next.next.next = head1.next; let interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (!interPt) console.log("-1"); else console.log(interPt.data); [Expected Approach - 3] Intersection Detection using List Reversal and Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm
If two linked lists intersect, the intersection point is the place where their paths merge into one. One way to detect this is to convert the problem into a cycle detection problem. If we somehow make the shared portion of the two lists form a loop, then standard cycle detection techniques can be applied to locate the intersection.
To achieve this, we reverse the second list and connect it to the end of the first list. If the lists intersect, this connection will create a cycle and first node of cycle will be our intersection point.
Now, the problem become finding the first node of a loop in a linked list.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // reverses a linked list Node* reverse(Node* node) { Node *prev = nullptr, *curr = node; while (curr) { Node *temp = curr->next; curr->next = prev; prev = curr; curr = temp; } return prev; } // finds the intersection point of two // linked lists Node* intersectPoint(Node* head1, Node* head2) { if (!head1 || !head2) return nullptr; // reverse the second list Node* revHead2 = reverse(head2); // attach reversed second list to the // end of the first Node* temp = head1; while (temp->next) temp = temp->next; temp->next = revHead2; // detect cycle using Floyd’s algorithm Node* slow = head1; Node* fast = head1; while (fast && fast->next) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next->next; if (slow == fast) { slow = head1; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; } return slow; } } return nullptr; } int main() { // first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head1 = new Node(10); head1->next = new Node(15); head1->next->next = new Node(30); // second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node *head2 = new Node(3); head2->next = new Node(6); head2->next->next = new Node(9); // intersection at node with value 15 head2->next->next->next = head1->next; Node *interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == nullptr) cout << "-1"; else cout << interPt->data << endl; } class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // reverses a linked list static Node reverse(Node node) { Node prev = null, curr = node; while (curr != null) { Node temp = curr.next; curr.next = prev; prev = curr; curr = temp; } return prev; } // finds the intersection point of two // linked lists static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { if (head1 == null || head2 == null) return null; // reverse the second list Node revHead2 = reverse(head2); // attach reversed second list to the // end of the first Node temp = head1; while (temp.next != null) temp = temp.next; temp.next = revHead2; // detect cycle using Floyd’s algorithm Node slow = head1; Node fast = head1; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { slow = head1; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } } return null; } public static void main(String[] args) { // first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // intersection at node with value 15 head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) System.out.println("-1"); else System.out.println(interPt.data); } } class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # reverses a linked list def reverse(node): prev = None curr = node while curr: temp = curr.next curr.next = prev prev = curr curr = temp return prev # finds the intersection point of two # linked lists def intersectPoint(head1, head2): if not head1 or not head2: return None # reverse the second list revHead2 = reverse(head2) # attach reversed second list to the # end of the first temp = head1 while temp.next: temp = temp.next temp.next = revHead2 # detect cycle using Floyd’s algorithm slow = head1 fast = head1 while fast and fast.next: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next.next if slow == fast: slow = head1 while slow != fast: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next return slow return None if __name__ == "__main__": # first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 head1 = Node(10) head1.next = Node(15) head1.next.next = Node(30) # second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 head2 = Node(3) head2.next = Node(6) head2.next.next = Node(9) # intersection at node with value 15 head2.next.next.next = head1.next interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2) if interPt is None: print("-1") else: print(interPt.data) using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // reverses a linked list static Node reverse(Node node) { Node prev = null, curr = node; while (curr != null) { Node temp = curr.next; curr.next = prev; prev = curr; curr = temp; } return prev; } // finds the intersection point of two // linked lists static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { if (head1 == null || head2 == null) return null; // reverse the second list Node revHead2 = reverse(head2); // attach reversed second list to the // end of the first Node temp = head1; while (temp.next != null) temp = temp.next; temp.next = revHead2; // detect cycle using Floyd’s algorithm Node slow = head1; Node fast = head1; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow == fast) { slow = head1; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } } return null; } static void Main(string[] args) { // first list: 10 -> 15 -> 30 Node head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); // second list: 3 -> 6 -> 9 -> 15 -> 30 Node head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // intersection at node with value 15 head2.next.next.next = head1.next; Node interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt == null) Console.WriteLine("-1"); else Console.WriteLine(interPt.data); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // reverses a linked list function reverse(node) { let prev = null, curr = node; while (curr) { let temp = curr.next; curr.next = prev; prev = curr; curr = temp; } return prev; } // finds the intersection point of two // linked lists function intersectPoint(head1, head2) { if (!head1 || !head2) return null; // reverse the second list let revHead2 = reverse(head2); // attach reversed second list to the // end of the first let temp = head1; while (temp.next) temp = temp.next; temp.next = revHead2; // detect cycle using Floyd’s algorithm let slow = head1; let fast = head1; while (fast && fast.next) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (slow === fast) { slow = head1; while (slow !== fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } } return null; } // Driver Code let head1 = new Node(10); head1.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next = new Node(30); let head2 = new Node(3); head2.next = new Node(6); head2.next.next = new Node(9); // intersection at node with value 15 head2.next.next.next = head1.next; let interPt = intersectPoint(head1, head2); if (interPt === null) console.log("-1"); else console.log(interPt.data); Time Complexity: O(m + n), where m and n are the lengths of the two linked lists. Reversing one list, traversing to attach it, and running Floyd’s cycle detection each take linear time in the size of the lists.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile