Sum of digit of a number using recursion
Last Updated : 17 Mar, 2025
Given a number, we need to find sum of its digits using recursion.
Examples:
Input: 12345
Output: 15
Explanation: Sum of digits → 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15
Input: 45632
Output: 20
Approach:
To understand the algorithm, consider the number 12345 and refer to the illustration below..
- Extract the last digit: 12345 % 10 = 5, pass 1234 to the next step.
- Extract next digit: 1234 % 10 = 4, pass 123 to the next step.
- Extract next digit: 123 % 10 = 3, pass 12 to the next step.
- Extract next digit: 12 % 10 = 2, pass 1 to the next step.
- Extract last digit: 1 % 10 = 1, pass 0, stopping recursion.
Each step adds the extracted digit to the sum, forming 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 = 15
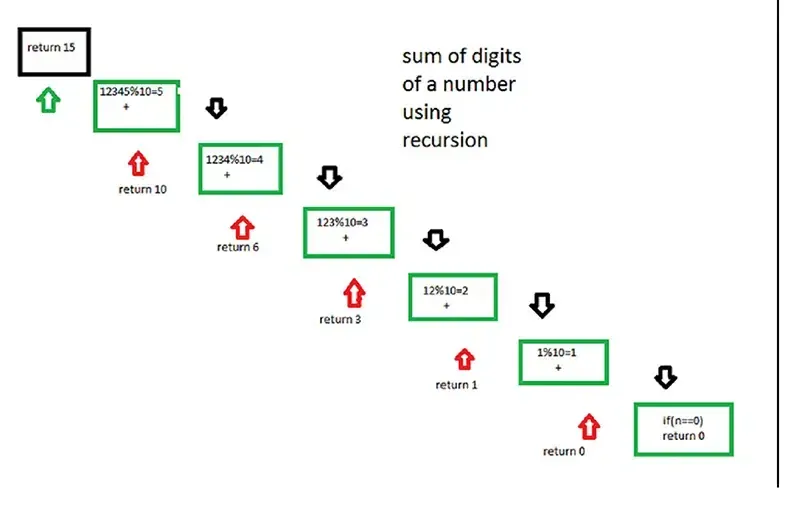 Recursive Sum of Digits for 12345
Recursive Sum of Digits for 12345
Note: Instead of if (n == 0) return 0;, we can use if (n < 10) return n;, eliminating extra function calls for single-digit numbers without changing the output.
C++ // Recursive C++ program to find sum of digits // of a number #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to check sum of digit using recursion int sum_of_digit(int n) { if (n == 0) return 0; return (n % 10 + sum_of_digit(n / 10)); } // Driven code int main() { int num = 12345; int result = sum_of_digit(num); cout << result << endl; return 0; } // Recursive C program to find sum of digits // of a number #include <stdio.h> // Function to check sum of digit using recursion int sum_of_digit(int n) { if (n == 0) return 0; return (n % 10 + sum_of_digit(n / 10)); } // Driven Program to check above int main() { int num = 12345; int result = sum_of_digit(num); printf("%d", result); return 0; } import java.io.*; class GfG { // Function to check sum // of digit using recursion static int sum_of_digit(int n) { if (n == 0) return 0; return (n % 10 + sum_of_digit(n / 10)); } // Driven Program to check above public static void main(String args[]) { int num = 12345; int result = sum_of_digit(num); System.out.println(result); } } # Function to check sum of # digit using recursion def sum_of_digit( n ): if n == 0: return 0 return (n % 10 + sum_of_digit(int(n / 10))) # Driven code to check above num = 12345 result = sum_of_digit(num) print(result)
using System; class GfG { // Function to check sum // of digit using recursion static int sum_of_digit(int n) { if (n == 0) return 0; return (n % 10 + sum_of_digit(n / 10)); } // Driven Program to check above public static void Main() { int num = 12345; int result = sum_of_digit(num); Console.WriteLine(result); } } // Function to check sum of digit using recursion function sum_of_digit(n) { if (n == 0) return 0; return (n % 10 + sum_of_digit(parseInt(n / 10))); } // Driven code var num = 12345; var result = sum_of_digit(num); console.log(result ); Besides writing (n==0 , then return 0) in the code given above we can also write it in this manner , there will be no change in the output .
if (n <1 0) return n; by writing this there will be no need to call the function for the numbers which are less than 10
Time Complexity: O(log10n), Traverse through all the digits, as there are log10n bits.
Auxiliary Space: O(log10n), due to recursive function calls stored in the call stack.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile