Succinct Encoding of Binary Tree
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
A succinct encoding of Binary Tree takes close to the minimum possible space. The number of structurally different binary trees on n nodes is n'th Catalan number. For large n, this is about 4n; thus we need at least about log2 4n = 2n bits to encode it. A succinct binary tree therefore would occupy 2n + O(n) bits.
One simple representation that meets this bound is to visit the nodes of the tree in preorder, outputting "1" for a not-null node and "0" for a null node. If the tree contains data, we can simply simultaneously store it in a consecutive array in preorder.
Example:
Input:
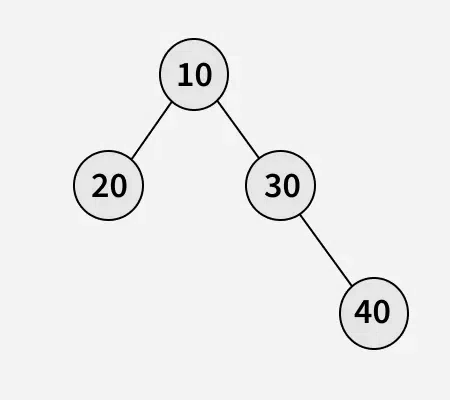
Output: 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
Explanation: 1 indicates data and 0 indicates NULL.
Approach for encoding binary tree - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to perform pre-order traversal of the binary tree. If the node is null, then append '0' to the string. Otherwise append '1' to the string and push the node value into a data array. Return the string and data array.
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++ // C++ program to encode a // binary tree. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node (int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; // Recursive pre-order function to // encode a binary tree. void encodeTreeRecur(Node* root, string &s, vector<int> &arr) { // For null nodes if (root == nullptr) { s.push_back('0'); return; } s.push_back('1'); // Store pre-order in array. arr.push_back(root->data); // Apply pre-order to left and // right subtree. encodeTreeRecur(root->left, s, arr); encodeTreeRecur(root->right, s, arr); } pair<string, vector<int>> encodeTree(Node* root) { string s = ""; vector<int> arr; encodeTreeRecur(root, s, arr); return make_pair(s, arr); } int main() { // Binary tree // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ \ // 40 50 70 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(20); root->right = new Node(30); //root->left->left = new Node(40); //root->left->right = new Node(50); root->right->right = new Node(70); pair<string, vector<int>> ans = encodeTree(root); cout << ans.first << endl; for (auto num: ans.second) cout << num << " "; cout << endl; return 0; } // Java program to encode a // binary tree. import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class Pair { String s; ArrayList<Integer> arr; Pair(String s1, ArrayList<Integer> arr1) { s = s1; arr = arr1; } } class GfG { // Recursive pre-order function to // encode a binary tree. static void encodeTreeRecur(Node root, StringBuilder s, ArrayList<Integer> arr) { // For null nodes if (root == null) { s.append('0'); return; } s.append('1'); // Store pre-order in array. arr.add(root.data); // Apply pre-order to left and // right subtree. encodeTreeRecur(root.left, s, arr); encodeTreeRecur(root.right, s, arr); } static Pair encodeTree(Node root) { StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(); ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>(); encodeTreeRecur(root, s, arr); return new Pair(s.toString(), arr); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Binary tree // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ \ // 40 50 70 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(50); root.right.right = new Node(70); Pair ans = encodeTree(root); System.out.println(ans.s); for (int num : ans.arr) System.out.print(num + " "); System.out.println(); } } # Python program to encode a # binary tree. class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Recursive pre-order function to # encode a binary tree. def encodeTreeRecur(root, s, arr): # For null nodes if root is None: s.append('0') return s.append('1') # Store pre-order in array. arr.append(root.data) # Apply pre-order to left and # right subtree. encodeTreeRecur(root.left, s, arr) encodeTreeRecur(root.right, s, arr) def encodeTree(root): s = [] arr = [] encodeTreeRecur(root, s, arr) return ''.join(s), arr if __name__ == "__main__": # Binary tree # 10 # / \ # 20 30 # / \ \ # 40 50 70 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(20) root.right = Node(30) root.left.left = Node(40) root.left.right = Node(50) root.right.right = Node(70) ans = encodeTree(root) print(ans[0]) for num in ans[1]: print(num, end=" ") print() // C# program to encode a // binary tree. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // Recursive pre-order function to // encode a binary tree. static void encodeTreeRecur(Node root, ref string s, List<int> arr) { // For null nodes if (root == null) { s += '0'; return; } s += '1'; // Store pre-order in array. arr.Add(root.data); // Apply pre-order to left and // right subtree. encodeTreeRecur(root.left, ref s, arr); encodeTreeRecur(root.right, ref s, arr); } static Tuple<string, List<int>> encodeTree(Node root) { string s = ""; List<int> arr = new List<int>(); encodeTreeRecur(root, ref s, arr); return new Tuple<string, List<int>>(s, arr); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Binary tree // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ \ // 40 50 70 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(50); root.right.right = new Node(70); Tuple<string, List<int>> ans = encodeTree(root); Console.WriteLine(ans.Item1); foreach (int num in ans.Item2) Console.Write(num + " "); Console.WriteLine(); } } // JavaScript program to encode a // binary tree. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Recursive pre-order function to // encode a binary tree. function encodeTreeRecur(root, s, arr) { // For null nodes if (root === null) { s.push('0'); return; } s.push('1'); // Store pre-order in array. arr.push(root.data); // Apply pre-order to left and // right subtree. encodeTreeRecur(root.left, s, arr); encodeTreeRecur(root.right, s, arr); } function encodeTree(root) { let s = []; let arr = []; encodeTreeRecur(root, s, arr); return [s.join(''), arr]; } // Binary tree // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ \ // 40 50 70 let root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(50); root.right.right = new Node(70); const ans = encodeTree(root); console.log(ans[0]); console.log(ans[1].join(" ")); Output1110010010100 10 20 40 50 30 70
Approach for decoding binary tree - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to perform pre-order traversal of the string. If the current character is '0', return null. Otherwise create a new node with value equal to current element of the data array. Return the root node.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ program to decode a // binary tree. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node (int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; // Recursive pre-order function to // decode a binary tree. Node* decodeTreeRecur(int &i, string &s, int &j, vector<int> &arr) { // if s[i]==0, return null node if (s[i] == '0') { i++; return nullptr; } // Create a new Node Node* root = new Node(arr[j++]); i++; // Construct left and right subtree. root->left = decodeTreeRecur(i,s,j,arr); root->right = decodeTreeRecur(i,s,j,arr); return root; } Node* decodeTree(string s, vector<int> arr) { int i = 0, j = 0; return decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); } void printInorder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; printInorder(root->left); cout << root->data << " "; printInorder(root->right); } int main() { string s = "1110010010100"; vector<int> arr = {10, 20, 40, 50, 30, 70}; Node* root = decodeTree(s, arr); printInorder(root); return 0; } // Java program to decode a // binary tree. import java.util.ArrayList; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // Recursive pre-order function to // decode a binary tree. static Node decodeTreeRecur(int[] i, String s, int[] j, ArrayList<Integer> arr) { // if s[i]==0, return null node if (s.charAt(i[0]) == '0') { i[0]++; return null; } // Create a new Node Node root = new Node(arr.get(j[0]++)); i[0]++; // Construct left and right subtree. root.left = decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); root.right = decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); return root; } static Node decodeTree(String s, ArrayList<Integer> arr) { int[] i = {0}, j = {0}; return decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); } static void printInorder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; printInorder(root.left); System.out.print(root.data + " "); printInorder(root.right); } public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "1110010010100"; ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<>(); arr.add(10); arr.add(20); arr.add(40); arr.add(50); arr.add(30); arr.add(70); Node root = decodeTree(s, arr); printInorder(root); } } # Python program to decode a # binary tree. class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Recursive pre-order function to # decode a binary tree. def decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr): # if s[i]==0, return null node if s[i[0]] == '0': i[0] += 1 return None # Create a new Node root = Node(arr[j[0]]) j[0] += 1 i[0] += 1 # Construct left and right subtree. root.left = decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr) root.right = decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr) return root def decodeTree(s, arr): i = [0] j = [0] return decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr) def printInorder(root): if root is None: return printInorder(root.left) print(root.data, end=" ") printInorder(root.right) if __name__ == "__main__": s = "1110010010100" arr = [10, 20, 40, 50, 30, 70] root = decodeTree(s, arr) printInorder(root)
// C# program to decode a // binary tree. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // Recursive pre-order function to // decode a binary tree. static Node decodeTreeRecur(ref int i, string s, ref int j, List<int> arr) { // if s[i]==0, return null node if (s[i] == '0') { i++; return null; } // Create a new Node Node root = new Node(arr[j++]); i++; // Construct left and right subtree. root.left = decodeTreeRecur(ref i, s, ref j, arr); root.right = decodeTreeRecur(ref i, s, ref j, arr); return root; } static Node decodeTree(string s, List<int> arr) { int i = 0, j = 0; return decodeTreeRecur(ref i, s, ref j, arr); } static void printInorder(Node root) { if (root == null) return; printInorder(root.left); Console.Write(root.data + " "); printInorder(root.right); } static void Main(string[] args) { string s = "1110010010100"; List<int> arr = new List<int> {10, 20, 40, 50, 30, 70}; Node root = decodeTree(s, arr); printInorder(root); } } // JavaScript program to decode a // binary tree. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Recursive pre-order function to // decode a binary tree. function decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr) { // if s[i]==0, return null node if (s[i[0]] === '0') { i[0]++; return null; } // Create a new Node const root = new Node(arr[j[0]++]); i[0]++; // Construct left and right subtree. root.left = decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); root.right = decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); return root; } function decodeTree(s, arr) { let i = [0]; let j = [0]; return decodeTreeRecur(i, s, j, arr); } function printInorder(root) { if (root === null) return; printInorder(root.left); console.log(root.data); printInorder(root.right); } let s = "1110010010100"; let arr = [10, 20, 40, 50, 30, 70]; let root = decodeTree(s, arr); printInorder(root);
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile