Sort a Stack using Recursion
Last Updated : 15 Sep, 2025
Given a stack of integers st[], Sort the stack in ascending order (smallest element at the bottom and largest at the top).
Example:
Input: st[] = [1, 2, 3]
Output: [3, 2, 1]
Explanation: The stack is already sorted in ascending order.
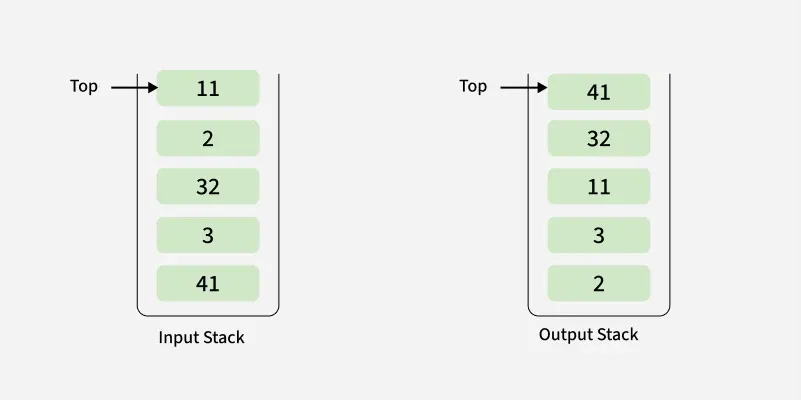
Input: st[] = [41, 3, 32, 2, 11]
Output: [41, 32, 11, 3, 2]
Explanation: After sorting, the smallest element (2) is at the bottom and the largest element (41) is at the top.
[Approach] Using Recursion
We use recursion to sort the stack without relying on extra data structures. The approach will be:
- Remove the top element of the stack.
- Recursively sort the remaining stack.
- Insert the removed element back into the stack in its correct sorted position.
How Recursion Works
- Remove the top element of the stack and hold it temporarily.
- Recursively sort the remaining stack, which is now smaller (it has one fewer element).
- Once the smaller stack is sorted, insert the held element back into its correct position:
If the stack is empty or the top element is smaller than the held element, push it directly.
Otherwise, remove the top element, recursively find the correct position for the held element, and then push back the removed element. - Repeat this process as recursion unwinds until all elements are sorted in ascending order, with the smallest at the bottom and the largest at the top.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std; // Insert element into sorted stack void sortedInsert(stack<int> &st, int x) { // If stack is empty or // top element is smaller, push x if (st.empty() || st.top() <= x) { st.push(x); return; } int top = st.top(); st.pop(); // Recursively insert x in sorted order sortedInsert(st, x); st.push(top); } // Sort the stack recursively void sortStack(stack<int> &st) { if (st.empty()) return; int top = st.top(); st.pop(); // Recursively sort the remaining stack sortStack(st); sortedInsert(st, top); } int main() { stack<int> st; st.push(41); st.push(3); st.push(32); st.push(2); st.push(11); sortStack(st); while (!st.empty()) { cout << st.top() << " "; st.pop(); } return 0; } import java.util.Stack; class GfG { // Insert element into sorted stack static void sortedInsert(Stack<Integer> st, int x) { // If stack is empty or // top element is smaller, push x if (st.isEmpty() || st.peek() <= x) { st.push(x); return; } int top = st.pop(); // Recursively insert x in sorted order sortedInsert(st, x); st.push(top); } // Sort the stack recursively static void sortStack(Stack<Integer> st) { if (st.isEmpty()) return; int top = st.pop(); // Recursively sort the remaining stack sortStack(st); sortedInsert(st, top); } public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>(); st.push(41); st.push(3); st.push(32); st.push(2); st.push(11); sortStack(st); while (!st.isEmpty()) { System.out.print(st.pop() + " "); } } } # Insert element into sorted stack def sortedInsert(st, x): # If stack is empty or # top element is smaller, push x if not st or st[-1] <= x: st.append(x) return top = st.pop() # Recursively insert x in sorted order sortedInsert(st, x) st.append(top) # Sort the stack recursively def sortStack(st): if not st: return top = st.pop() # Recursively sort the remaining stack sortStack(st) sortedInsert(st, top) if __name__ == "__main__": st = [41, 3, 32, 2, 11] sortStack(st) while st: print(st.pop(), end=" ")
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // Insert element into sorted stack static void sortedInsert(Stack<int> st, int x) { // If stack is empty // or top element is smaller, push x if (st.Count == 0 || st.Peek() <= x) { st.Push(x); return; } int top = st.Pop(); // Recursively insert x in sorted order sortedInsert(st, x); st.Push(top); } // Sort the stack recursively static void sortStack(Stack<int> st) { if (st.Count == 0) return; int top = st.Pop(); // Recursively sort the remaining stack sortStack(st); sortedInsert(st, top); } static void Main() { Stack<int> st = new Stack<int>(); st.Push(41); st.Push(3); st.Push(32); st.Push(2); st.Push(11); sortStack(st); while (st.Count > 0) { Console.Write(st.Pop() + " "); } } } function sortedInsert(st, x) { // If stack is empty or // top element is smaller, push x if (st.length === 0 || st[st.length - 1] <= x) { st.push(x); return; } let top = st.pop(); // Recursively insert x in sorted order sortedInsert(st, x); st.push(top); } function sortStack(st) { if (st.length === 0) return; let top = st.pop(); // Recursively sort the remaining stack sortStack(st); sortedInsert(st, top); } // Driver Code let st = []; st.push(41); st.push(3); st.push(32); st.push(2); st.push(11); sortStack(st); let res = []; while (st.length > 0) { res.push(st.pop()); } console.log(res.join(" ")); Time Complexity: O(n2)
Auxiliary Space: O(n), due to call stack.
To read about iterative approach Refer, Sort a stack using a temporary stack
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile