Given the head of a linked list, reverse the list and return the new head.
Examples:
Input:
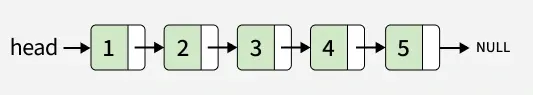
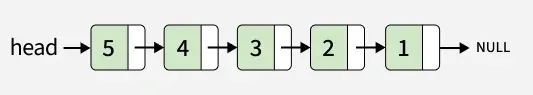
Output: 5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
[Approach] Using Iterative Method - O(n) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is to reverse the linked list by changing the direction of links using three pointers: prev, curr, and next. At each step, point the current node to its previous node and then move all three pointers forward until the list is fully reversed.
Step Step By Implementations:
- Initialize three pointers prev as NULL, curr as head, and next as NULL.
- Iterate through the linked list. In a loop, do the following:
- Store the next node, next = curr -> next
- Update the next pointer of curr to prev, curr -> next = prev
- Update prev as curr and curr as next, prev = curr and curr = next
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = nullptr; } }; Node *reverseList(Node *head) { Node *curr = head, *prev = nullptr, *next; // Traverse all the nodes of Linked List while (curr != nullptr) { // Store next next = curr->next; // Reverse current node's next pointer curr->next = prev; // Move pointers one position ahead prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } void printList(Node *node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if (node->next) cout << " -> "; node = node->next; } } int main() { Node *head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; struct Node *reverseList(struct Node *head) { struct Node *curr = head, *prev = NULL, *next; // traverse all the nodes of Linked List while (curr != NULL) { // store next next = curr->next; // reverse current node's next pointer curr->next = prev; // move pointers one position ahead prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } void printList(struct Node *node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d", node->data); if (node->next) printf(" -> "); node = node->next; } } struct Node *createNode(int new_data) { struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } int main() { struct Node *head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); return 0; } class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node reverseList(Node head) { Node curr = head, prev = null, next; // Traverse all the nodes of Linked List while (curr != null) { // Store next next = curr.next; // Reverse current node's next pointer curr.next = prev; // Move pointers one position ahead prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if (node.next != null) System.out.print(" -> "); node = node.next; } } public static void main(String[] args){ Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, newData): self.data = newData self.next = None def reverseList(head): curr = head prev = None # traverse all the nodes of Linked List while curr is not None: # store next nextNode = curr.next # reverse current node's next pointer curr.next = prev # move pointers one position ahead prev = curr curr = nextNode return prev def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head = reverseList(head) printList(head) using System; class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node(int newData) { Data = newData; Next = null; } } class GfG { static Node ReverseList(Node head) { Node curr = head; Node prev = null; Node next; // traverse all the nodes of Linked List while (curr != null) { // store next next = curr.Next; // reverse current node's next pointer curr.Next = prev; // move pointers one position ahead prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { Console.Write("" + node.Data); if (node.Next != null) Console.Write(" -> "); node = node.Next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main() { Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); head = ReverseList(head); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(newData) { this.data = newData; this.next = null; } } function reverseList(head) { let curr = head; let prev = null; let next; // traverse all the nodes of Linked List while (curr !== null) { // store next next = curr.next; // reverse current node's next pointer curr.next = prev; // move pointers one position ahead prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev; } function printList(node) { let result = []; while (node !== null) { result.push(node.data); node = node.next; } console.log(result.join(" -> ")); } // Driver Code let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); Output5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
[Alternate Approach 1] Using Recursion Method- O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use recursion to reach the last node of the list, which becomes the new head after reversal. As the recursion starts returning, each node makes its next node point back to itself, effectively reversing the links one by one until the entire list is reversed.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = nullptr; } }; Node *reverseList(Node *head) { if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head; // reverse the rest of linked list and put // the first element at the end Node *rest = reverseList(head->next); // Make the current head as last node of // remaining linked list head->next->next = head; // Update next of current head to NULL head->next = NULL; return rest; } void printList(Node *node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if (node->next) cout << " -> "; node = node->next; } } int main() { Node *head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; struct Node *reverseList(struct Node *head) { if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head; // reverse the rest of linked list and put // the first element at the end struct Node *rest = reverseList(head->next); // make the current head as last node of // remaining linked list head->next->next = head; // update next of current head to NULL head->next = NULL; return rest; } void printList(struct Node *node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d", node->data); if (node->next) printf(" -> "); node = node->next; } printf("\n"); } struct Node *createNode(int new_data) { struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } int main() { struct Node *head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); return 0; } class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node reverseList(Node head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return head; // reverse the rest of linked list and put // the first element at the end Node rest = reverseList(head.next); // make the current head as last node of // remaining linked list head.next.next = head; // update next of current head to null head.next = null; return rest; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if (node.next != null) System.out.print(" -> "); node = node.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, newData): self.data = newData self.next = None def reverseList(head): if head is None or head.next is None: return head # reverse the rest of linked list and put the # first element at the end rest = reverseList(head.next) # make the current head as last node of # remaining linked list head.next.next = head # update next of current head to NULL head.next = None return rest def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a hard-coded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head = reverseList(head) printList(head) using System; class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node(int newData) { Data = newData; Next = null; } } class GfG { static Node ReverseList(Node head) { if (head == null || head.Next == null) return head; // reverse the rest of linked list and // put the first element at the end Node rest = ReverseList(head.Next); // make the current head as last node // of remaining linked list head.Next.Next = head; // update next of current head to null head.Next = null; return rest; } static void PrintList(Node node) { while (node != null) { Console.Write("" + node.Data); if (node.Next != null) Console.Write(" -> "); node = node.Next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main() { Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); head = ReverseList(head); PrintList(head); } } class Node { constructor(new_data) { this.data = new_data; this.next = null; } } function reverseList(head) { if (head === null || head.next === null) return head; // reverse the rest of linked list let rest = reverseList(head.next); // make the current head as last node of // remaining linked list head.next.next = head; // update next of current head to null head.next = null; return rest; } function printList(node) { let result = []; while (node !== null) { result.push(node.data); node = node.next; } console.log(result.join(" -> ")); } // Driver code let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); Output5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
[Alternate Approach 2] Using Stack - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to traverse the linked list and push all nodes except the last node into the stack. Make the last node as the new head of the reversed linked list. Now, start popping the element and append each node to the reversed Linked List. Finally, return the head of the reversed linked list.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = nullptr; } }; Node *reverseList(Node *head) { stack<Node *> s; Node *temp = head; // push all nodes except the last node into stack while (temp->next != NULL) { s.push(temp); temp = temp->next; } // make the last node as new head of the linked list head = temp; // pop all the nodes and append to the linked list while (!s.empty()) { // append the top value of stack in list temp->next = s.top(); s.pop(); temp = temp->next; } // update the next pointer of last node of stack to null temp->next = NULL; return head; } void printList(Node *node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if (node->next) cout << " -> "; node = node->next; } } int main() { Node *head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; struct Node *createNode(int new_data) { struct Node *new_node = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } struct Node *reverseList(struct Node *head) { struct Node *stack[100000]; int top = -1; struct Node *temp = head; // push all nodes into stack while (temp != NULL) { stack[++top] = temp; temp = temp->next; } // make the last node as new head of the linked list if (top >= 0) { head = stack[top]; temp = head; // pop all the nodes and append to the linked list while (top > 0) { // append the top value of stack in list temp->next = stack[--top]; temp = temp->next; } // update the next pointer of last node of stack to null temp->next = NULL; } return head; } void printList(struct Node *node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d", node->data); if (node->next) printf(" -> "); node = node->next; } printf("\n"); } int main() { struct Node *head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); return 0; } import java.util.Stack; class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node reverseList(Node head) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); Node temp = head; // push all nodes into stack while (temp != null) { stack.push(temp); temp = temp.next; } // make the last node as new head of the linked list if (!stack.isEmpty()) { head = stack.pop(); temp = head; // pop all the nodes and append to the linked list while (!stack.isEmpty()) { // append the top value of stack in list temp.next = stack.pop(); temp = temp.next; } // update the next pointer of last node to null temp.next = null; } return head; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if (node.next != null) System.out.print(" -> "); node = node.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, new_data): self.data = new_data self.next = None def reverseList(head): stack = [] temp = head # push all nodes except the last node into stack while temp.next is not None: stack.append(temp) temp = temp.next head = temp # pop all the nodes and append to the linked list while stack: # append the top value of stack in list temp.next = stack.pop() temp = temp.next temp.next = None return head def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # create a hard-coded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head = reverseList(head) printList(head) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int Data; public Node Next; public Node(int newData) { Data = newData; Next = null; } } class GfG { static Node ReverseList(Node head) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>(); Node temp = head; // push all nodes into stack while (temp != null) { stack.Push(temp); temp = temp.Next; } // make the last node as new head of the linked list if (stack.Count > 0) { head = stack.Pop(); temp = head; // pop all the nodes and append to the linked list while (stack.Count > 0) { temp.Next = stack.Pop(); temp = temp.Next; } temp.Next = null; } return head; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { Console.Write("" + node.Data); if (node.Next != null) Console.Write(" -> "); node = node.Next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main() { Node head = new Node(1); head.Next = new Node(2); head.Next.Next = new Node(3); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(4); head.Next.Next.Next.Next = new Node(5); head = ReverseList(head); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(newData) { this.data = newData; this.next = null; } } function reverseList(head) { let stack = []; let temp = head; // push all nodes into stack while (temp !== null) { stack.push(temp); temp = temp.next; } // make the last node as new head of the linked list if (stack.length > 0) { head = stack.pop(); temp = head; // pop all the nodes and append to the linked list while (stack.length > 0) { temp.next = stack.pop(); temp = temp.next; } temp.next = null; } return head; } function printList(node) { let result = []; while (node !== null) { result.push(node.data); node = node.next; } console.log(result.join(" -> ")); } // driver code let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = reverseList(head); printList(head); Output5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile