Print root to leaf paths without using recursion
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Given a Binary Tree of nodes, the task is to find all the possible paths from the root node to all the leaf nodes of the binary tree.
Example:
Input:
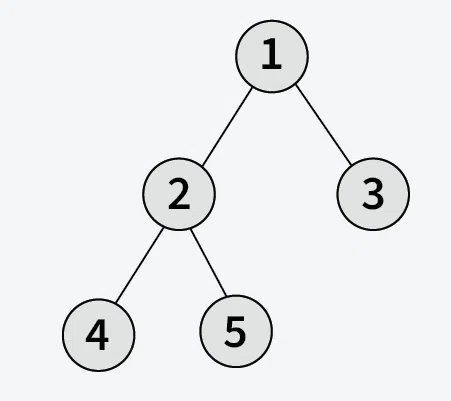
Output:
1 2 4
1 2 5
1 3
[Expected Approach - 1] Using Parent HashMap - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use a preorder traversal technique using a stack, and maintain hashmap to keep track of each node's parent, When we reach at leaf node, print path from root to that lead node using parent map.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Push the root node onto the stack and Store the root's parent as null in the parent map.
- While the stack is not empty, pop the top node
- If the node is a leaf node then Trace the path from the leaf node to the root using the parent map and print the path.
- If the node has a right child, push it onto the stack and store its parent in the map.
- If the node has a left child, push it onto the stack and store its parent in the map.
Below is the implementation of this idea.
C++ // C++ program to Print root to leaf path without // using recursion #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Function to print root to leaf path for a leaf // using parent nodes stored in map void printTopToBottomPath(Node* curr, unordered_map<Node*, Node*>& parent) { stack<Node*> stk; // start from leaf node and keep on pushing // nodes into stack till root node is reached while (curr) { stk.push(curr); curr = parent[curr]; } // Start popping nodes from stack and print them while (!stk.empty()) { curr = stk.top(); stk.pop(); cout << curr->data << " "; } cout << endl; } // An iterative function to do preorder traversal // of binary tree and print root to leaf path // without using recursion void printRootToLeaf(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; // Create an empty stack and push root // to it stack<Node*> nodeStack; nodeStack.push(root); // Create a map to store parent pointers // of binary tree nodes unordered_map<Node*, Node*> parent; // parent of root is NULL parent[root] = nullptr; while (!nodeStack.empty()) { // Pop the top item from stack Node* current = nodeStack.top(); nodeStack.pop(); // If leaf node encountered, print Top To // Bottom path if (!(current->left) && !(current->right)){ printTopToBottomPath(current, parent); } // Push right & left children of the popped node // to stack. Also set their parent pointer in // the map // Note that right child is pushed first so that // left is processed first if (current->right) { parent[current->right] = current; nodeStack.push(current->right); } if (current->left) { parent[current->left] = current; nodeStack.push(current->left); } } } int main() { // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(2); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->left = new Node(2); printRootToLeaf(root); return 0; } // Java program to Print root to leaf path without // using recursion import java.util.*; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to print root to leaf path for a leaf // using parent nodes stored in map static void printTopToBottomPath(Node curr, Map<Node, Node> parent) { Stack<Node> stk = new Stack<>(); // start from leaf node and keep on pushing // nodes into stack till root node is reached while (curr != null) { stk.push(curr); curr = parent.get(curr); } // Start popping nodes from stack and print them while (!stk.isEmpty()) { curr = stk.pop(); System.out.print(curr.data + " "); } System.out.println(); } // An iterative function to do preorder traversal // of binary tree and print root to leaf path // without using recursion static void printRootToLeaf(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty stack and push root to it Stack<Node> nodeStack = new Stack<>(); nodeStack.push(root); // Create a map to store parent pointers of binary // tree nodes Map<Node, Node> parent = new HashMap<>(); // parent of root is NULL parent.put(root, null); while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) { // Pop the top item from stack Node current = nodeStack.pop(); // If leaf node encountered, print Top To // Bottom path if (current.left == null && current.right == null) { printTopToBottomPath(current, parent); } // Push right & left children of the popped node // to stack. Also set their parent pointer in // the map // Note that right child is pushed first so that // left is processed first if (current.right != null) { parent.put(current.right, current); nodeStack.push(current.right); } if (current.left != null) { parent.put(current.left, current); nodeStack.push(current.left); } } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(2); printRootToLeaf(root); } } # Python program to Print root to leaf path without # using recursion class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # Function to print root to leaf path for a leaf # using parent nodes stored in map def printTopToBottomPath(curr, parent): stk = [] # start from leaf node and keep on pushing # nodes into stack till root node is reached while curr: stk.append(curr) curr = parent[curr] # Start popping nodes from stack and print them while stk: curr = stk.pop() print(curr.data, end=" ") print() # An iterative function to do preorder traversal # of binary tree and print root to leaf path # without using recursion def printRootToLeaf(root): if root is None: return # Create an empty stack and push root to it nodeStack = [] nodeStack.append(root) # Create a dictionary to store parent pointers # of binary tree nodes parent = {} # parent of root is None parent[root] = None while nodeStack: # Pop the top item from stack current = nodeStack.pop() # If leaf node encountered, print Top To # Bottom path if not current.left and not current.right: printTopToBottomPath(current, parent) # Push right & left children of the popped node # to stack. Also set their parent pointer in # the dictionary # Note that right child is pushed first so that # left is processed first if current.right: parent[current.right] = current nodeStack.append(current.right) if current.left: parent[current.left] = current nodeStack.append(current.left) # Constructed binary tree is # 10 # / \ # 8 2 # / \ / # 3 5 2 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(3) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.left = Node(2) printRootToLeaf(root) // C# program to Print root to leaf path without // using recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to print root to leaf path for a leaf // using parent nodes stored in map static void printTopToBottomPath(Node curr, Dictionary<Node, Node> parent) { Stack<Node> stk = new Stack<Node>(); // start from leaf node and keep on pushing // nodes into stack till root node is reached while (curr != null) { stk.Push(curr); curr = parent[curr]; } // Start popping nodes from stack and print them while (stk.Count > 0) { curr = stk.Pop(); Console.Write(curr.data + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); } // An iterative function to do preorder traversal // of binary tree and print root to leaf path // without using recursion static void printRootToLeaf(Node root) { if (root == null) return; // Create an empty stack and push root to it Stack<Node> nodeStack = new Stack<Node>(); nodeStack.Push(root); // Create a map to store parent pointers of binary // tree nodes Dictionary<Node, Node> parent = new Dictionary<Node, Node>(); // parent of root is NULL parent[root] = null; while (nodeStack.Count > 0) { // Pop the top item from stack Node current = nodeStack.Pop(); // If leaf node encountered, print Top To // Bottom path if (current.left == null && current.right == null) { printTopToBottomPath(current, parent); } // Push right & left children of the popped node // to stack. Also set their parent pointer in // the map // Note that right child is pushed first so that // left is processed first if (current.right != null) { parent[current.right] = current; nodeStack.Push(current.right); } if (current.left != null) { parent[current.left] = current; nodeStack.Push(current.left); } } } static void Main() { // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(2); printRootToLeaf(root); } } // Javascript program to Print root to leaf path without // using recursion class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function to print root to leaf path for a leaf // using parent nodes stored in map function printTopToBottomPath(curr, parent) { let stk = []; // start from leaf node and keep on pushing // nodes into stack till root node is reached while (curr) { stk.push(curr); curr = parent.get(curr); } // Start popping nodes from stack and print them while (stk.length > 0) { curr = stk.pop(); process.stdout.write(curr.data + " "); } console.log(); } // An iterative function to do preorder traversal // of binary tree and print root to leaf path // without using recursion function printRootToLeaf(root) { if (root === null) return; // Create an empty stack and push root to it let nodeStack = []; nodeStack.push(root); // Create a map to store parent pointers of binary // tree nodes let parent = new Map(); // parent of root is NULL parent.set(root, null); while (nodeStack.length > 0) { // Pop the top item from stack let current = nodeStack.pop(); // If leaf node encountered, print Top To // Bottom path if (!current.left && !current.right) { printTopToBottomPath(current, parent); } // Push right & left children of the popped node // to stack. Also set their parent pointer in // the map // Note that right child is pushed first so that // left is processed first if (current.right) { parent.set(current.right, current); nodeStack.push(current.right); } if (current.left) { parent.set(current.left, current); nodeStack.push(current.left); } } } // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 let root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(2); printRootToLeaf(root); Output10 8 3 10 8 5 10 2 2
Note : We can optimize this approach. We do not need to maintain parent map. Below there is another approach by we can print all path from root to leaf without using parent array.
[Expected Approach - 2] Using Stack - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use stack to store pairs of nodes and their respective paths from the root, starting with the root node and its value, traverse iteratively by processing each node by popping it from the stack. if the node is a leaf, its path is added to the result. else if the node has children, the right and left children are pushed onto the stack along with their updated paths.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize stack, that stores pairs of nodes and the path from the root to that node.
- Push the root node and its path (starting with just the root’s value) onto the stack.
- While the stack isn't empty, pop a pair of node and its path from the stack.
- If the current node is a leaf, add its path to the result.
- If the current node has a right child, push the right child and its updated path onto the stack.
- If the current node has a left child, push the left child and its updated path onto the stack.
- return result which represents all the paths from root-to-leaf.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ code of print all paths from root node // to leaf node using stack #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <stack> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Function to get all paths from root // to leaf nodes using a stack vector<vector<int>> Paths(Node* root) { vector<vector<int>> result; if (!root) return result; // Stack to store pairs of nodes and the // path from the root to that node stack<pair<Node*, vector<int>>> stk; stk.push({root, {root->data}}); while (!stk.empty()) { // Get the current node and its // associated path from the stack auto curr = stk.top(); stk.pop(); Node* currNode = curr.first; vector<int> path = curr.second; // If the current node is a leaf node, // add its path to the result if (!currNode->left && !currNode->right) { result.push_back(path); } // If the current node has a right child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode->right) { vector<int> rightPath = path; rightPath.push_back(currNode->right->data); stk.push({currNode->right, rightPath}); } // If the current node has a left child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode->left) { vector<int> leftPath = path; leftPath.push_back(currNode->left->data); stk.push({currNode->left, leftPath}); } } return result; } int main() { // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(2); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->left = new Node(2); vector<vector<int>> paths = Paths(root); for (const auto& path : paths) { for (int nodeValue : path) { cout << nodeValue << " "; } cout << endl; } return 0; } // Java code of print all paths from root node // to leaf node using stack import java.util.*; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class Pair { Node node; List<Integer> path; public Pair(Node node, List<Integer> path) { this.node = node; this.path = path; } } class GfG { // Function to get all paths from root // to leaf nodes using a stack static List<List<Integer>> Paths(Node root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); if (root == null) return result; // Stack to store pairs of nodes and the // path from the root to that node Stack<Pair> stk = new Stack<>(); // Create an ArrayList with the root node's data List<Integer> rootPath = new ArrayList<>(); rootPath.add(root.data); stk.push(new Pair(root, rootPath)); while (!stk.isEmpty()) { // Get the current node and its // associated path from the stack Pair curr = stk.pop(); Node currNode = curr.node; List<Integer> path = curr.path; // If the current node is a leaf node, // add its path to the result if (currNode.left == null && currNode.right == null) { result.add(path); } // If the current node has a right child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode.right != null) { List<Integer> rightPath = new ArrayList<>(path); rightPath.add(currNode.right.data); stk.push(new Pair(currNode.right, rightPath)); } // If the current node has a left child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode.left != null) { List<Integer> leftPath = new ArrayList<>(path); leftPath.add(currNode.left.data); stk.push(new Pair(currNode.left, leftPath)); } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(2); List<List<Integer>> paths = Paths(root); for (List<Integer> path : paths) { for (int nodeValue : path) { System.out.print(nodeValue + " "); } System.out.println(); } } } # Python code to print all paths from # root node to leaf node using stack. class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Function to get all paths from root # to leaf nodes using a stack def Paths(root): result = [] if not root: return result # Stack to store pairs of nodes and the # path from the root to that node stk = [(root, [root.data])] while stk: # Get the current node and its # associated path from the stack currNode, path = stk.pop() # If the current node is a leaf node, # add its path to the result if not currNode.left and not currNode.right: result.append(path) # If the current node has a right child, # push it to the stack with its path if currNode.right: rightPath = path + [currNode.right.data] stk.append((currNode.right, rightPath)) # If the current node has a left child, # push it to the stack with its path if currNode.left: leftPath = path + [currNode.left.data] stk.append((currNode.left, leftPath)) return result if __name__ == "__main__": # Constructed binary tree is # 10 # / \ # 8 2 # / \ / # 3 5 2 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(3) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.left = Node(2) paths = Paths(root) for path in paths: print(" ".join(map(str, path))) // C# code to print all paths from root // node to leaf node using stack. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to get all paths from root // to leaf nodes using a stack static List<List<int>> Paths(Node root) { List<List<int>> result = new List<List<int>>(); if (root == null) return result; // Stack to store pairs of nodes and the // path from the root to that node Stack<Tuple<Node, List<int>>> stk = new Stack<Tuple<Node, List<int>>>(); stk.Push(Tuple.Create(root, new List<int> { root.data })); while (stk.Count > 0) { // Get the current node and its // associated path from the stack var curr = stk.Pop(); Node currNode = curr.Item1; List<int> path = curr.Item2; // If the current node is a leaf node, // add its path to the result if (currNode.left == null && currNode.right == null) { result.Add(path); } // If the current node has a right child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode.right != null) { List<int> rightPath = new List<int>(path); rightPath.Add(currNode.right.data); stk.Push(Tuple.Create(currNode.right, rightPath)); } // If the current node has a left child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode.left != null) { List<int> leftPath = new List<int>(path); leftPath.Add(currNode.left.data); stk.Push(Tuple.Create(currNode.left, leftPath)); } } return result; } static void Main() { // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(2); List<List<int>> paths = Paths(root); foreach (var path in paths) { Console.WriteLine(string.Join(" ", path)); } } } // JavaScript code to print all paths from // root node to leaf node using stack. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function to get all paths from root // to leaf nodes using a stack function Paths(root) { const result = []; if (!root) return result; // Stack to store pairs of nodes and the // path from the root to that node const stk = [[root, [root.data]]]; while (stk.length > 0) { // Get the current node and its // associated path from the stack const [currNode, path] = stk.pop(); // If the current node is a leaf node, // add its path to the result if (!currNode.left && !currNode.right) { result.push(path); } // If the current node has a right child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode.right) { const rightPath = [...path, currNode.right.data]; stk.push([currNode.right, rightPath]); } // If the current node has a left child, // push it to the stack with its path if (currNode.left) { const leftPath = [...path, currNode.left.data]; stk.push([currNode.left, leftPath]); } } return result; } // Constructed binary tree is // 10 // / \ // 8 2 // / \ / // 3 5 2 const root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.left = new Node(2); const allPaths = Paths(root); allPaths.forEach(path => { console.log(path.join(' ')); }); Output10 8 3 10 8 5 10 2 2
Related article:
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile