Given a head of Singly Linked List, we have to print all the elements in the list.
Examples:
Input:
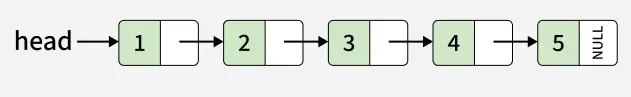
Output: 1->2->3->4->5
Input:
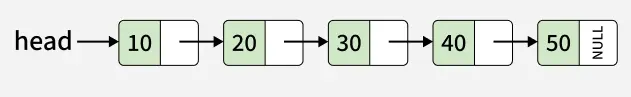
Output: 10->20->30->40->50
[Approach 1] Using Iterative Method - O(n) Time and O(1) Space
Start from the head and follow the next pointer to visit each node, printing the data until the next pointer is NULL.
Steps to solve the problem:
- Start from the head node.
- While the current node is not
NULL: - Print the node's data.
- Move to the next node using the next pointer
Program to Print the Singly Linked List using Iteration.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; // A linked list node class Node { public: int data; Node* next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data Node(int new_data) { this->data = new_data; this->next = nullptr; } }; // Function to print the singly linked list void printList(Node* head) { // A loop that runs till head is nullptr while (head != nullptr) { // Printing data of current node cout << head->data ; if(head->next) cout<<"->"; // Moving to the next node head = head->next; } } int main() { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 Node* head = new Node(10); head->next = new Node(20); head->next->next = new Node(30); head->next->next->next = new Node(40); printList(head); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // A linked list node struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; // Function to create a new node struct Node* createNode(int new_data) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = new_data; node->next = NULL; return node; } // Function to print the singly linked list void printList(struct Node* head) { // A loop that runs till head is NULL while (head != NULL) { // Printing data of current node printf("%d", head->data); if(head->next) printf("->"); // Moving to the next node head = head->next; } } int main() { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 struct Node* head = createNode(10); head->next = createNode(20); head->next->next = createNode(30); head->next->next->next = createNode(40); printList(head); return 0; } class Node { int data; Node next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data Node(int newData) { this.data = newData; this.next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to print the singly linked list static void printList(Node head) { // A loop that runs till head is null while (head != null) { // Printing data of current node System.out.print(head.data); if(head.next!=null) System.out.print("->"); // Moving to the next node head = head.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 Node head = new Node(10); head.next = new Node(20); head.next.next = new Node(30); head.next.next.next = new Node(40); printList(head); } } # A linked list node class Node: def __init__(self, newData): # Constructor to initialize a new node with data self.data = newData self.next = None # Function to print the singly linked list def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print("->", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 head = Node(10) head.next = Node(20) head.next.next = Node(30) head.next.next.next = Node(40) printList(head) using System; class Node { public int data; public Node next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data public Node(int new_data) { this.data = new_data; this.next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to print the singly linked list static void printList(Node head) { // A loop that runs till head is null while (head != null) { // Printing data of current node Console.Write(head.data + ""); if(head.next!=null) Console.Write("->"); // Moving to the next node head = head.next; } } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 Node head = new Node(10); head.next = new Node(20); head.next.next = new Node(30); head.next.next.next = new Node(40); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(newData) { // Constructor to initialize a new node with data this.data = newData; this.next = null; } } // Function to print the singly linked list function printList(node) { while (node !== null) { process.stdout.write(node.data.toString()); if (node.next !== null) { process.stdout.write("->"); } node = node.next; } process.stdout.write("\n"); } // Driver Code // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 const head = new Node(10); head.next = new Node(20); head.next.next = new Node(30); head.next.next.next = new Node(40); printList(head); [Approach 2] Using Recursion Method- O(n) Time and O(n) Space
At each node, print the data and recursively call the function using the next pointer until the node becomes NULL.
Program to Print the Singly Linked List using Recursion.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; // A linked list node class Node { public: int data; Node* next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data Node(int new_data) { this->data = new_data; this->next = nullptr; } }; // Function to print the singly linked list void printList(Node* head) { // Base condition is when the head is nullptr if (head == nullptr) { return; } // Printing the current node data cout << head->data; if(head->next) cout<<"->"; // Moving to the next node printList(head->next); } int main() { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 Node* head = new Node(10); head->next = new Node(20); head->next->next = new Node(30); head->next->next->next = new Node(40); printList(head); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // A linked list node struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; // Function to create a new node with given data struct Node* createNode(int new_data) { struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = new_data; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } // Function to print the singly linked list void printList(struct Node* head) { // Base condition is when the head is nullptr if (head == NULL) { return; } // Printing the current node data printf("%d", head->data); if(head->next) printf("->"); // Moving to the next node printList(head->next); } int main() { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 struct Node* head = createNode(10); head->next = createNode(20); head->next->next = createNode(30); head->next->next->next = createNode(40); printList(head); return 0; } // A linked list node class Node { int data; Node next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data Node(int new_data) { data = new_data; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to print the singly linked list static void printList(Node head) { // Base condition is when the head is nullptr if (head == null) { return; } // Printing the current node data System.out.print(head.data); if(head.next!=null) System.out.print("->"); // Moving to the next node printList(head.next); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 Node head = new Node(10); head.next = new Node(20); head.next.next = new Node(30); head.next.next.next = new Node(40); printList(head); } } # A linked list node class Node: def __init__(self, data): # Constructor to initialize a new node with data self.data = data self.next = None # Function to print the singly linked list def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print("->", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 head = Node(10) head.next = Node(20) head.next.next = Node(30) head.next.next.next = Node(40) printList(head) using System; // A linked list node class Node { public int Data { get;set; } public Node Next { get;set; } // Constructor to initialize a new node with data public Node(int newData) { Data = newData; Next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to print the singly linked list static void printList(Node head) { // Base condition is when the head is nullptr if (head == null) { return; } // Printing the current node data Console.Write(head.Data + ""); if(head.Data!=null) Console.Write("->"); // Moving to the next node printList(head.Next); } static void Main() { // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 Node head = new Node(10); head.Next = new Node(20); head.Next.Next = new Node(30); head.Next.Next.Next = new Node(40); printList(head); } } // A linked list node class Node { constructor(new_data) { // Constructor to initialize a new node with data this.data = new_data; this.next = null; } } // Function to print the singly linked list function printList(head) { // Base condition is when the head is null if (head === null) { return; } // Printing the current node data process.stdout.write(head.data.toString()); if (head.next !== null) { process.stdout.write("->"); } // Moving to the next node printList(head.next); } // Create a linked list: 10 -> 20 -> 30 -> 40 let head = new Node(10); head.next = new Node(20); head.next.next = new Node(30); head.next.next.next = new Node(40); printList(head);
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile