Preorder Traversal of Binary Tree
Last Updated : 07 Oct, 2025
Given the root of a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of the binary tree.
Preorder Traversal is a method to traverse a tree such that for each node, you first visit the node itself, then traverse its left subtree, and finally traverse its right subtree.
Examples:
Input:
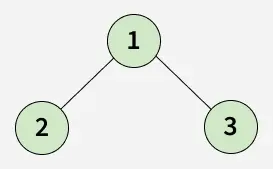
Output: [1, 2, 3]
Explanation: The Preorder Traversal visits the nodes in the following order: Root, Left, Right. Therefore, we visit the root node 1, then the left node 2 and lastly the right node 3.
Input :
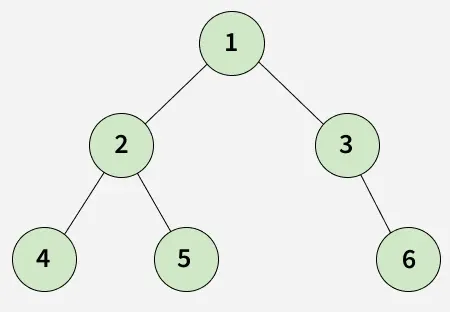
Output: [1, 2, 4, 5, 3, 6]
Explanation: Preorder Traversal (Root -> Left -> Right). Visit 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 5 -> 3 -> 6, resulting in 1 2 4 5 3 6.
[Approach] Using Recursion
The main idea is to traverse the tree recursively, starting from the root node, first visit the root node itself, then completely traverse the left subtree, and finally completely traverse the right subtree.
How does Preorder Traversal work?
C++ #include<iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; //Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = NULL; } }; void preOrder(Node* node, vector<int>& res) { if (node == nullptr) return; // Visit the current node first res.push_back(node->data); // Traverse the left subtree preOrder(node->left, res); // Traverse the right subtree preOrder(node->right, res); } int main() { // Create binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ \ // 4 5 6 Node* root = new Node(1); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(3); root->left->left = new Node(4); root->left->right = new Node(5); root->right->right = new Node(6); vector<int> res; preOrder(root, res); for(int node : res) cout << node << " "; return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Node Structure struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; }; // Function to create a new node struct Node* newNode(int x) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = x; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node; } void preOrder(struct Node* node) { if (node == NULL) return; // Visit the current node first printf("%d ", node->data); // Traverse the left subtree preOrder(node->left); // Traverse the right subtree preOrder(node->right); } int main() { // Create binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ \ // 4 5 6 struct Node* root = newNode(1); root->left = newNode(2); root->right = newNode(3); root->left->left = newNode(4); root->left->right = newNode(5); root->right->right = newNode(6); preOrder(root); printf("\n"); return 0; } import java.util.ArrayList; //Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int v) { data = v; left = right = null; } } class GFG { public static void preOrder(Node node, ArrayList<Integer> res) { if (node == null) return; // Visit the current node first res.add(node.data); // Traverse the left subtree preOrder(node.left, res); // Traverse the right subtree preOrder(node.right, res); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ \ // 4 5 6 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.right = new Node(6); ArrayList<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); preOrder(root, result); for (int val : result) { System.out.print(val + " "); } } } #Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None def preOrder(node, res): if not node: return # Visit the current node first res.append(node.data) # Traverse the left subtree preOrder(node.left, res) # Traverse the right subtree preOrder(node.right, res) if __name__ == "__main__": # Create binary tree # 1 # / \ # 2 3 # / \ \ # 4 5 6 root = Node(1) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(3) root.left.left = Node(4) root.left.right = Node(5) root.right.right = Node(6) result = [] preOrder(root, result) print(*result)
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; //Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int v) { data = v; left = right = null; } } class GFG { public static void preOrder(Node node, List<int> res) { if (node == null) return; // Visit the current node first res.Add(node.data); // Traverse the left subtree preOrder(node.left, res); // Traverse the right subtree preOrder(node.right, res); } static void Main() { // Create binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ \ // 4 5 6 Node root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.right = new Node(6); List<int> result = new List<int>(); preOrder(root, result); foreach (int val in result) Console.Write(val + " "); } } //Node Structure class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function preOrder(node, res) { if (!node) return; // Visit the current node first res.push(node.data); // Traverse the left subtree preOrder(node.left, res); // Traverse the right subtree preOrder(node.right, res); } // Driver code // Create binary tree // 1 // / \ // 2 3 // / \ \ // 4 5 6 let root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); root.right.right = new Node(6); let result = []; preOrder(root, result); console.log(...result); Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(h), h is the height of the tree
- In the worst case, h can be the same as n (when the tree is a skewed tree)
- In the best case, h can be the same as log n (when the tree is a complete tree)
Key Properties:
Related Articles:
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile