Given a 2D array mat[][] of size n*m. The cost of a path is defined as the maximum absolute difference between the values of any two consecutive cells along that path. You are allowed to move up, down, left, or right to adjacent cells. Find the minimum possible cost of a path from (0, 0) to (n-1, m-1).
Examples:
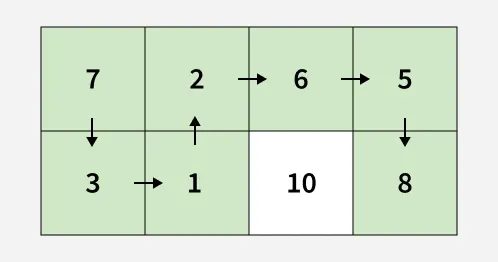
Input: mat[][] = [[7, 2, 6, 5],
[3, 1, 10, 8]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The route [7, 3, 1, 2, 6, 5, 8] has a minimum value of maximum absolute difference between two any consecutive cells in the route, i.e., 4.
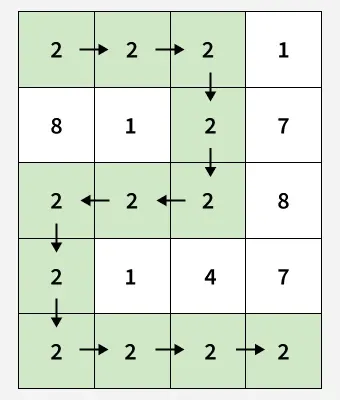
Input: mat[][] = [[2, 2, 2, 1],
[8, 1, 2, 7],
[2, 2, 2, 8],
[2, 1, 4, 7],
[2, 2, 2, 2],
Output: 0
Explanation: The route [2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2] has a minimum value of maximum absolute difference between two any consecutive cells in the route, i.e., 0.
[Naive Approach] - Using Backtracking
The idea is to explore every possible path from the current cell to the destination using backtracking.
At each step, we move in all valid directions and keep track of the maximum absolute difference between consecutive cell values along the current path.
When we finally reach the destination, we compare the cost of this path with the global minimum and update the minimum cost if the current path offers a smaller value.
To avoid revisiting cells within the same path, the current cell is temporarily marked as visited and restored afterward.
C++ //Driver Code Starts #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <climits> using namespace std; //Driver Code Ends int minCost = INT_MAX; // directions: up, down, right, left int dirArr[4][2] = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; // checks if the next cell is within bounds and not visited bool isSafe(int x, int y, int d[2], vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); if (x + d[0] >= 0 && x + d[0] < n && y + d[1] >= 0 && y + d[1] < m && mat[x + d[0]][y + d[1]] != -1) return true; return false; } // explores all possible paths using backtracking and updates minimum cost void findMinCost(int i, int j, int maxDiff, vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); // reached destination → update global minimum if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) { minCost = min(minCost, maxDiff); return; } int curr = mat[i][j]; // mark current cell as visited mat[i][j] = -1; for (auto& d : dirArr) { // move only if next cell is valid if (isSafe(i, j, d, mat)) { // continue path with updated maximum difference findMinCost(i + d[0], j + d[1], max(maxDiff, abs(mat[i + d[0]][j + d[1]] - curr)), mat); } } // restore cell value for other paths mat[i][j] = curr; } // initiates backtracking and // returns minimum possible path cost int minCostPath(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { minCost = INT_MAX; findMinCost(0, 0, 0, mat); return minCost; } //Driver Code Starts int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; cout << minCostPath(mat); } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static int minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // directions: up, down, right, left static int[][] dirArr = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; // checks if next cell is valid and not visited static boolean isSafe(int x, int y, int[] d, int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; int nx = x + d[0]; int ny = y + d[1]; return nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && mat[nx][ny] != -1; } // explores all possible paths and updates minimum cost static void findMinCost(int i, int j, int maxDiff, int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; // reached destination → update minimum if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) { minCost = Math.min(minCost, maxDiff); return; } int curr = mat[i][j]; // mark as visited mat[i][j] = -1; for (int[] d : dirArr) { // valid movement if (isSafe(i, j, d, mat)) { // continue with updated cost findMinCost(i + d[0], j + d[1], Math.max(maxDiff, Math.abs(mat[i + d[0]][j + d[1]] - curr)), mat); } } // restore for other paths mat[i][j] = curr; } // initiates backtracking static int minCostPath(int[][] mat) { minCost = Integer.MAX_VALUE; findMinCost(0, 0, 0, mat); return minCost; } //Driver Code Starts public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; System.out.println(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends minCost = float('inf') # directions: up, down, right, left dirArr = [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]] # checks if next cell is valid and not visited def isSafe(x, y, d, mat): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) nx = x + d[0] ny = y + d[1] return 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m and mat[nx][ny] != -1 # explores all possible paths and updates minimum cost def findMinCost(i, j, maxDiff, mat): global minCost n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) # reached destination → update minimum if i == n - 1 and j == m - 1: minCost = min(minCost, maxDiff) return curr = mat[i][j] # mark as visited mat[i][j] = -1 for d in dirArr: # valid movement if isSafe(i, j, d, mat): # continue with updated cost findMinCost(i + d[0], j + d[1], max(maxDiff, abs(mat[i + d[0]][j + d[1]] - curr)), mat) # restore for other paths mat[i][j] = curr # initiates backtracking def minCostPath(mat): global minCost minCost = float('inf') findMinCost(0, 0, 0, mat) return minCost #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == '__main__': mat = [ [7, 2, 6, 5], [3, 1, 10, 8] ] print(minCostPath(mat)) #Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts using System; class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static int minCost = int.MaxValue; // directions: up, down, right, left static int[,] dirArr = { {-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} }; // checks if next cell is valid and not visited static bool isSafe(int x, int y, int[] d, int[,] mat) { int n = mat.GetLength(0); int m = mat.GetLength(1); int nx = x + d[0]; int ny = y + d[1]; return nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && mat[nx, ny] != -1; } // explores all possible paths and updates minimum cost static void findMinCost(int i, int j, int maxDiff, int[,] mat) { int n = mat.GetLength(0); int m = mat.GetLength(1); // reached destination → update minimum if (i == n - 1 && j == m - 1) { minCost = Math.Min(minCost, maxDiff); return; } int curr = mat[i, j]; // mark as visited mat[i, j] = -1; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int[] d = { dirArr[k, 0], dirArr[k, 1] }; // valid movement if (isSafe(i, j, d, mat)) { // continue with updated cost int nx = i + d[0]; int ny = j + d[1]; findMinCost(nx, ny, Math.Max(maxDiff, Math.Abs(mat[nx, ny] - curr)), mat); } } // restore for other paths mat[i, j] = curr; } // initiates backtracking static int minCostPath(int[,] mat) { minCost = int.MaxValue; findMinCost(0, 0, 0, mat); return minCost; } //Driver Code Starts static void Main() { int[,] mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; Console.WriteLine(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends let minCost = Infinity; // directions: up, down, right, left let dirArr = [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]]; // checks if next cell is valid and not visited function isSafe(x, y, d, mat) { let n = mat.length; let m = mat[0].length; let nx = x + d[0]; let ny = y + d[1]; return nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && mat[nx][ny] !== -1; } // explores all possible paths and updates minimum cost function findMinCost(i, j, maxDiff, mat) { let n = mat.length; let m = mat[0].length; // reached destination → update minimum if (i === n - 1 && j === m - 1) { minCost = Math.min(minCost, maxDiff); return; } let curr = mat[i][j]; // mark as visited mat[i][j] = -1; for (let d of dirArr) { // valid movement if (isSafe(i, j, d, mat)) { // continue with updated cost let nx = i + d[0]; let ny = j + d[1]; findMinCost(nx, ny, Math.max(maxDiff, Math.abs(mat[nx][ny] - curr)), mat); } } // restore for other paths mat[i][j] = curr; } // initiates backtracking function minCostPath(mat) { minCost = Infinity; findMinCost(0, 0, 0, mat); return minCost; } //Driver Code Starts // Driver Code let mat = [ [7, 2, 6, 5], [3, 1, 10, 8] ]; console.log(minCostPath(mat)); //Driver Code Ends Time complexity: 3(n*m), Since each of the m×n cells can branch into at most 3 new directions (excluding the previous cell), the overall time complexity is O(3^(m*n)).
Auxiliary Space: O(n*m), stack space for a path from source to destination
[Better Approach] - Using Binary Search with Graph Traversal
The key idea is that the minimum possible maximum difference lies within a numeric range, so instead of checking all paths, we binary search on this value. For a given limit mid, we check whether a path exists from (0,0) to (n-1,m-1) such that every move satisfies:
abs(mat[next] - mat[curr]) ≤ mid
To verify this, we run a DFS/BFS and only move to neighbors that follow the limit. If the destination is reachable under this constraint, we try a smaller value; otherwise, we search higher.
Why we are not unmarking visited[][] array
We do not unmark visited cells because, for a fixed mid, DFS only needs to check whether a path exists (true/false), not compute any path value.
When a cell is visited the first time, DFS explores all valid neighbors from it under the same mid condition.
If a neighbor was already visited, its entire reachable area has already been checked, so revisiting it cannot lead to a different outcome.
C++ //Driver Code Starts #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <climits> using namespace std; //Driver Code Ends // directions: up, down, right, left int dirArr[4][2] = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; // DFS to check if we can reach destination // with max allowed difference = limit bool dfs(int x, int y, int limit, vector<vector<int>>& mat, vector<vector<int>>& vis) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); // reached destination if (x == n - 1 && y == m - 1) return true; vis[x][y] = 1; for (auto& d : dirArr) { int nx = x + d[0]; int ny = y + d[1]; // valid move inside grid and not visited if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && !vis[nx][ny]) { // move only if difference is within allowed limit if (abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y]) <= limit) { if (dfs(nx, ny, limit, mat, vis)) return true; } } } return false; } // checks if path exists for given maximum allowed difference bool canReach(int limit, vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> vis(n, vector<int>(m, 0)); return dfs(0, 0, limit, mat, vis); } // binary search on minimum possible maximum difference int minCostPath(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int low = 0, high = 0; int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); // compute upper bound of differences for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (i + 1 < n) high = max(high, abs(mat[i+1][j] - mat[i][j])); if (j + 1 < m) high = max(high, abs(mat[i][j+1] - mat[i][j])); } } int ans = high; // binary search to find smallest feasible limit while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (canReach(mid, mat)) { ans = mid; high = mid - 1; } else { low = mid + 1; } } return ans; } //Driver Code Starts int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; cout << minCostPath(mat); } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts class GFG { //Driver Code Ends // directions: up, down, right, left static int[][] dirArr = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; // DFS to check if we can reach destination // with allowed difference = limit static boolean dfs(int x, int y, int limit, int[][] mat, int[][] vis) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; if (x == n - 1 && y == m - 1) return true; vis[x][y] = 1; for (int[] d : dirArr) { int nx = x + d[0]; int ny = y + d[1]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && vis[nx][ny] == 0) { if (Math.abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y]) <= limit) { if (dfs(nx, ny, limit, mat, vis)) return true; } } } return false; } // checks if path exists for this limit static boolean canReach(int limit, int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; int[][] vis = new int[n][m]; return dfs(0, 0, limit, mat, vis); } // binary search on minimum possible maximum difference static int minCostPath(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; int low = 0, high = 0; // compute upper bound for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (i + 1 < n) high = Math.max(high, Math.abs(mat[i+1][j] - mat[i][j])); if (j + 1 < m) high = Math.max(high, Math.abs(mat[i][j+1] - mat[i][j])); } } int ans = high; while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (canReach(mid, mat)) { ans = mid; high = mid - 1; } else { low = mid + 1; } } return ans; } //Driver Code Starts public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; System.out.println(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends # directions: up, down, right, left dirArr = [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]] # DFS to check if destination is # reachable with allowed difference = limit def dfs(x, y, limit, mat, vis): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) if x == n - 1 and y == m - 1: return True vis[x][y] = 1 for dx, dy in dirArr: nx = x + dx ny = y + dy if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m and vis[nx][ny] == 0: if abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y]) <= limit: if dfs(nx, ny, limit, mat, vis): return True return False # checks if path exists for this limit def canReach(limit, mat): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) vis = [[0]*m for _ in range(n)] return dfs(0, 0, limit, mat, vis) # binary search on minimum possible maximum difference def minCostPath(mat): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) low, high = 0, 0 # compute upper bound for i in range(n): for j in range(m): if i + 1 < n: high = max(high, abs(mat[i+1][j] - mat[i][j])) if j + 1 < m: high = max(high, abs(mat[i][j+1] - mat[i][j])) ans = high while low <= high: mid = (low + high) // 2 if canReach(mid, mat): ans = mid high = mid - 1 else: low = mid + 1 return ans #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == '__main__': mat = [ [7, 2, 6, 5], [3, 1, 10, 8] ] print(minCostPath(mat)) #Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts using System; class GFG { //Driver Code Ends // directions: up, down, right, left static int[,] dirArr = { {-1,0},{1,0},{0,1},{0,-1} }; // DFS to check if destination is reachable // with allowed difference = limit static bool dfs(int x, int y, int limit, int[,] mat, int[,] vis) { int n = mat.GetLength(0); int m = mat.GetLength(1); if (x == n - 1 && y == m - 1) return true; vis[x, y] = 1; for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int nx = x + dirArr[k, 0]; int ny = y + dirArr[k, 1]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && vis[nx, ny] == 0) { if (Math.Abs(mat[nx, ny] - mat[x, y]) <= limit) { if (dfs(nx, ny, limit, mat, vis)) return true; } } } return false; } // checks if path exists for this limit static bool canReach(int limit, int[,] mat) { int n = mat.GetLength(0); int m = mat.GetLength(1); int[,] vis = new int[n, m]; return dfs(0, 0, limit, mat, vis); } // binary search on minimum possible maximum difference static int minCostPath(int[,] mat) { int n = mat.GetLength(0); int m = mat.GetLength(1); int low = 0, high = 0; // compute upper bound for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (i + 1 < n) high = Math.Max(high, Math.Abs(mat[i+1, j] - mat[i, j])); if (j + 1 < m) high = Math.Max(high, Math.Abs(mat[i, j+1] - mat[i, j])); } } int ans = high; while (low <= high) { int mid = (low + high) / 2; if (canReach(mid, mat)) { ans = mid; high = mid - 1; } else { low = mid + 1; } } return ans; } //Driver Code Starts static void Main() { int[,] mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; Console.WriteLine(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends // directions: up, down, right, left let dirArr = [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,1],[0,-1]]; // DFS to check if destination is // reachable with allowed difference = limit function dfs(x, y, limit, mat, vis) { let n = mat.length; let m = mat[0].length; if (x === n - 1 && y === m - 1) return true; vis[x][y] = 1; for (let d of dirArr) { let nx = x + d[0]; let ny = y + d[1]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m && vis[nx][ny] === 0) { if (Math.abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y]) <= limit) { if (dfs(nx, ny, limit, mat, vis)) return true; } } } return false; } // checks if path exists for this limit function canReach(limit, mat) { let n = mat.length; let m = mat[0].length; let vis = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(0)); return dfs(0, 0, limit, mat, vis); } // binary search on minimum possible maximum difference function minCostPath(mat) { let n = mat.length; let m = mat[0].length; let low = 0, high = 0; // compute upper bound for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) { if (i + 1 < n) high = Math.max(high, Math.abs(mat[i+1][j] - mat[i][j])); if (j + 1 < m) high = Math.max(high, Math.abs(mat[i][j+1] - mat[i][j])); } } let ans = high; while (low <= high) { let mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2); if (canReach(mid, mat)) { ans = mid; high = mid - 1; } else { low = mid + 1; } } return ans; } //Driver Code Starts // Driver Code let mat = [ [7, 2, 6, 5], [3, 1, 10, 8] ]; console.log(minCostPath(mat)); //Driver Code Ends Time complexity: O((n*m) * log(k)), where k is max the values in the matrix, therefore, the maximum possible difference between the values of 2 consecutive cells can be k, hence the maximum cost can be k. And for each cost, we explore the grid, therefore the time complexity of exploring the grid is n*m
Auxiliary Space: O(n*m)
[Expected Approach - 1] - Using Dijkstra's Algorithm
We can observe that along any path, the maximum difference so far never decreases—it either increases or stays the same. This property allows us to solve the problem using Dijkstra’s algorithm.
We treat each cell as a node, and edges connect adjacent cells with weights equal to the absolute difference of their values. We maintain a cost matrix where cost[i][j] is the minimum maximum difference needed to reach (i,j).
At each step, we process the cell with the current smallest cost and explore its neighbors. For each neighbor, the new cost is:
newCost = max(currentCost, abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y]))
If newCost is smaller than the neighbor’s recorded cost, we update it.
When the destination is reached, its cost in the matrix gives the minimum possible maximum difference along any path.
C++ //Driver Code Starts #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; //Driver Code Ends // Directions: up, down, left, right int dir[4][2] = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; int minCostPath(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); vector<vector<int>> cost(n, vector<int>(m, INT_MAX)); cost[0][0] = 0; // {current cost, {x, y}} priority_queue<pair<int,pair<int,int>>, vector<pair<int,pair<int,int>>>, greater<>> pq; pq.push({0, {0,0}}); while(!pq.empty()) { auto [currCost, cell] = pq.top(); pq.pop(); int x = cell.first, y = cell.second; // Skip if this is an outdated entry if(currCost != cost[x][y]) continue; // Destination reached if(x == n-1 && y == m-1) return currCost; for(auto d : dir) { int nx = x + d[0], ny = y + d[1]; if(nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m) { // Maximum difference along this path int newCost = max(currCost, abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y])); // Update if newCost improves the neighbor if(newCost < cost[nx][ny]) { cost[nx][ny] = newCost; pq.push({newCost, {nx, ny}}); } } } } return cost[n-1][m-1]; } //Driver Code Starts int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = { {7, 2, 6, 5}, {3, 1, 10, 8} }; cout << minCostPath(mat); } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts import java.util.PriorityQueue; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.Arrays; class GFG { //Driver Code Ends // Directions: up, down, left, right static int[][] dir = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; static int minCostPath(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length, m = mat[0].length; int[][] cost = new int[n][m]; for(int[] row : cost) Arrays.fill(row, Integer.MAX_VALUE); cost[0][0] = 0; // {current cost, x, y} PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>( Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0])); pq.add(new int[]{0,0,0}); while(!pq.isEmpty()) { int[] top = pq.poll(); int currCost = top[0], x = top[1], y = top[2]; // Skip if this is an outdated entry if(currCost != cost[x][y]) continue; // Destination reached if(x == n-1 && y == m-1) return currCost; for(int[] d : dir) { int nx = x + d[0], ny = y + d[1]; if(nx >= 0 && nx < n && ny >= 0 && ny < m) { // Maximum difference along this path int newCost = Math.max(currCost, Math.abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y])); // Update if newCost improves the neighbor if(newCost < cost[nx][ny]) { cost[nx][ny] = newCost; pq.add(new int[]{newCost, nx, ny}); } } } } return cost[n-1][m-1]; } //Driver Code Starts public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { {7,2,6,5}, {3,1,10,8} }; System.out.println(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends #Driver Code Starts import heapq #Driver Code Ends # Directions: up, down, left, right dir = [(-1,0),(1,0),(0,-1),(0,1)] def minCostPath(mat): n, m = len(mat), len(mat[0]) cost = [[float('inf')]*m for _ in range(n)] cost[0][0] = 0 # {current cost, x, y} pq = [(0,0,0)] while pq: currCost, x, y = heapq.heappop(pq) # Skip if this is an outdated entry if currCost != cost[x][y]: continue # Destination reached if x == n-1 and y == m-1: return currCost for dx, dy in dir: nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m: # Maximum difference along this path newCost = max(currCost, abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y])) # Update if newCost improves the neighbor if newCost < cost[nx][ny]: cost[nx][ny] = newCost heapq.heappush(pq, (newCost, nx, ny)) return cost[n-1][m-1] #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == '__main__': mat = [ [7,2,6,5], [3,1,10,8] ] print(minCostPath(mat)) #Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Cell class for priority queue class Cell : IComparable<Cell> { public int cost, x, y; public Cell(int c, int i, int j) { cost=c; x=i; y=j; } public int CompareTo(Cell other) { if (this.cost != other.cost) return this.cost - other.cost; if (this.x != other.x) return this.x - other.x; return this.y - other.y; } } // Custom min-heap class MinHeap { private List<Cell> heap = new List<Cell>(); private void Swap(int i,int j){ var tmp = heap[i]; heap[i] = heap[j]; heap[j] = tmp; } public void Push(Cell c){ heap.Add(c); int i = heap.Count-1; while(i>0){ int parent=(i-1)/2; if(heap[i].CompareTo(heap[parent])>=0) break; Swap(i,parent); i=parent; } } public Cell Pop(){ var top = heap[0]; Swap(0,heap.Count-1); heap.RemoveAt(heap.Count-1); int i=0; while(true){ int left=2*i+1, right=2*i+2, smallest=i; if(left<heap.Count && heap[left].CompareTo(heap[smallest])<0) smallest=left; if(right<heap.Count && heap[right].CompareTo(heap[smallest])<0) smallest=right; if(smallest==i) break; Swap(i,smallest); i=smallest; } return top; } public int Count() => heap.Count; } class GFG { //Driver Code Ends // Directions: up, down, left, right static int[,] dir = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; static int minCostPath(int[,] mat) { int n=mat.GetLength(0), m=mat.GetLength(1); int[,] cost = new int[n,m]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cost[i,j] = int.MaxValue; cost[0,0]=0; MinHeap pq = new MinHeap(); pq.Push(new Cell(0,0,0)); while(pq.Count()>0){ Cell top = pq.Pop(); int currCost=top.cost, x=top.x, y=top.y; // Skip outdated entries if(currCost!=cost[x,y]) continue; // Destination reached if(x==n-1 && y==m-1) return currCost; for(int k=0;k<4;k++){ int nx=x+dir[k,0], ny=y+dir[k,1]; if(nx>=0 && nx<n && ny>=0 && ny<m){ int newCost = Math.Max(currCost, Math.Abs(mat[nx,ny]-mat[x,y])); if(newCost<cost[nx,ny]){ cost[nx,ny]=newCost; pq.Push(new Cell(newCost,nx,ny)); } } } } return cost[n-1,m-1]; } //Driver Code Starts static void Main() { int[,] mat = { {7,2,6,5}, {3,1,10,8} }; Console.WriteLine(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts // Min-heap priority queue class PriorityQueue { constructor() { this.heap = []; } push(cell) { this.heap.push(cell); this._heapifyUp(); } pop() { if(this.size() === 0) return null; const top = this.heap[0]; const last = this.heap.pop(); if(this.size() > 0) { this.heap[0] = last; this._heapifyDown(); } return top; } size() { return this.heap.length; } _heapifyUp() { let idx = this.heap.length - 1; while(idx > 0) { let parent = Math.floor((idx - 1) / 2); if(this.heap[idx].cost >= this.heap[parent].cost) break; [this.heap[idx], this.heap[parent]] = [this.heap[parent], this.heap[idx]]; idx = parent; } } _heapifyDown() { let idx = 0; const n = this.heap.length; while(true) { let left = 2*idx + 1, right = 2*idx + 2; let smallest = idx; if(left < n && this.heap[left].cost < this.heap[smallest].cost) smallest = left; if(right < n && this.heap[right].cost < this.heap[smallest].cost) smallest = right; if(smallest === idx) break; [this.heap[idx], this.heap[smallest]] = [this.heap[smallest], this.heap[idx]]; idx = smallest; } } } //Driver Code Ends // Cell class class Cell { constructor(cost, x, y) { this.cost = cost; this.x = x; this.y = y; } } // Directions: up, down, left, right const dir = [[-1,0],[1,0],[0,-1],[0,1]]; // Dijkstra-based minimum maximum path function minCostPath(mat) { const n = mat.length, m = mat[0].length; const cost = Array.from({length:n}, ()=>Array(m).fill(Infinity)); cost[0][0] = 0; // {current cost, x, y} const pq = new PriorityQueue(); pq.push(new Cell(0,0,0)); while(pq.size()) { const top = pq.pop(); const currCost = top.cost, x = top.x, y = top.y; // Skip if this is an outdated entry if(currCost !== cost[x][y]) continue; // Destination reached if(x === n-1 && y === m-1) return currCost; for(const d of dir) { const nx = x + d[0], ny = y + d[1]; if(nx >=0 && nx < n && ny >=0 && ny < m) { // Maximum difference along this path const newCost = Math.max(currCost, Math.abs(mat[nx][ny] - mat[x][y])); // Update if newCost improves the neighbor if(newCost < cost[nx][ny]) { cost[nx][ny] = newCost; pq.push(new Cell(newCost, nx, ny)); } } } } return cost[n-1][m-1]; } //Driver Code Starts // Driver code const mat = [ [7,2,6,5], [3,1,10,8] ]; console.log(minCostPath(mat)); //Driver Code Ends Time complexity: O((n*m) * log (n*m)), as the priority queue may contain n*m elements at max, and the cost of insertion/deletion of each element is log (size of priority queue).
Auxiliary Space: O(n*m), the maximum size of priority queue
[Expected Approach - 2] - Using DSU - O((n*m) log(n*m)) Time and O(n*m) Space
We can treat each cell as a node and connect it to its neighbors with edges weighted by the absolute difference of their values. To represent each cell uniquely in DSU, we assign it a number using i*m + j, where i and j are the row and column indices and m is the number of columns.
We start connecting cells using the edges with the smallest differences first. Iteratively, we union the two cells of each edge. The moment the start (0, 0) and destination (n-1, m-1) become connected, the weight of the current edge is the minimum maximum difference along a path.
This works because by connecting edges from smallest to largest, the first time the start and end are connected ensures that the largest difference along the path is minimized, giving the correct answer.
C++ //Driver Code Starts #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; // DSU class class DSU { vector<int> parent, rank; public: DSU(int n) { parent.resize(n); rank.resize(n,0); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } int find(int x) { if(parent[x]!=x) parent[x]=find(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void unite(int x, int y) { int px = find(x), py = find(y); if(px==py) return; if(rank[px]<rank[py]) parent[px]=py; else if(rank[px]>rank[py]) parent[py]=px; else { parent[py]=px; rank[px]++; } } bool connected(int x,int y) { return find(x)==find(y); } }; //Driver Code Ends int minCostPath(vector<vector<int>>& mat) { int n = mat.size(), m = mat[0].size(); int total = n*m; // Store edges: {weight, cell1, cell2} vector<array<int,3>> edges; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { for(int j=0;j<m;j++) { int u = i*m + j; // Only right and down neighbors to avoid duplicates if(i+1 < n) edges.push_back({ abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i+1][j]), u, (i+1)*m+j}); if(j+1 < m) edges.push_back({ abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i][j+1]), u, i*m + (j+1)}); } } // Sort edges by weight (smallest first) sort(edges.begin(), edges.end()); DSU dsu(total); // Connect cells using edges in increasing order for(auto &e : edges) { int w = e[0], u = e[1], v = e[2]; dsu.unite(u,v); // Check if start and end are connected if(dsu.connected(0, total-1)) return w; } // Only occurs if single cell return 0; } //Driver Code Starts int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = { {7,2,6,5}, {3,1,10,8} }; cout << minCostPath(mat); } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts // DSU class class DSU { int[] parent, rank; DSU(int n) { parent = new int[n]; rank = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } int find(int x) { if(parent[x]!=x) parent[x]=find(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } void unite(int x,int y) { int px=find(x), py=find(y); if(px==py) return; if(rank[px]<rank[py]) parent[px]=py; else if(rank[px]>rank[py]) parent[py]=px; else { parent[py]=px; rank[px]++; } } boolean connected(int x,int y){ return find(x)==find(y); } } class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static int minCostPath(int[][] mat){ int n=mat.length, m=mat[0].length, total=n*m; java.util.ArrayList<int[]> edges=new java.util.ArrayList<>(); // Store edges: {weight, cell1, cell2} for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ int u=i*m+j; // Only right and down neighbors if(i+1<n) edges.add(new int[]{ Math.abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i+1][j]), u, (i+1)*m+j}); if(j+1<m) edges.add(new int[]{ Math.abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i][j+1]), u, i*m+j+1}); } } // Sort edges by weight edges.sort((a,b)->a[0]-b[0]); DSU dsu=new DSU(total); // Connect cells using edges in increasing order for(int[] e: edges){ int w=e[0], u=e[1], v=e[2]; dsu.unite(u,v); // Check if start and end are connected if(dsu.connected(0,total-1)) return w; } // Single cell case return 0; } //Driver Code Starts public static void main(String[] args){ int[][] mat={{7,2,6,5},{3,1,10,8}}; System.out.println(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends #Driver Code Starts # DSU class class DSU: def __init__(self,n): self.parent = list(range(n)) self.rank = [0]*n def find(self,x): if self.parent[x]!=x: self.parent[x]=self.find(self.parent[x]) return self.parent[x] def unite(self,x,y): px, py = self.find(x), self.find(y) if px==py: return if self.rank[px]<self.rank[py]: self.parent[px]=py elif self.rank[px]>self.rank[py]: self.parent[py]=px else: self.parent[py]=px self.rank[px]+=1 def connected(self,x,y): return self.find(x)==self.find(y) #Driver Code Ends def minCostPath(mat): n,m=len(mat),len(mat[0]) total = n*m # Store edges: (weight, cell1, cell2) edges=[] for i in range(n): for j in range(m): u = i*m+j # Only right and down neighbors if i+1<n: edges.append([abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i+1][j]), u, (i+1)*m+j]) if j+1<m: edges.append([abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i][j+1]), u, i*m+j+1]) # Sort edges by weight edges.sort() dsu = DSU(total) # Connect cells using edges in increasing order for w,u,v in edges: dsu.unite(u,v) # Check if start and end are connected if dsu.connected(0,total-1): return w # Single cell case return 0 #Driver Code Starts if __name__ == '__main__': mat = [[7,2,6,5],[3,1,10,8]] print(minCostPath(mat)) #Driver Code Ends
//Driver Code Starts using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class DSU { int[] parent, rank; public DSU(int n){ parent = new int[n]; rank = new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) parent[i]=i; } public int find(int x){ if(parent[x]!=x) parent[x]=find(parent[x]); return parent[x]; } public void unite(int x,int y){ int px=find(x), py=find(y); if(px==py) return; if(rank[px]<rank[py]) parent[px]=py; else if(rank[px]>rank[py]) parent[py]=px; else { parent[py]=px; rank[px]++; } } public bool connected(int x,int y){ return find(x)==find(y); } } class GFG { //Driver Code Ends static int minCostPath(int[,] mat){ int n = mat.GetLength(0), m = mat.GetLength(1), total = n*m; // Store edges: {weight, cell1, cell2} List<int[]> edges = new List<int[]>(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ for(int j=0;j<m;j++){ int u = i*m+j; if(i+1<n) edges.Add(new int[]{ Math.Abs(mat[i,j]-mat[i+1,j]), u, (i+1)*m+j}); if(j+1<m) edges.Add(new int[]{ Math.Abs(mat[i,j]-mat[i,j+1]), u, i*m+j+1}); } } // Sort edges by weight edges.Sort((a,b)=>a[0]-b[0]); DSU dsu = new DSU(total); // Connect cells using edges in increasing order foreach(var e in edges){ int w=e[0], u=e[1], v=e[2]; dsu.unite(u,v); // Check if start and end are connected if(dsu.connected(0,total-1)) return w; } // Single cell case return 0; } //Driver Code Starts static void Main(){ int[,] mat={{7,2,6,5},{3,1,10,8}}; Console.WriteLine(minCostPath(mat)); } } //Driver Code Ends //Driver Code Starts // DSU class class DSU { constructor(n){ this.parent = Array.from({length:n},(_,i)=>i); this.rank = Array(n).fill(0); } find(x){ if(this.parent[x]!=x) this.parent[x]=this.find(this.parent[x]); return this.parent[x]; } unite(x,y){ let px=this.find(x), py=this.find(y); if(px===py) return; if(this.rank[px]<this.rank[py]) this.parent[px]=py; else if(this.rank[px]>this.rank[py]) this.parent[py]=px; else { this.parent[py]=px; this.rank[px]++; } } connected(x,y){ return this.find(x)===this.find(y); } } //Driver Code Ends function minCostPath(mat){ const n=mat.length, m=mat[0].length, total=n*m; const edges=[]; // Store edges: [weight, cell1, cell2] for(let i=0;i<n;i++){ for(let j=0;j<m;j++){ let u=i*m+j; if(i+1<n) edges.push([Math.abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i+1][j]), u, (i+1)*m+j]); if(j+1<m) edges.push([Math.abs(mat[i][j]-mat[i][j+1]), u, i*m+j+1]); } } // Sort edges by weight edges.sort((a,b)=>a[0]-b[0]); const dsu = new DSU(total); // Connect cells using edges in increasing order for(const e of edges){ const [w,u,v]=e; dsu.unite(u,v); // Check if start and end are connected if(dsu.connected(0,total-1)) return w; } // Single cell case return 0; } //Driver Code Starts // Driver Code const mat=[[7,2,6,5],[3,1,10,8]]; console.log(minCostPath(mat)); //Driver Code Ends
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile