Minimum swap required to convert binary tree to binary search tree
Last Updated : 25 Nov, 2024
Given an array arr[] which represents a Complete Binary Tree i.e., if index i is the parent, index 2*i + 1 is the left child and index 2*i + 2 is the right child. The task is to find the minimum number of swaps required to convert it into a Binary Search Tree.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11]
Output: 3
Explanation:
Binary tree of the given array:
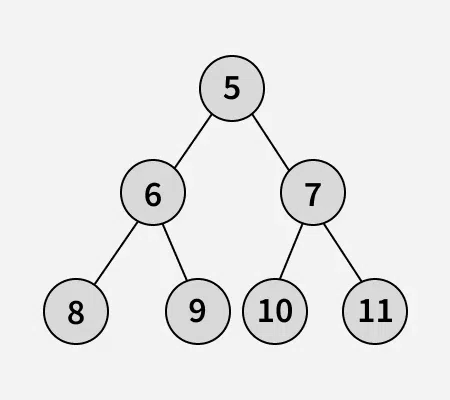
Swap 1: Swap node 8 with node 5.
Swap 2: Swap node 9 with node 10.
Swap 3: Swap node 10 with node 7.
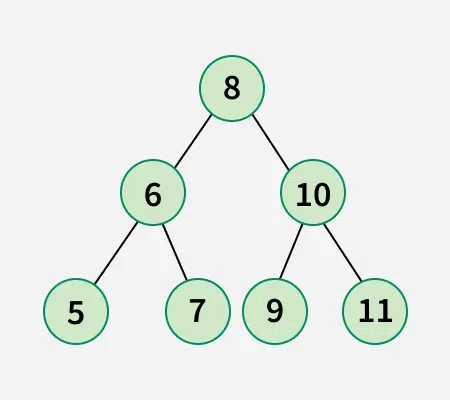
So, minimum 3 swaps are required to obtain the below binary search tree:
Input: arr[] = [1, 2, 3]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Binary tree of the given array:
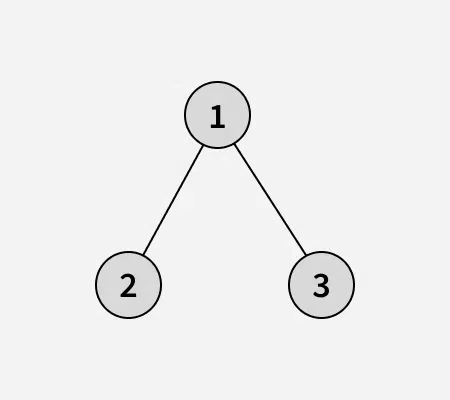
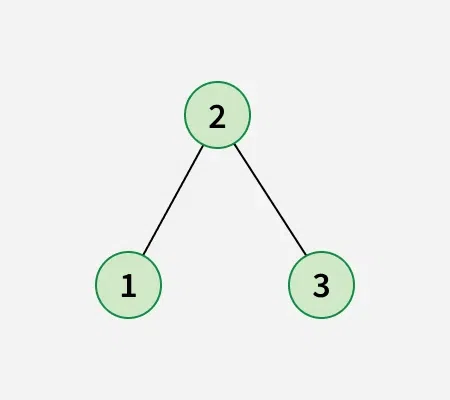
After swapping node 1 with node 2, obtain the below binary search tree:
Approach:
The idea is to use the fact that inorder traversal of Binary Search Tree is in increasing order of their value.
So, find the inorder traversal of the Binary Tree and store it in the array and try to sort the array. The minimum number of swap required to get the array sorted will be the answer.
C++ // C++ program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in vector v void inorder(vector<int>& arr, vector<int>& inorderArr, int index) { int n = arr.size(); // If index is out of bounds, return if (index >= n) return; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 1); // Store current node value in vector inorderArr.push_back(arr[index]); // Recursively visit right subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 2); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps // to sort inorder traversal int minSwaps(vector<int>& arr) { int n = arr.size(); vector<int> inorderArr; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 0); // Create an array of pairs to store value // and original index vector<pair<int, int>> t(inorderArr.size()); int ans = 0; // Store the value and its index for (int i = 0; i < inorderArr.size(); i++) t[i] = {inorderArr[i], i}; // Sort the pair array based on values // to get BST order sort(t.begin(), t.end()); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i++) { // If the element is already in the // correct position, continue if (i == t[i].second) continue; // Otherwise, perform swaps until the element // is in the right place else { // Swap elements to correct positions swap(t[i].first, t[t[i].second].first); swap(t[i].second, t[t[i].second].second); } // Check if the element is still not // in the correct position if (i != t[i].second) --i; // Increment swap count ans++; } return ans; } int main() { vector<int> arr = { 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 }; cout << minSwaps(arr) << endl; } // Java program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree import java.util.Arrays; class GfG { // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in an array static void inorder(int[] arr, int[] inorderArr, int index, int[] counter) { int n = arr.length; // Base case: if index is out of bounds, return if (index >= n) return; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 1, counter); // Store current node value in the inorder array inorderArr[counter[0]] = arr[index]; counter[0]++; // Recursively visit right subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 2, counter); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps // to sort inorder traversal static int minSwaps(int[] arr) { int n = arr.length; int[] inorderArr = new int[n]; int[] counter = new int[1]; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 0, counter); // Create an array of pairs to store the value // and its original index int[][] t = new int[n][2]; int ans = 0; // Store the value and its original index for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { t[i][0] = inorderArr[i]; t[i][1] = i; } // Sort the array based on values to get BST order Arrays.sort(t, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0])); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles boolean[] visited = new boolean[n]; // Iterate through the array to find cycles for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // If the element is already visited or in // the correct place, continue if (visited[i] || t[i][1] == i) continue; // Start a cycle and find the number of // nodes in the cycle int cycleSize = 0; int j = i; while (!visited[j]) { visited[j] = true; j = t[j][1]; cycleSize++; } // If there is a cycle, we need (cycleSize - 1) // swaps to sort the cycle if (cycleSize > 1) { ans += (cycleSize - 1); } } // Return the total number of swaps return ans; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11}; System.out.println(minSwaps(arr)); } } # Python program for Minimum swap required # to convert binary tree to binary search tree # Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree # and store it in an array def inorder(arr, inorderArr, index): # If index is out of bounds, return n = len(arr) if index >= n: return # Recursively visit left subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 1) # Store current node value in inorderArr inorderArr.append(arr[index]) # Recursively visit right subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 2) # Function to calculate minimum swaps # to sort inorder traversal def minSwaps(arr): inorderArr = [] # Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 0) # Create a list of pairs to store value and original index t = [(inorderArr[i], i) for i in range(len(inorderArr))] ans = 0 # Sort the list of pairs based on values # to get BST order t.sort() # Initialize visited array visited = [False] * len(t) # Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for i in range(len(t)): # If already visited or already in the # correct place, skip if visited[i] or t[i][1] == i: continue # Start a cycle and find the number of # nodes in the cycle cycleSize = 0 j = i # Process all elements in the cycle while not visited[j]: visited[j] = True j = t[j][1] cycleSize += 1 # If there is a cycle of size `cycle_size`, we # need `cycle_size - 1` swaps if cycleSize > 1: ans += (cycleSize - 1) # Return total number of swaps return ans if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11] print(minSwaps(arr))
// C# program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree using System; using System.Linq; class GfG { // Function to perform inorder traversal of the binary tree // and store it in an array static void Inorder(int[] arr, int[] inorderArr, int index, ref int counter) { int n = arr.Length; // Base case: if index is out of bounds, return if (index >= n) return; // Recursively visit left subtree Inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 1, ref counter); // Store current node value in inorderArr inorderArr[counter] = arr[index]; counter++; // Recursively visit right subtree Inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 2, ref counter); } // Function to calculate minimum // swaps to sort inorder traversal static int MinSwaps(int[] arr) { int n = arr.Length; int[] inorderArr = new int[n]; int counter = 0; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree Inorder(arr, inorderArr, 0, ref counter); // Create an array of pairs to store value // and original index var t = new (int, int)[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { t[i] = (inorderArr[i], i); } // Sort the array based on values to get BST order Array.Sort(t, (a, b) => a.Item1.CompareTo(b.Item1)); // Initialize visited array bool[] visited = new bool[n]; int ans = 0; // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // If already visited or already in // the correct place, skip if (visited[i] || t[i].Item2 == i) continue; // Start a cycle and find the number // of nodes in the cycle int cycleSize = 0; int j = i; // Process all elements in the cycle while (!visited[j]) { visited[j] = true; j = t[j].Item2; cycleSize++; } // If there is a cycle of size `cycle_size`, we // need `cycle_size - 1` swaps if (cycleSize > 1) { ans += (cycleSize - 1); } } // Return total number of swaps return ans; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = { 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 }; Console.WriteLine(MinSwaps(arr)); } } // Javascript program for Minimum swap required // to convert binary tree to binary search tree // Inorder traversal to get values in sorted order function inorder(arr, inorderArr, index) { // If index is out of bounds, return if (index >= arr.length) return; // Recursively visit left subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 1); // Store current node value in array inorderArr.push(arr[index]); // Recursively visit right subtree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 2 * index + 2); } // Function to calculate minimum swaps to sort inorder // traversal function minSwaps(arr) { let inorderArr = []; // Get the inorder traversal of the binary tree inorder(arr, inorderArr, 0); // Create an array of pairs to store value and original // index let t = inorderArr.map((val, i) => [val, i]); let ans = 0; // Sort the pair array based on values to get BST order t.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]); // Find minimum swaps by detecting cycles let visited = Array(arr.length) .fill(false); for (let i = 0; i < t.length; i++) { // If the element is already in the correct // position, continue if (visited[i] || t[i][1] === i) continue; // Otherwise, perform swaps until the element is in // the right place let cycleSize = 0; let j = i; while (!visited[j]) { visited[j] = true; j = t[j][1]; cycleSize++; } // If there is a cycle, we need (cycleSize - 1) // swaps to sort the cycle if (cycleSize > 1) { ans += (cycleSize - 1); } } // Return total number of swaps return ans; } let arr = [ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 ]; console.log(minSwaps(arr)); Time Complexity: O(n*logn) where n is the number of elements in array.
Auxiliary Space: O(n) because it is using extra space for array
Exercise: Can we extend this to normal binary tree, i.e., a binary tree represented using left and right pointers, and not necessarily complete?
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile