Minimum Cost Path in a directed graph via given set of intermediate nodes
Last Updated : 15 Jul, 2025
Given a weighted, directed graph G, an array V[] consisting of vertices, the task is to find the Minimum Cost Path passing through all the vertices of the set V, from a given source S to a destination D.
Examples:
Input: V = {7}, S = 0, D = 6
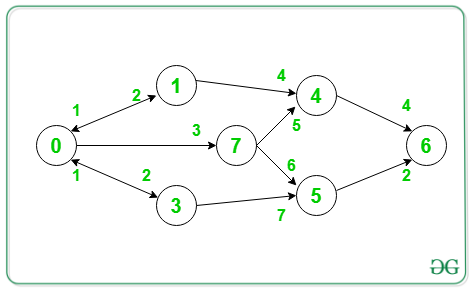
Output: 11
Explanation:
Minimum path 0->7->5->6.
Therefore, the cost of the path = 3 + 6 + 2 = 11
Input: V = {7, 4}, S = 0, D = 6

Output: 12
Explanation:
Minimum path 0->7->4->6.
Therefore the cost of the path = 3 + 5 + 4 = 12
Approach:
To solve the problem, the idea is to use Breadth-First-Search traversal. BFS is generally used to find the Shortest Paths in the graph and the minimum distance of all nodes from Source, intermediate nodes, and Destination can be calculated by the BFS from these nodes.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize minSum to INT_MAX.
- Traverse the graph from the source node S using BFS.
- Mark each neighbouring node of the source as the new source and perform BFS from that node.
- Once the destination node D is encountered, then check if all the intermediate nodes are visited or not.
- If all the intermediate nodes are visited, then update the minSum and return the minimum value.
- If all the intermediate nodes are not visited, then return minSum.
- Mark the source as unvisited.
- Print the final value of minSum obtained.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Program to implement // the above approach #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Stores minimum-cost of path from source int minSum = INT_MAX; // Function to Perform BFS on graph g // starting from vertex v void getMinPathSum(unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int> > >& graph, vector<bool>& visited, vector<int> necessary, int src, int dest, int currSum) { // If destination is reached if (src == dest) { // Set flag to true bool flag = true; // Visit all the intermediate nodes for (int i : necessary) { // If any intermediate node // is not visited if (!visited[i]) { flag = false; break; } } // If all intermediate // nodes are visited if (flag) // Update the minSum minSum = min(minSum, currSum); return; } else { // Mark the current node // visited visited[src] = true; // Traverse adjacent nodes for (auto node : graph[src]) { if (!visited[node.first]) { // Mark the neighbour visited visited[node.first] = true; // Find minimum cost path // considering the neighbour // as the source getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, node.first, dest, currSum + node.second); // Mark the neighbour unvisited visited[node.first] = false; } } // Mark the source unvisited visited[src] = false; } } // Driver Code int main() { // Stores the graph unordered_map<int, vector<pair<int, int> > > graph; graph[0] = { { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 2 } }; graph[1] = { { 4, 4 }, { 0, 1 } }; graph[2] = { { 4, 5 }, { 5, 6 } }; graph[3] = { { 5, 7 }, { 0, 1 } }; graph[4] = { { 6, 4 } }; graph[5] = { { 6, 2 } }; graph[6] = { { 7, 11 } }; // Number of nodes int n = 7; // Source int source = 0; // Destination int dest = 6; // Keeps a check on visited // and unvisited nodes vector<bool> visited(n, false); // Stores intermediate nodes vector<int> necessary{ 2, 4 }; getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0); // If no path is found if (minSum == INT_MAX) cout << "-1\n"; else cout << minSum << '\n'; return 0; } // Java program to implement // the above approach import java.util.*; class GFG{ static class pair { int first, second; pair(int f, int s) { this.first = f; this.second = s; } } // Stores minimum-cost of path from source static int minSum = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Function to Perform BFS on graph g // starting from vertex v static void getMinPathSum(Map<Integer, ArrayList<pair>> graph, boolean[] visited, ArrayList<Integer> necessary, int source, int dest, int currSum) { // If destination is reached if (src == dest) { // Set flag to true boolean flag = true; // Visit all the intermediate nodes for(int i : necessary) { // If any intermediate node // is not visited if (!visited[i]) { flag = false; break; } } // If all intermediate // nodes are visited if (flag) // Update the minSum minSum = Math.min(minSum, currSum); return; } else { // Mark the current node // visited visited[src] = true; // Traverse adjacent nodes for(pair node : graph.get(src)) { if (!visited[node.first]) { // Mark the neighbour visited visited[node.first] = true; // Find minimum cost path // considering the neighbour // as the source getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, node.first, dest, currSum + node.second); // Mark the neighbour unvisited visited[node.first] = false; } } // Mark the source unvisited visited[src] = false; } } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // Stores the graph Map<Integer, ArrayList<pair>> graph = new HashMap<>(); for(int i = 0; i <= 6; i++) graph.put(i, new ArrayList<pair>()); graph.get(0).add(new pair(1, 2)); graph.get(0).add(new pair(2, 3)); graph.get(0).add(new pair(3, 2)); graph.get(1).add(new pair(4, 4)); graph.get(1).add(new pair(0, 1)); graph.get(2).add(new pair(4, 5)); graph.get(2).add(new pair(5, 6)); graph.get(3).add(new pair(5, 7)); graph.get(3).add(new pair(0, 1)); graph.get(4).add(new pair(6, 4)); graph.get(5).add(new pair(4, 2)); graph.get(6).add(new pair(7, 11)); // Number of nodes int n = 7; // Source int source = 0; // Destination int dest = 6; // Keeps a check on visited // and unvisited nodes boolean[] visited = new boolean[n]; // Stores intermediate nodes ArrayList<Integer> necessary = new ArrayList<>( Arrays.asList(2, 4)); getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0); // If no path is found if (minSum == Integer.MAX_VALUE) System.out.println(-1); else System.out.println(minSum); } } // This code is contributed by offbeat # Python3 Program to implement # the above approach # Stores minimum-cost of path from source minSum = 1000000000 # Function to Perform BFS on graph g # starting from vertex v def getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, currSum): global minSum # If destination is reached if (src == dest): # Set flag to true flag = True; # Visit all the intermediate nodes for i in necessary: # If any intermediate node # is not visited if (not visited[i]): flag = False; break; # If all intermediate # nodes are visited if (flag): # Update the minSum minSum = min(minSum, currSum); return; else: # Mark the current node # visited visited[src] = True; # Traverse adjacent nodes for node in graph[src]: if not visited[node[0]]: # Mark the neighbour visited visited[node[0]] = True; # Find minimum cost path # considering the neighbour # as the source getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, node[0], dest, currSum + node[1]); # Mark the neighbour unvisited visited[node[0]] = False; # Mark the source unvisited visited[src] = False; # Driver Code if __name__=='__main__': # Stores the graph graph=dict() graph[0] = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 2, 3 ], [ 3, 2 ] ]; graph[1] = [ [ 4, 4 ], [ 0, 1 ] ]; graph[2] = [ [ 4, 5 ], [ 5, 6 ] ]; graph[3] = [ [ 5, 7 ], [ 0, 1 ] ]; graph[4] = [ [ 6, 4 ] ]; graph[5] = [ [ 6, 2 ] ]; graph[6] = [ [ 7, 11 ] ]; # Number of nodes n = 7; # Source source = 0; # Destination dest = 6; # Keeps a check on visited # and unvisited nodes visited=[ False for i in range(n + 1)] # Stores intermediate nodes necessary = [ 2, 4 ]; getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0); # If no path is found if (minSum == 1000000000): print(-1) else: print(minSum) # This code is contributed by pratham76
// C# program to implement // the above approach using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG{ class pair { public int first, second; public pair(int f, int s) { this.first = f; this.second = s; } } // Stores minimum-cost of path from source static int minSum = 100000000; // Function to Perform BFS on graph g // starting from vertex v static void getMinPathSum(Dictionary<int, ArrayList> graph, bool[] visited, ArrayList necessary, int source, int dest, int currSum) { // If destination is reached if (src == dest) { // Set flag to true bool flag = true; // Visit all the intermediate nodes foreach(int i in necessary) { // If any intermediate node // is not visited if (!visited[i]) { flag = false; break; } } // If all intermediate // nodes are visited if (flag) // Update the minSum minSum = Math.Min(minSum, currSum); return; } else { // Mark the current node // visited visited[src] = true; // Traverse adjacent nodes foreach(pair node in graph[source]) { if (!visited[node.first]) { // Mark the neighbour visited visited[node.first] = true; // Find minimum cost path // considering the neighbour // as the source getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, node.first, dest, currSum + node.second); // Mark the neighbour unvisited visited[node.first] = false; } } // Mark the source unvisited visited[src] = false; } } // Driver code public static void Main(string[] args) { // Stores the graph Dictionary<int, ArrayList> graph = new Dictionary<int, ArrayList>(); for(int i = 0; i <= 6; i++) graph[i] = new ArrayList(); graph[0].Add(new pair(1, 2)); graph[0].Add(new pair(2, 3)); graph[0].Add(new pair(3, 2)); graph[1].Add(new pair(4, 4)); graph[1].Add(new pair(0, 1)); graph[2].Add(new pair(4, 5)); graph[2].Add(new pair(5, 6)); graph[3].Add(new pair(5, 7)); graph[3].Add(new pair(0, 1)); graph[4].Add(new pair(6, 4)); graph[5].Add(new pair(4, 2)); graph[6].Add(new pair(7, 11)); // Number of nodes int n = 7; // Source int source = 0; // Destination int dest = 6; // Keeps a check on visited // and unvisited nodes bool[] visited = new bool[n]; // Stores intermediate nodes ArrayList necessary = new ArrayList(); necessary.Add(2); necessary.Add(4); getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0); // If no path is found if (minSum == 100000000) Console.WriteLine(-1); else Console.WriteLine(minSum); } } // This code is contributed by rutvik_56 <script> // Javascript program to implement // the above approach class pair { constructor(f, s) { this.first = f; this.second = s; } } // Stores minimum-cost of path from source var minSum = 100000000; // Function to Perform BFS on graph g // starting from vertex v function getMinPathSum(graph, visited,necessary, src, dest, currSum) { // If destination is reached if (src == dest) { // Set flag to true var flag = true; // Visit all the intermediate nodes for(var i of necessary) { // If any intermediate node // is not visited if (!visited[i]) { flag = false; break; } } // If all intermediate // nodes are visited if (flag) // Update the minSum minSum = Math.min(minSum, currSum); return; } else { // Mark the current node // visited visited[src] = true; // Traverse adjacent nodes for(var node of graph[src]) { if (!visited[node.first]) { // Mark the neighbour visited visited[node.first] = true; // Find minimum cost path // considering the neighbour // as the source getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, node.first, dest, currSum + node.second); // Mark the neighbour unvisited visited[node.first] = false; } } // Mark the source unvisited visited[src] = false; } } // Driver code // Stores the graph var graph = Array.from(Array(7), ()=>Array()); graph[0].push(new pair(1, 2)); graph[0].push(new pair(2, 3)); graph[0].push(new pair(3, 2)); graph[1].push(new pair(4, 4)); graph[1].push(new pair(0, 1)); graph[2].push(new pair(4, 5)); graph[2].push(new pair(5, 6)); graph[3].push(new pair(5, 7)); graph[3].push(new pair(0, 1)); graph[4].push(new pair(6, 4)); graph[5].push(new pair(4, 2)); graph[6].push(new pair(7, 11)); // Number of nodes var n = 7; // Source var source = 0; // Destination var dest = 6; // Keeps a check on visited // and unvisited nodes var visited = Array(n).fill(false); // Stores intermediate nodes var necessary = []; necessary.push(2); necessary.push(4); getMinPathSum(graph, visited, necessary, source, dest, 0); // If no path is found if (minSum == 100000000) document.write(-1); else document.write(minSum); </script> Time Complexity: O(N*M)
Auxiliary Space: O(N+M)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile