Merge K sorted linked lists
Last Updated : 26 Aug, 2025
Given k sorted linked lists of different sizes, we need to merge them into a single list while maintaining their sorted order.
Examples:
Input:
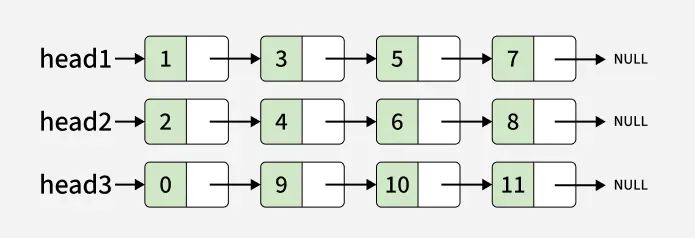
Output:
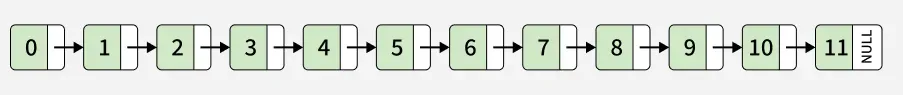
Explanation: Merged lists in a sorted order where every element is greater than the previous element.
Input:
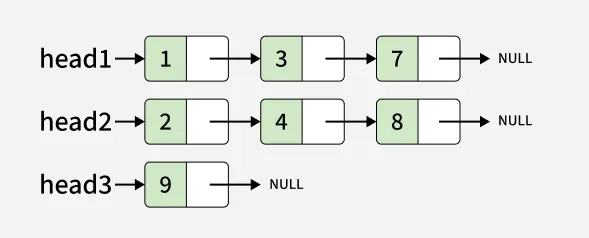
Output:
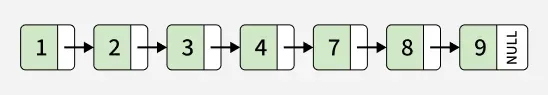
[Naive Approach - 1] - By Merging List One by One
The idea is to initialize the result as empty. Now one by one merge every linked list into the resultant list using the idea of merging two sorted linked lists. We always consider the result as first list and other list as second. At the end, we return result.
C++ #include <iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Function to merge only 2 lists Node* mergeTwo(Node* head1, Node* head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node* dummy = new Node(-1); Node* curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != nullptr && head2 != nullptr) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1->data <= head2->data) { curr->next = head1; head1 = head1->next; } else { curr->next = head2; head2 = head2->next; } curr = curr->next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != nullptr) { curr->next = head1; } else { curr->next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy->next; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists Node* mergeKLists(vector<Node*>& arr) { // Initialize result as empty Node *res = nullptr; // One by one merge all lists with // res and keep updating res for (Node *node : arr) res = mergeTwo(res, node); return res; } void printList(Node* node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if(node->next) cout<<" -> "; node = node->next; } } int main() { int k = 3; vector<Node*> arr(k); arr[0] = new Node(1); arr[0]->next = new Node(3); arr[0]->next->next = new Node(5); arr[0]->next->next->next = new Node(7); arr[1] = new Node(2); arr[1]->next = new Node(4); arr[1]->next->next = new Node(6); arr[1]->next->next->next = new Node(8); arr[2] = new Node(0); arr[2]->next = new Node(9); arr[2]->next->next = new Node(10); arr[2]->next->next->next = new Node(11); Node* head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* createNode(int data); // Function to merge only 2 lists struct Node* mergeTwo(struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process struct Node* dummy = createNode(-1); struct Node* curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != NULL && head2 != NULL) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1->data <= head2->data) { curr->next = head1; head1 = head1->next; } else { curr->next = head2; head2 = head2->next; } curr = curr->next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != NULL) { curr->next = head1; } else { curr->next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node struct Node* merged = dummy->next; free(dummy); return merged; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists struct Node* mergeKLists(struct Node** arr, int k) { // Initialize result as empty struct Node* res = NULL; // One by one merge all lists with // res and keep updating res for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) res = mergeTwo(res, arr[i]); return res; } void printList(struct Node* node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d", node->data); if(node->next) printf(" -> "); node = node->next; } } struct Node* createNode(int data) { struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); newNode->data = data; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } int main() { int k = 3; struct Node* arr[k]; arr[0] = createNode(1); arr[0]->next = createNode(3); arr[0]->next->next = createNode(5); arr[0]->next->next->next = createNode(7); arr[1] = createNode(2); arr[1]->next = createNode(4); arr[1]->next->next = createNode(6); arr[1]->next->next->next = createNode(8); arr[2] = createNode(0); arr[2]->next = createNode(9); arr[2]->next->next = createNode(10); arr[2]->next->next->next = createNode(11); struct Node* head = mergeKLists(arr, k); printList(head); return 0; } import java.util.List; import java.util.ArrayList; class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to merge only 2 lists static Node mergeTwo(Node head1, Node head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node dummy = new Node(-1); Node curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != null && head2 != null) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1.data <= head2.data) { curr.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { curr.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } curr = curr.next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != null) { curr.next = head1; } else { curr.next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy.next; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists static Node mergeKLists(List<Node> arr) { // Initialize result as empty Node res = null; // One by one merge all lists with // res and keep updating res for (Node node : arr) res = mergeTwo(res, node); return res; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if(node.next!=null) System.out.print(" -> "); node = node.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { List<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>(); arr.add(new Node(1)); arr.get(0).next = new Node(3); arr.get(0).next.next = new Node(5); arr.get(0).next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.add(new Node(2)); arr.get(1).next = new Node(4); arr.get(1).next.next = new Node(6); arr.get(1).next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.add(new Node(0)); arr.get(2).next = new Node(9); arr.get(2).next.next = new Node(10); arr.get(2).next.next.next = new Node(11); Node head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Function to merge only 2 lists def mergeTwo(head1, head2): # Create a dummy node to simplify # the merging process dummy = Node(-1) curr = dummy # Iterate through both linked lists while head1 is not None and head2 is not None: # Add the smaller node to the merged list if head1.data <= head2.data: curr.next = head1 head1 = head1.next else: curr.next = head2 head2 = head2.next curr = curr.next # If any list is left, append it to # the merged list if head1 is not None: curr.next = head1 else: curr.next = head2 # Return the merged list starting # from the next of dummy node return dummy.next # Function to merge K sorted linked lists def mergeKLists(arr): # Initialize result as empty res = None # One by one merge all lists with # res and keep updating res for node in arr: res = mergeTwo(res, node) return res def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [] node1 = Node(1) node1.next = Node(3) node1.next.next = Node(5) node1.next.next.next = Node(7) arr.append(node1) node2 = Node(2) node2.next = Node(4) node2.next.next = Node(6) node2.next.next.next = Node(8) arr.append(node2) node3 = Node(0) node3.next = Node(9) node3.next.next = Node(10) node3.next.next.next = Node(11) arr.append(node3) head = mergeKLists(arr) printList(head) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node mergeTwo(Node head1, Node head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node dummy = new Node(-1); Node curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != null && head2 != null) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1.data <= head2.data) { curr.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { curr.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } curr = curr.next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != null) { curr.next = head1; } else { curr.next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy.next; } static Node mergeKLists(List<Node> arr) { // Initialize result as empty Node res = null; // One by one merge all lists with // res and keep updating res foreach (Node node in arr) res = mergeTwo(res, node); return res; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ""); if(temp.next!=null) Console.Write(" -> "); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { List<Node> arr = new List<Node>(); Node node1 = new Node(1); node1.next = new Node(3); node1.next.next = new Node(5); node1.next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.Add(node1); Node node2 = new Node(2); node2.next = new Node(4); node2.next.next = new Node(6); node2.next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.Add(node2); Node node3 = new Node(0); node3.next = new Node(9); node3.next.next = new Node(10); node3.next.next.next = new Node(11); arr.Add(node3); Node head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Function to merge only 2 lists function mergeTwo(head1, head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process let dummy = new Node(-1); let curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 !== null && head2 !== null) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1.data <= head2.data) { curr.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { curr.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } curr = curr.next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 !== null) { curr.next = head1; } else { curr.next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy.next; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists function mergeKLists(arr) { // Initialize result as empty let res = null; // One by one merge all lists with // res and keep updating res for (let node of arr) res = mergeTwo(res, node); return res; } function printList(node) { while (node !== null) { console.log(node.data + " "); node = node.next; } } // Driver Code let arr = []; let node1 = new Node(1); node1.next = new Node(3); node1.next.next = new Node(5); node1.next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.push(node1); let node2 = new Node(2); node2.next = new Node(4); node2.next.next = new Node(6); node2.next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.push(node2); let node3 = new Node(0); node3.next = new Node(9); node3.next.next = new Node(10); node3.next.next.next = new Node(11); arr.push(node3); let head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); Output0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11
Time complexity: O(n*k*k), For simplicity, let us assume that every list is of equal size n. In the worst case. we take n + 2n + 3n ..... + k * n time. The sum of this series is n * k * (k + 1) / 2 which is O(n * k * k).
Auxiliary Space: O(1).
[Naive Approach - 2] - By repeatedly selecting the minimum node
The idea is to iterate through all the k head nodes and append the head node with minimum value to the resultant list. Increment the head to next node. Repeat this process until all nodes are processed.
Step by step approach:
- Initialize a dummy head for the resultant list.
- Find the node with the smallest value in all the k lists.
- Increment the current pointer to the next node of the list where the smallest node is found.
- Append the node with smallest value to the resultant list.
- Repeat these steps till all nodes have been used.
C++ #include <iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Function to get node with minimum value Node* getMinNode(vector<Node*> &arr) { Node* mini = nullptr; int index = -1; for (int i=0; i<arr.size(); i++) { // If current list is processed if (arr[i]==nullptr) continue; // If min node is not set or // current head has smaller value. if (mini==nullptr || arr[i]->data<mini->data) { index = i; mini = arr[i]; } } // Increment the head node if (index!=-1) arr[index] = arr[index]->next; return mini; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists Node* mergeKLists(vector<Node*>& arr) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node* dummy = new Node(-1); Node* tail = dummy; Node* mini = getMinNode(arr); // Process all nodes. while (mini != nullptr) { // Append min node to the result. tail->next = mini; tail = mini; // Find the next min node mini = getMinNode(arr); } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy->next; } void printList(Node* node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if(node->next) cout<<" -> "; node = node->next; } } int main() { int k = 3; vector<Node*> arr(k); arr[0] = new Node(1); arr[0]->next = new Node(3); arr[0]->next->next = new Node(5); arr[0]->next->next->next = new Node(7); arr[1] = new Node(2); arr[1]->next = new Node(4); arr[1]->next->next = new Node(6); arr[1]->next->next->next = new Node(8); arr[2] = new Node(0); arr[2]->next = new Node(9); arr[2]->next->next = new Node(10); arr[2]->next->next->next = new Node(11); Node* head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); return 0; } import java.util.List; import java.util.ArrayList; class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to get node with minimum value static Node getMinNode(List<Node> arr) { Node mini = null; int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { // If current list is processed if (arr.get(i) == null) continue; // If min node is not set or // current head has smaller value. if (mini == null || arr.get(i).data < mini.data) { index = i; mini = arr.get(i); } } // Increment the head node if (index != -1) arr.set(index, arr.get(index).next); return mini; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists static Node mergeKLists(List<Node> arr) { Node dummy = new Node(-1); Node tail = dummy; Node mini = getMinNode(arr); // Process all nodes. while (mini != null) { // Append min node to the result. tail.next = mini; tail = mini; // Find the next min node mini = getMinNode(arr); } return dummy.next; } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if(node.next!=null) { System.out.print(" -> "); } node = node.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { List<Node> arr = new ArrayList<>(); arr.add(new Node(1)); arr.get(0).next = new Node(3); arr.get(0).next.next = new Node(5); arr.get(0).next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.add(new Node(2)); arr.get(1).next = new Node(4); arr.get(1).next.next = new Node(6); arr.get(1).next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.add(new Node(0)); arr.get(2).next = new Node(9); arr.get(2).next.next = new Node(10); arr.get(2).next.next.next = new Node(11); Node head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Function to get node with minimum value def getMinNode(arr): mini = None index = -1 for i in range(len(arr)): # If current list is processed if arr[i] is None: continue # If min node is not set or # current head has smaller value. if mini is None or arr[i].data < mini.data: index = i mini = arr[i] # Increment the head node if index != -1: arr[index] = arr[index].next return mini # Function to merge K sorted linked lists def mergeKLists(arr): dummy = Node(-1) tail = dummy mini = getMinNode(arr) # Process all nodes. while mini: # Append min node to the result. tail.next = mini tail = mini # Find the next min node mini = getMinNode(arr) return dummy.next def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [None] * 3 arr[0] = Node(1) arr[0].next = Node(3) arr[0].next.next = Node(5) arr[0].next.next.next = Node(7) arr[1] = Node(2) arr[1].next = Node(4) arr[1].next.next = Node(6) arr[1].next.next.next = Node(8) arr[2] = Node(0) arr[2].next = Node(9) arr[2].next.next = Node(10) arr[2].next.next.next = Node(11) head = mergeKLists(arr) printList(head) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to get node with minimum value static Node getMinNode(List<Node> arr) { Node mini = null; int index = -1; for (int i = 0; i < arr.Count; i++) { // If current list is processed if (arr[i] == null) continue; // If min node is not set or // current head has smaller value. if (mini == null || arr[i].data < mini.data) { index = i; mini = arr[i]; } } // Increment the head node if (index != -1) arr[index] = arr[index].next; return mini; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists static Node mergeKLists(List<Node> arr) { Node dummy = new Node(-1); Node tail = dummy; Node mini = getMinNode(arr); // Process all nodes. while (mini != null) { // Append min node to the result. tail.next = mini; tail = mini; // Find the next min node mini = getMinNode(arr); } return dummy.next; } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ""); if(temp.next!=null) Console.Write(" -> "); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main() { List<Node> arr = new List<Node>(); arr.Add(new Node(1)); arr[0].next = new Node(3); arr[0].next.next = new Node(5); arr[0].next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.Add(new Node(2)); arr[1].next = new Node(4); arr[1].next.next = new Node(6); arr[1].next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.Add(new Node(0)); arr[2].next = new Node(9); arr[2].next.next = new Node(10); arr[2].next.next.next = new Node(11); Node head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Function to get node with minimum value function getMinNode(arr) { let mini = null; let index = -1; for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { // If current list is processed if (arr[i] === null) continue; // If min node is not set or // current head has smaller value. if (mini === null || arr[i].data < mini.data) { index = i; mini = arr[i]; } } // Increment the head node if (index !== -1) arr[index] = arr[index].next; return mini; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists function mergeKLists(arr) { let dummy = new Node(-1); let tail = dummy; let mini = getMinNode(arr); // Process all nodes. while (mini !== null) { // Append min node to the result. tail.next = mini; tail = mini; // Find the next min node mini = getMinNode(arr); } return dummy.next; } function printList(node) { while (node !== null) { process.stdout.write(node.data.toString()); if (node.next !== null) { process.stdout.write(" -> "); } node = node.next; } } let arr = []; arr.push(new Node(1)); arr[0].next = new Node(3); arr[0].next.next = new Node(5); arr[0].next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.push(new Node(2)); arr[1].next = new Node(4); arr[1].next.next = new Node(6); arr[1].next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.push(new Node(0)); arr[2].next = new Node(9); arr[2].next.next = new Node(10); arr[2].next.next.next = new Node(11); let head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); Output0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11
Time complexity: O(n * k2), There are n*k nodes in total (assuming every list has O(n) nodes) and to find the smallest node it takes k times so for the n*k nodes it will take n*k*k time.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
[Expected Approach - 1] - Using Min Heap (Works better for unequal sized lists)
This solution is mainly an optimization over the previous approach. Instead of linearly traversing the array to find the minimum, we use min heap data structure and reduce the time complexity of this operation to O(Log k).
For a more detailed solution and code, refer to article Merge k sorted linked lists Using Min Heap.
Time Complexity: O(n * k * log k) if we have k lists of size O(n) each. We can also say O(n * Log k) where n is the total number of nodes.
Auxiliary Space: O(k)
[Expected Approach - 2] - Using Divide and Conquer (Works better for equal sized lists)
The idea is to use divide and conquer by recursively splitting the k lists into two halves until we have pairs of lists to merge, then merge these pairs using a two-way merge procedure (similar to merge sort's merge step), and continue this process back up through the recursion tree until all lists are merged into a single sorted list.
Step by step approach:
- Split k lists into two parts: lists[0...mid] and lists[mid+1...end].
- Recursively merge the left half of lists to get first sorted list.
- Recursively merge the right half of lists to get second sorted list.
- Merge the above two sorted lists using two-pointer approach.
- Return the final merged sorted list.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Function to merge two sorted lists. Node* mergeTwo(Node* head1, Node* head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node* dummy = new Node(-1); Node* curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != nullptr && head2 != nullptr) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1->data <= head2->data) { curr->next = head1; head1 = head1->next; } else { curr->next = head2; head2 = head2->next; } curr = curr->next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != nullptr) { curr->next = head1; } else { curr->next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy->next; } Node* mergeListsRecur(int i, int j, vector<Node*> &arr) { // If single list is left if (i == j) return arr[i]; // Find the middle of lists int mid = i + (j-i)/2; // Merge lists from i to mid Node* head1 = mergeListsRecur(i, mid, arr); // Merge lists from mid+1 to j Node* head2 = mergeListsRecur(mid+1, j, arr); // Merge the above 2 lists Node* head = mergeTwo(head1, head2); return head; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists Node* mergeKLists(vector<Node*>& arr) { // Base case for 0 lists if (arr.size()==0) return nullptr; return mergeListsRecur(0, arr.size()-1, arr); } void printList(Node* node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if(node->next) cout<<" -> "; node = node->next; } } int main() { int k = 3; vector<Node*> arr(k); arr[0] = new Node(1); arr[0]->next = new Node(3); arr[0]->next->next = new Node(5); arr[0]->next->next->next = new Node(7); arr[1] = new Node(2); arr[1]->next = new Node(4); arr[1]->next->next = new Node(6); arr[1]->next->next->next = new Node(8); arr[2] = new Node(0); arr[2]->next = new Node(9); arr[2]->next->next = new Node(10); arr[2]->next->next->next = new Node(11); Node* head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); return 0; } import java.util.List; class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to merge two sorted lists. static Node mergeTwo(Node head1, Node head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node dummy = new Node(-1); Node curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != null && head2 != null) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1.data <= head2.data) { curr.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { curr.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } curr = curr.next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != null) { curr.next = head1; } else { curr.next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy.next; } static Node mergeListsRecur(int i, int j, List<Node> arr) { // If single list is left if (i == j) return arr.get(i); // Find the middle of lists int mid = i + (j - i) / 2; // Merge lists from i to mid Node head1 = mergeListsRecur(i, mid, arr); // Merge lists from mid+1 to j Node head2 = mergeListsRecur(mid + 1, j, arr); // Merge the above 2 lists Node head = mergeTwo(head1, head2); return head; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists static Node mergeKLists(List<Node> arr) { // Base case for 0 lists if (arr.size() == 0) return null; return mergeListsRecur(0, arr.size() - 1, arr); } static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if(node.next!=null) { System.out.print(" -> "); } node = node.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 3; List<Node> arr = new java.util.ArrayList<>(); arr.add(new Node(1)); arr.get(0).next = new Node(3); arr.get(0).next.next = new Node(5); arr.get(0).next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.add(new Node(2)); arr.get(1).next = new Node(4); arr.get(1).next.next = new Node(6); arr.get(1).next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.add(new Node(0)); arr.get(2).next = new Node(9); arr.get(2).next.next = new Node(10); arr.get(2).next.next.next = new Node(11); Node head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Function to merge two sorted lists. def mergeTwo(head1, head2): # Create a dummy node to simplify # the merging process dummy = Node(-1) curr = dummy # Iterate through both linked lists while head1 is not None and head2 is not None: # Add the smaller node to the merged list if head1.data <= head2.data: curr.next = head1 head1 = head1.next else: curr.next = head2 head2 = head2.next curr = curr.next # If any list is left, append it to # the merged list if head1 is not None: curr.next = head1 else: curr.next = head2 # Return the merged list starting # from the next of dummy node return dummy.next def mergeListsRecur(i, j, arr): # If single list is left if i == j: return arr[i] # Find the middle of lists mid = i + (j - i) // 2 # Merge lists from i to mid head1 = mergeListsRecur(i, mid, arr) # Merge lists from mid+1 to j head2 = mergeListsRecur(mid + 1, j, arr) # Merge the above 2 lists head = mergeTwo(head1, head2) return head # Function to merge K sorted linked lists def mergeKLists(arr): # Base case for 0 lists if len(arr) == 0: return None return mergeListsRecur(0, len(arr) - 1, arr) def printList(node): while node is not None: print(f"{node.data}", end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": k = 3 arr = [None] * k arr[0] = Node(1) arr[0].next = Node(3) arr[0].next.next = Node(5) arr[0].next.next.next = Node(7) arr[1] = Node(2) arr[1].next = Node(4) arr[1].next.next = Node(6) arr[1].next.next.next = Node(8) arr[2] = Node(0) arr[2].next = Node(9) arr[2].next.next = Node(10) arr[2].next.next.next = Node(11) head = mergeKLists(arr) printList(head) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Function to merge two sorted lists. static Node mergeTwo(Node head1, Node head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process Node dummy = new Node(-1); Node curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 != null && head2 != null) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1.data <= head2.data) { curr.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { curr.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } curr = curr.next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 != null) { curr.next = head1; } else { curr.next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy.next; } static Node mergeListsRecur(int i, int j, List<Node> arr) { // If single list is left if (i == j) return arr[i]; // Find the middle of lists int mid = i + (j - i) / 2; // Merge lists from i to mid Node head1 = mergeListsRecur(i, mid, arr); // Merge lists from mid+1 to j Node head2 = mergeListsRecur(mid + 1, j, arr); // Merge the above 2 lists Node head = mergeTwo(head1, head2); return head; } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists static Node mergeKLists(List<Node> arr) { // Base case for 0 lists if (arr.Count == 0) return null; return mergeListsRecur(0, arr.Count - 1, arr); } static void printList(Node head) { Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { Console.Write(temp.data + ""); if(temp.next!=null) Console.Write(" -> "); temp = temp.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { List<Node> arr = new List<Node>(); arr.Add(new Node(1)); arr[0].next = new Node(3); arr[0].next.next = new Node(5); arr[0].next.next.next = new Node(7); arr.Add(new Node(2)); arr[1].next = new Node(4); arr[1].next.next = new Node(6); arr[1].next.next.next = new Node(8); arr.Add(new Node(0)); arr[2].next = new Node(9); arr[2].next.next = new Node(10); arr[2].next.next.next = new Node(11); Node head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Function to merge two sorted lists. function mergeTwo(head1, head2) { // Create a dummy node to simplify // the merging process let dummy = new Node(-1); let curr = dummy; // Iterate through both linked lists while (head1 !== null && head2 !== null) { // Add the smaller node to the merged list if (head1.data <= head2.data) { curr.next = head1; head1 = head1.next; } else { curr.next = head2; head2 = head2.next; } curr = curr.next; } // If any list is left, append it to // the merged list if (head1 !== null) { curr.next = head1; } else { curr.next = head2; } // Return the merged list starting // from the next of dummy node return dummy.next; } function mergeListsRecur(i, j, arr) { // If single list is left if (i === j) return arr[i]; // Find the middle of lists let mid = i + Math.floor((j - i) / 2); // Merge lists from i to mid let head1 = mergeListsRecur(i, mid, arr); // Merge lists from mid+1 to j let head2 = mergeListsRecur(mid + 1, j, arr); // Merge the above 2 lists return mergeTwo(head1, head2); } // Function to merge K sorted linked lists function mergeKLists(arr) { // Base case for 0 lists if (arr.length === 0) return null; return mergeListsRecur(0, arr.length - 1, arr); } function printList(node) { while (node !== null) { process.stdout.write(node.data.toString()); if (node.next !== null) { process.stdout.write(" -> "); } node = node.next; } } // Driver Code let k = 3; let arr = []; arr[0] = new Node(1); arr[0].next = new Node(3); arr[0].next.next = new Node(5); arr[0].next.next.next = new Node(7); arr[1] = new Node(2); arr[1].next = new Node(4); arr[1].next.next = new Node(6); arr[1].next.next.next = new Node(8); arr[2] = new Node(0); arr[2].next = new Node(9); arr[2].next.next = new Node(10); arr[2].next.next.next = new Node(11); let head = mergeKLists(arr); printList(head); Output0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 7 -> 8 -> 9 -> 10 -> 11
Time Complexity: O(n * k * log k), where n is the number of nodes in the longest list.
Auxiliary Space: O(log k), used for recursion.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile