Maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix
Last Updated : 28 Jul, 2025
Given a 2D matrix mat[][] of integers, find the submatrix (i.e., a rectangular section of the matrix) that has the maximum possible sum among all possible submatrices.
Example:
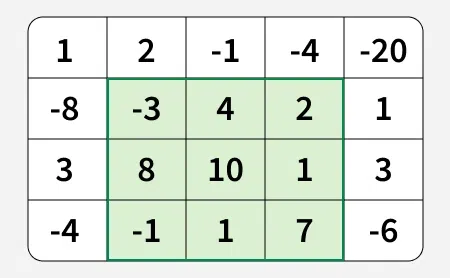
Input: mat[][] = [[1, 2, -1, -4, -20],
[-8, -3, 4, 2, 1],
[3, 8, 10, 1, 3],
[-4, -1, 1, 7, -6]]
Output: 29
Explanation: The matrix is as follows and the green rectangle denotes the maximum sum rectangle which is equal to 29.
This problem is mainly an extension of the Maximum Subarray Sum.
[Naive approach] Iterating Over All Possible Submatrices
We explore all possible rectangles in the given 2D array, by using four variables: two to define the left and right boundaries and two more to define the top and bottom boundaries and calculate their sums, and keep track of the maximum sum found.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <climits> using namespace std; int maxRectSum(vector<vector<int>> &mat) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); int maxSum = INT_MIN; for (int up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (int left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (int down = up; down < n; down++) { for (int right = left; right < m; right++) { // Find the sum of submatrix(up, right, down, left) int sum = 0; for (int i = up; i <= down; i++) { for (int j = left; j <= right; j++) { sum += mat[i][j]; } } // Update maxSum if sum > maxSum. if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; } } } } } return maxSum; } int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = {{1, 2, -1, -4, -20}, {-8, -3, 4, 2, 1}, {3, 8, 10, 1, 3}, {-4, -1, 1, 7, -6}}; cout << maxRectSum(mat) << endl; return 0; } class GfG { static int maxRectSum(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (int left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (int down = up; down < n; down++) { for (int right = left; right < m; right++) { // Find the sum of // submatrix(up, right, down, left) int sum = 0; for (int i = up; i <= down; i++) { for (int j = left; j <= right; j++) { sum += mat[i][j]; } } // Update maxSum if sum > maxSum. if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; } } } } } return maxSum; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 }, { -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 }, { 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 }, { -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } }; System.out.println(maxRectSum(mat)); } } def maxRectSum(mat): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) maxSum = float('-inf') for up in range(n): for left in range(m): for down in range(up, n): for right in range(left, m): # Calculate the sum of submatrix # (up, left, down, right) subMatrixSum = 0 for i in range(up, down + 1): for j in range(left, right + 1): subMatrixSum += mat[i][j] # Update maxSum if a larger sum is found maxSum = max(maxSum, subMatrixSum) return maxSum if __name__ == "__main__": mat = [ [1, 2, -1, -4, -20], [-8, -3, 4, 2, 1], [3, 8, 10, 1, 3], [-4, -1, 1, 7, -6] ] print(maxRectSum(mat)) using System; class GfG { static int maxRectSum(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.Length; int m = mat[0].Length; int maxSum = int.MinValue; for (int up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (int left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (int down = up; down < n; down++) { for (int right = left; right < m; right++) { // Calculate the sum of submatrix // (up, left, down, right) int subMatrixSum = 0; for (int i = up; i <= down; i++) { for (int j = left; j <= right; j++) { subMatrixSum += mat[i][j]; } } // Update maxSum if a larger sum is found maxSum = Math.Max(maxSum, subMatrixSum); } } } } return maxSum; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[][] mat = { new int[] { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 }, new int[] { -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 }, new int[] { 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 }, new int[] { -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } }; Console.WriteLine(maxRectSum(mat)); } } function maxRectSum(mat) { const n = mat.length; const m = mat[0].length; let maxSum = -Infinity; for (let up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (let left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (let down = up; down < n; down++) { for (let right = left; right < m; right++) { // Calculate the sum of submatrix // (up, left, down, right) let subMatrixSum = 0; for (let i = up; i <= down; i++) { for (let j = left; j <= right; j++) { subMatrixSum += mat[i][j]; } } // Update maxSum if a larger sum is // found maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, subMatrixSum); } } } } return maxSum; } // Driver Code const mat = [ [ 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 ], [ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 ], [ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 ], [ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 ] ]; console.log(maxRectSum(mat)); Time Complexity: O((n*m)3), as we iterate over all the boundaries of the rectangle in O((n*m)2) time. For each rectangle, we find its sum in O(n*m) time.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
[Better Approach] Using Prefix Sum
In this approach, we used prefix sum matrix to efficiently compute the sum of any submatrix. We first precompute the prefix sum such that pref[i][j] stores the sum of all elements in the submatrix from the top-left corner (0, 0) to the cell (i, j). This preprocessing allows us to calculate the sum of any arbitrary submatrix in constant time using the inclusion-exclusion principle, thereby eliminating redundant computations and significantly improving performance.
Step by Step Approach:
- Initialize a 2D prefix sum matrix
pref[][] of the same size as the input matrix. - Precompute the prefix sum for each cell : pref[i][j] = matrix[i][j] + pref[i−1][j] + pref[i][j−1] − pref[i−1][j−1] (Handle edges separately to avoid index out-of-bound errors.)
- Iterate over all possible top-left corners
(up, left) and bottom-right corners (down, right) to define submatrices. - For each such submatrix, compute the sum using the prefix sum matrix in constant time: sum = pref[down][right] − pref[up - 1][right] − pref[down][left−1] + pref[up-1][left - 1]
- Track the maximum sum obtained across all submatrices.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <climits> using namespace std; int findSum(int up, int left, int down, int right, vector<vector<int>> &pref) { // Start with the sum of the entire submatrix (0, 0) to (down, right) int sum = pref[down][right]; // Subtract the area to the left of the submatrix, if it exists if (left - 1 >= 0) { sum -= pref[down][left - 1]; } // Subtract the area above the submatrix, if it exists if (up - 1 >= 0) { sum -= pref[up - 1][right]; } // Add back the overlapping area that was subtracted twice if (up - 1 >= 0 && left - 1 >= 0) { sum += pref[up - 1][left - 1]; } return sum; } // function to find the maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix int maxRectSum(vector<vector<int>> &mat) { int n = mat.size(); int m = mat[0].size(); // Initialize the prefix sum matrix vector<vector<int>> pref(n, vector<int>(m, 0)); // Row-wise sum for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { pref[i][j] = mat[i][j]; if (j - 1 >= 0) { pref[i][j] += pref[i][j - 1]; } } } // Column-wise sum for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i - 1 >= 0) { pref[i][j] += pref[i - 1][j]; } } } int maxSum = INT_MIN; for (int up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (int left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (int down = up; down < n; down++) { for (int right = left; right < m; right++) { // Find the sum of submatrix(up, right, down, left) int sum = findSum(up, left, down, right, pref); // Update maxSum if sum > maxSum. if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; } } } } } return maxSum; } int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = {{1, 2, -1, -4, -20}, {-8, -3, 4, 2, 1}, {3, 8, 10, 1, 3}, {-4, -1, 1, 7, -6}}; cout << maxRectSum(mat) << endl; } import java.util.*; class GfG { static int findSum(int up, int left, int down, int right, int[][] pref) { // Start with the sum of the entire submatrix // (0, 0) to (down, right) int sum = pref[down][right]; // Subtract the area to the left of the submatrix, if it exists if (left - 1 >= 0) { sum -= pref[down][left - 1]; } // Subtract the area above the submatrix, if it exists if (up - 1 >= 0) { sum -= pref[up - 1][right]; } // Add back the overlapping area that was subtracted twice if (up - 1 >= 0 && left - 1 >= 0) { sum += pref[up - 1][left - 1]; } return sum; } // function to find the maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix public static int maxRectSum(int[][] mat) { int n = mat.length; int m = mat[0].length; // Initialize the prefix sum matrix int[][] pref = new int[n][m]; // Row-wise sum for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { pref[i][j] = mat[i][j]; if (j - 1 >= 0) { pref[i][j] += pref[i][j - 1]; } } } // Column-wise sum for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i - 1 >= 0) { pref[i][j] += pref[i - 1][j]; } } } // Find the maximum sum rectangle int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (int left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (int down = up; down < n; down++) { for (int right = left; right < m; right++) { // Find the sum of the submatrix // (up, left) to // (down, right) int sum = findSum( up, left, down, right, pref); // Update maxSum if sum > maxSum if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; } } } } } return maxSum; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 }, { -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 }, { 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 }, { -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } }; System.out.println(maxRectSum(mat)); } } def findSum(up, left, down, right, pref): # Start with the sum of the entire submatrix (0, 0) to (down, right) totalSum = pref[down][right] # Subtract the area to the left of the submatrix, if it exists if left - 1 >= 0: totalSum -= pref[down][left - 1] # Subtract the area above the submatrix, if it exists if up - 1 >= 0: totalSum -= pref[up - 1][right] # Add back the overlapping area that was subtracted twice if up - 1 >= 0 and left - 1 >= 0: totalSum += pref[up - 1][left - 1] return totalSum # Function to find the maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix def maxRectSum(mat): n = len(mat) m = len(mat[0]) # Initialize the prefix sum matrix pref = [[0] * m for _ in range(n)] # Row-wise sum for i in range(n): for j in range(m): pref[i][j] = mat[i][j] if j - 1 >= 0: pref[i][j] += pref[i][j - 1] # Column-wise sum for j in range(m): for i in range(n): if i - 1 >= 0: pref[i][j] += pref[i - 1][j] # Find the maximum sum rectangle maxSum = float('-inf') for up in range(n): for left in range(m): for down in range(up, n): for right in range(left, m): totalSum = findSum(up, left, down, right, pref) maxSum = max(maxSum, totalSum) return maxSum if __name__ == "__main__": mat = [ [1, 2, -1, -4, -20], [-8, -3, 4, 2, 1], [3, 8, 10, 1, 3], [-4, -1, 1, 7, -6] ] print(maxRectSum(mat)) using System; class GfG { static int findSum(int up, int left, int down, int right, int[,] pref) { // Start with the sum of the entire submatrix from (0,0) to (down,right) int sum = pref[down, right]; // Subtract the area to the left of the submatrix, if it exists if (left - 1 >= 0) sum -= pref[down, left - 1]; // Subtract the area above the submatrix, if it exists if (up - 1 >= 0) sum -= pref[up - 1, right]; // Add back the overlapping area that was subtracted twice if (up - 1 >= 0 && left - 1 >= 0) sum += pref[up - 1, left - 1]; return sum; } static int maxRectSum(int[,] mat) { int n = mat.GetLength(0); int m = mat.GetLength(1); // Initialize the prefix sum matrix int[,] pref = new int[n, m]; // Compute row-wise prefix sum for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { pref[i, j] = mat[i, j]; if (j - 1 >= 0) pref[i, j] += pref[i, j - 1]; } } // Compute column-wise prefix sum for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i - 1 >= 0) pref[i, j] += pref[i - 1, j]; } } int maxSum = int.MinValue; // Check all possible submatrices for (int up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (int left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (int down = up; down < n; down++) { for (int right = left; right < m; right++) { int totalSum = findSum(up, left, down, right, pref); if (totalSum > maxSum) maxSum = totalSum; } } } } return maxSum; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[,] mat = new int[,] { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 }, { -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 }, { 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 }, { -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } }; Console.WriteLine(maxRectSum(mat)); } } // Function to get the sum of submatrix (r1, c1) to (r2, c2) function findSum(up, left, down, right, pref) { // Start with the sum of the entire submatrix (0, 0) to (down, right) let sum = pref[down][right]; // Subtract the area to the left of the submatrix, if it exists if (left - 1 >= 0) { sum -= pref[down][left - 1]; } // Subtract the area above the submatrix, if it exists if (up - 1 >= 0) { sum -= pref[up - 1][right]; } // Add back the overlapping area that was subtracted twice if (up - 1 >= 0 && left - 1 >= 0) { sum += pref[up - 1][left - 1]; } return sum; } // function to find the maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix function maxRectSum(mat) { const n = mat.length; const m = mat[0].length; // Create and initialize prefix sum matrix const pref = Array.from({ length: n }, () => Array(m).fill(0)); // Row-wise prefix sum for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) { pref[i][j] = mat[i][j]; if (j - 1 >= 0) { pref[i][j] += pref[i][j - 1]; } } } // Column-wise prefix sum for (let j = 0; j < m; j++) { for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { if (i - 1 >= 0) { pref[i][j] += pref[i - 1][j]; } } } let maxSum = -Infinity; // Try all submatrices for (let up = 0; up < n; up++) { for (let left = 0; left < m; left++) { for (let down = up; down < n; down++) { for (let right = left; right < m; right++) { let sum = findSum(up, left, down, right, pref); if (sum > maxSum) { maxSum = sum; } } } } } return maxSum; } // Driver code const mat = [ [ 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 ], [ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 ], [ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 ], [ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 ] ]; console.log(maxRectSum(mat)); // Output: 29 Time Complexity: O((n*m)2)
Auxiliary Space: O(n*m), due to the prefix sum matrix.
[Expected Approach] Using Kadane’s Algorithm
Instead of checking every possible submatrix, we fix two column boundaries: left and right. For each pair of columns, we compress the 2D matrix into a 1D array, where each element represents the sum of rows between the current left and right columns. This 1D array (temp[]) represents the column-wise sum for a fixed column window.
Now, we can apply Kadane’s algorithm on this temp[] array to find the maximum subarray sum, which corresponds to a rectangular submatrix with the maximum sum between columns left and right.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <climits> using namespace std; // Kadane's algorithm to find the maximum sum // subarray in a 1D array int kadane(vector<int>& temp) { int rows = temp.size(); int currSum = 0; int maxSum = INT_MIN; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { currSum += temp[i]; // Update maxSum if the current sum is greater if (maxSum < currSum) { maxSum = currSum; } // If the current sum becomes negative, reset it to 0 if (currSum < 0) { currSum = 0; } } return maxSum; } // Function to find the maximum sum rectangle in a 2D matrix int maxRectSum(vector<vector<int>> &mat) { int rows = mat.size(); int cols = mat[0].size(); int maxSum = INT_MIN; // Initialize a temporary array to store row-wise // sums between left and right boundaries vector<int> temp(rows); // Check for all possible left and right boundaries for (int left = 0; left < cols; left++) { // Reset the temporary array for each new left boundary for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) temp[i] = 0; for (int right = left; right < cols; right++) { // Update the temporary array with the current // column's values for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) { temp[row] += mat[row][right]; } // Find the maximum sum of the subarray for the // current column boundaries int sum = kadane(temp); // Update the maximum sum found so far maxSum = max(maxSum, sum); } } return maxSum; } int main() { vector<vector<int>> mat = {{1, 2, -1, -4, -20}, {-8, -3, 4, 2, 1}, {3, 8, 10, 1, 3}, {-4, -1, 1, 7, -6}}; int res = maxRectSum(mat); cout << res << endl; return 0; } class GfG { // Kadane's algorithm to find the maximum sum subarray // in a 1D array static int kadane(int[] temp) { int rows = temp.length; int currSum = 0; int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { currSum += temp[i]; // Update maxSum if the current sum is greater if (maxSum < currSum) { maxSum = currSum; } // If the current sum becomes negative, reset it // to 0 if (currSum < 0) { currSum = 0; } } return maxSum; } // Function to find the maximum sum rectangle in a 2D // matrix static int maxRectSum(int[][] mat) { int rows = mat.length; int cols = mat[0].length; int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // Initialize a temporary array to store row-wise // sums between left and right boundaries int[] temp = new int[rows]; // Check for all possible left and right boundaries for (int left = 0; left < cols; left++) { // Reset the temporary array for each new left // boundary for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { temp[i] = 0; } for (int right = left; right < cols; right++) { // Update the temporary array with the // current column's values for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) { temp[row] += mat[row][right]; } // Find the maximum sum of the subarray for // the current column boundaries int sum = kadane(temp); // Update the maximum sum found so far maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, sum); } } return maxSum; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] mat = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 }, { -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 }, { 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 }, { -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } }; int res = maxRectSum(mat); System.out.println(res); } } def kadane(temp): rows = len(temp) currSum = 0 maxSum = float('-inf') for i in range(rows): currSum += temp[i] # Update maxSum if the current sum is greater if maxSum < currSum: maxSum = currSum # If the current sum becomes negative, reset it to 0 if currSum < 0: currSum = 0 return maxSum def maxRectSum(mat): rows = len(mat) cols = len(mat[0]) maxSum = float('-inf') # Initialize a temporary array to store row-wise # sums between left and right boundaries temp = [0] * rows # Check for all possible left and right boundaries for left in range(cols): # Reset the temporary array for each new left # boundary temp = [0] * rows for right in range(left, cols): # Update the temporary array with the current # column's values for row in range(rows): temp[row] += mat[row][right] # Find the maximum sum of the subarray for the # current column boundaries sumValue = kadane(temp) # Update the maximum sum found so far maxSum = max(maxSum, sumValue) return maxSum if __name__ == "__main__": mat = [ [1, 2, -1, -4, -20], [-8, -3, 4, 2, 1], [3, 8, 10, 1, 3], [-4, -1, 1, 7, -6] ] res = maxRectSum(mat) print(res) using System; class GfG { // Function to apply Kadane's algorithm to find the // maximum sum subarray static int kadane(int[] temp) { int rows = temp.Length; int currSum = 0; int maxSum = int.MinValue; for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) { currSum += temp[i]; // Update maxSum if the current sum is greater if (maxSum < currSum) { maxSum = currSum; } // If the current sum becomes negative, reset it // to 0 if (currSum < 0) { currSum = 0; } } return maxSum; } // Function to find the maximum sum of submatrix static int maxRectSum(int[, ] mat) { int rows = mat.GetLength(0); int cols = mat.GetLength(1); int maxSum = int.MinValue; // Initialize a temporary array to store row-wise // sums between left and right boundaries int[] temp = new int[rows]; // Check for all possible left and right boundaries for (int left = 0; left < cols; left++) { // Reset the temporary array for each new left // boundary Array.Clear(temp, 0, rows); for (int right = left; right < cols; right++) { // Update the temporary array with the // current column's values for (int row = 0; row < rows; row++) { temp[row] += mat[row, right]; } // Find the maximum sum of the subarray for // the current column boundaries int sumValue = kadane(temp); // Update the maximum sum found so far maxSum = Math.Max(maxSum, sumValue); } } return maxSum; } static void Main() { int[, ] mat = { { 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 }, { -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 }, { 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 }, { -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 } }; int res = maxRectSum(mat); Console.WriteLine(res); } } // Function to apply Kadane's algorithm to find the maximum // sum subarray function kadane(temp) { let rows = temp.length; let currSum = 0; let maxSum = -Infinity; for (let i = 0; i < rows; i++) { currSum += temp[i]; // Update maxSum if the current sum is greater if (maxSum < currSum) { maxSum = currSum; } // If the current sum becomes negative, reset it to // 0 if (currSum < 0) { currSum = 0; } } return maxSum; } // Function to find the maximum sum of submatrix function maxRectSum(mat) { const rows = mat.length; const cols = mat[0].length; let maxSum = -Infinity; // Initialize a temporary array to store row-wise sums // between left and right boundaries let temp = new Array(rows).fill(0); // Check for all possible left and right boundaries for (let left = 0; left < cols; left++) { // Reset the temporary array for each new left // boundary temp.fill(0); for (let right = left; right < cols; right++) { // Update the temporary array with the current // column's values for (let row = 0; row < rows; row++) { temp[row] += mat[row][right]; } // Find the maximum sum of the subarray for the // current column boundaries let sumValue = kadane(temp, rows); // Update the maximum sum found so far maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, sumValue); } } return maxSum; } // Driver Code const mat = [ [ 1, 2, -1, -4, -20 ], [ -8, -3, 4, 2, 1 ], [ 3, 8, 10, 1, 3 ], [ -4, -1, 1, 7, -6 ] ]; const res = maxRectSum(mat); console.log(res); Time complexity: O(n*m2)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile