Insertion in a Binary Tree in level order
Last Updated : 04 Dec, 2025
Given a binary tree and a key, the task is to insert the key into the binary tree at the first position available in level order manner.
Examples:
Input: key = 12

Output:
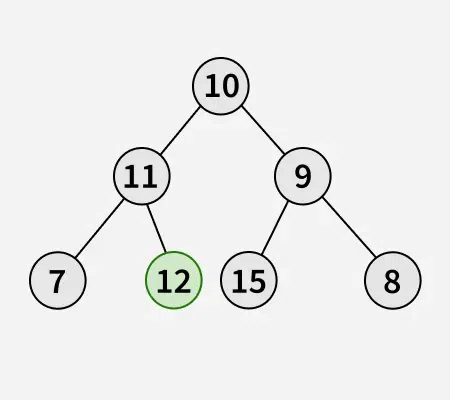
Explanation: Node with value 12 is inserted into the binary tree at the first position available in level order manner.
Approach:
The idea is to do an iterative level order traversal of the given tree using queue. If we find a node whose left child is empty, we make a new key as the left child of the node. Else if we find a node whose right child is empty, we make the new key as the right child. We keep traversing the tree until we find a node whose either left or right child is empty
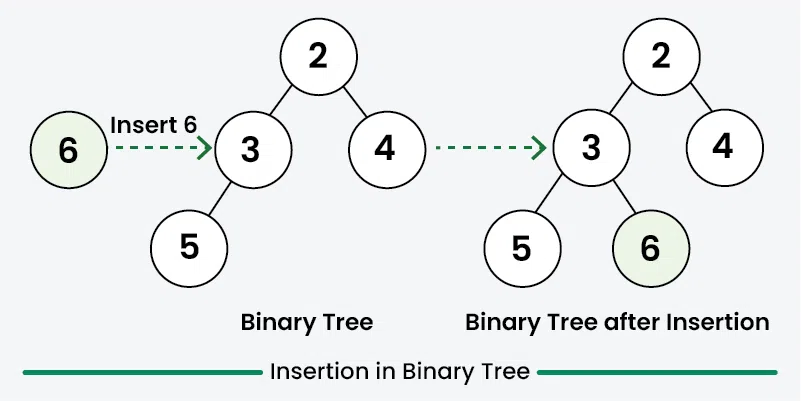
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ program to insert element (in level order) // in Binary Tree #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Function to insert element in binary tree Node* InsertNode(Node* root, int data) { // If the tree is empty, assign new // node address to root if (root == nullptr) { root = new Node(data); return root; } // Else, do level order traversal until we find an empty // place, i.e. either left child or right child of some // node is pointing to NULL. queue<Node*> q; q.push(root); while (!q.empty()) { // Fron a front element in queue Node* curr = q.front(); q.pop(); // First check left if left is null // insert node in left otherwise check for right if (curr->left != nullptr) q.push(curr->left); else { curr->left = new Node(data); return root; } if (curr->right != nullptr) q.push(curr->right); else { curr->right = new Node(data); return root; } } } // Inorder traversal of a binary tree void inorder(Node* curr) { if (curr == nullptr) return; inorder(curr->left); cout << curr->data << ' '; inorder(curr->right); } int main() { // Constructing the binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / / \ // 7 15 8 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(11); root->right = new Node(9); root->left->left = new Node(7); root->right->left = new Node(15); root->right->right = new Node(8); int key = 12; root = InsertNode(root, key); // After insertion 12 in binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / \ / \ // 7 12 15 8 inorder(root); return 0; } // Java program to insert element (in level order) // in Binary Tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to insert element // in binary tree static Node InsertNode(Node root, int data) { // If the tree is empty, assign new node // address to root if (root == null) { root = new Node(data); return root; } // Else, do level order traversal until we find an empty // place, i.e. either left child or right child of some // node is pointing to NULL. Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.add(root); while (!q.isEmpty()) { // Fron a front element in queue Node curr = q.poll(); // First check left if left is null insert // node in left otherwise check for right if (curr.left != null) q.add(curr.left); else { curr.left = new Node(data); return root; } if (curr.right != null) q.add(curr.right); else { curr.right = new Node(data); return root; } } return root; } // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node curr) { if (curr == null) return; inorder(curr.left); System.out.print(curr.data + " "); inorder(curr.right); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Constructing the binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / / \ // 7 15 8 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.right = new Node(9); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); int key = 12; root = InsertNode(root, key); // After insertion 12 in binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / \ / \ // 7 12 15 8 inorder(root); } } # Python program to insert element (in level order) # in Binary Tree from collections import deque class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Function to insert element # in binary tree def InsertNode(root, data): # If the tree is empty, assign new # node address to root if root is None: root = Node(data) return root # Else, do level order traversal until we find an empty # place, i.e. either left child or right child of some # node is pointing to NULL. q = deque() q.append(root) while q: # Fron a front element # in queue curr = q.popleft() # First check left if left is null # insert node in left otherwise check # for right if curr.left is not None: q.append(curr.left) else: curr.left = Node(data) return root if curr.right is not None: q.append(curr.right) else: curr.right = Node(data) return root # Inorder traversal of a binary tree def inorder(curr): if curr is None: return inorder(curr.left) print(curr.data, end=' ') inorder(curr.right) if __name__ == "__main__": # Constructing the binary tree # 10 # / \ # 11 9 # / / \ # 7 15 8 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(11) root.right = Node(9) root.left.left = Node(7) root.right.left = Node(15) root.right.right = Node(8) key = 12 root = InsertNode(root, key) # After insertion 12 in binary tree # 10 # / \ # 11 9 # / \ / \ # 7 12 15 8 inorder(root)
// C# program to insert element (in level order) // in Binary Tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = right = null; } } class GfG { // Function to insert element in binary tree static Node InsertNode(Node root, int data) { // If the tree is empty, assign new node // address to root if (root == null) { root = new Node(data); return root; } // Else, do level order traversal until we find an empty // place, i.e. either left child or right child of some // node is pointing to NULL. Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); q.Enqueue(root); while (q.Count > 0) { // Fron a front element in queue Node curr = q.Dequeue(); // First check left if left is null // insert node in left otherwise check // for right if (curr.left != null) q.Enqueue(curr.left); else { curr.left = new Node(data); return root; } if (curr.right != null) q.Enqueue(curr.right); else { curr.right = new Node(data); return root; } } return root; } // Inorder traversal of a binary tree static void inorder(Node curr) { if (curr == null) return; inorder(curr.left); Console.Write(curr.data + " "); inorder(curr.right); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Constructing the binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / / \ // 7 15 8 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.right = new Node(9); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); int key = 12; root = InsertNode(root, key); // After insertion 12 in binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / \ / \ // 7 12 15 8 inorder(root); } } // JavaScript program to insert element // (in level order) in Binary Tree class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function to insert element in binary tree function InsertNode(root, data) { // If the tree is empty, assign new // node address to root if (root == null) { root = new Node(data); return root; } // Else, do level order traversal until we find an empty // place, i.e. either left child or right child of some // node is pointing to NULL. let q = []; q.push(root); while (q.length > 0) { let curr = q.shift(); // First check left if left is null // insert node in left otherwise check for right if (curr.left !== null) q.push(curr.left); else { curr.left = new Node(data); return root; } if (curr.right !== null) q.push(curr.right); else { curr.right = new Node(data); return root; } } } // Inorder traversal of a binary tree function inorder(curr) { if (curr == null) return; inorder(curr.left); process.stdout.write(curr.data + ' '); inorder(curr.right); } // Constructing the binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / / \ // 7 15 8 let root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(11); root.right = new Node(9); root.left.left = new Node(7); root.right.left = new Node(15); root.right.right = new Node(8); let key = 12; root = InsertNode(root, key); // After insertion 12 in binary tree // 10 // / \ // 11 9 // / \ / \ // 7 12 15 8 inorder(root); Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the number of nodes.
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile