Insert Node at the End of a Linked List
Last Updated : 29 Aug, 2025
Given a head of the linked list, we need to insert a new node at the end of the linked list.
Examples:
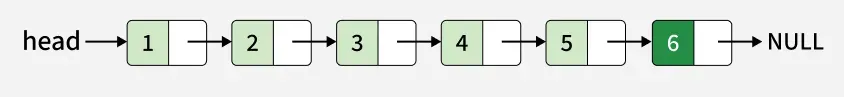
Input: x = 6
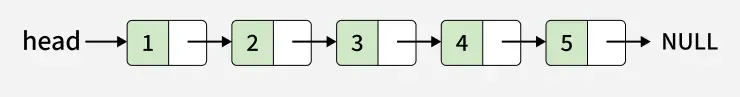
Output: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6
Explanation: We can see that 6 is inserted at the end of the linkedlist.
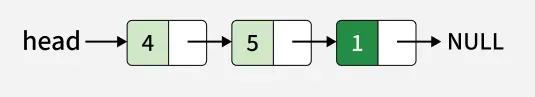
Input: x = 1
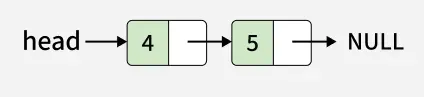
Output: 4 -> 5 -> 1
Explanation: We can see that 1 is inserted at the end of the linked list.
Approach:
Inserting at the end involves traversing the entire list until we reach the last node. We then set the last node's next reference to point to the new node, making the new node the last element in the list.
Following is the approach to add a new node at the end of the linked list:
- Create a new node and set its next pointer as NULL since it will be the last node.
- Store the head reference in a temporary variable
- If the Linked List is empty, make the new node as the head and return
- Else traverse till the last node
- Change the next pointer of the last node to point to the new node
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; // A linked list node class Node { public: int data; Node* next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Given the head of a list and an int, appends // a new node at the end and returns the head. Node* insertAtEnd(Node* head, int x) { // Create a new node Node* newNode = new Node(x); // If the Linked List is empty, make // the new node as the head and return if (head == nullptr) { return newNode; } // Store the head reference in a temporary variable Node* last = head; // Traverse till the last node while (last->next != nullptr) { last = last->next; } // Change the next pointer of the last node // to point to the new node last->next = newNode; // Return the head of the list return head; } // This function prints the contents // of the linked list starting from the head void printList(Node* node) { while (node != nullptr) { cout << node->data; if (node->next != nullptr) { cout << " -> "; } node = node->next; } cout << endl; } int main() { // Create a linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node* head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head = insertAtEnd(head, 6); printList(head); return 0; } // A linked list node class Node { int data; Node next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Given the head of a list and an int, appends // a new node at the end and returns the head. static Node inserAtEnd(Node head, int x) { // Create a new node Node newNode = new Node(x); // If the Linked List is empty, make // the new node as the head and return if (head == null) { return newNode; } // Store the head reference in a temporary variable Node last = head; // Traverse till the last node while (last.next != null) { last = last.next; } // Change the next pointer of the last node // to point to the new node last.next = newNode; // Return the head of the list return head; } // This function prints the contents // of the linked list starting from the head static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data); if (node.next != null) { System.out.print(" -> "); } node = node.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = inserAtEnd(head, 6); printList(head); } } # A linked list node class Node: def __init__(self, x): # Constructor to initialize a new node with data self.data = x self.next = None # Given the head of a list and an int, appends # a new node at the end and returns the head. def insertAtEnd(head, x): # Create a new node newNode = Node(x) # If the Linked List is empty, make # the new node as the head and return if head is None: return newNode # Store the head reference in a temporary variable last = head # Traverse till the last node while last.next is not None: last = last.next # Change the next pointer of the last node # to point to the new node last.next = newNode # Return the head of the list return head # This function prints the contents # of the linked list starting from the head def printList(node): while node is not None: print(node.data, end="") if node.next is not None: print(" -> ", end="") node = node.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head = insertAtEnd(head, 6) printList(head) using System; // A linked list node class Node { public int data; public Node next; // Constructor to initialize a new node with data public Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Given the head of a list and an int, appends // a new node at the end and returns the head. static Node insertAtEnd(Node head, int x) { // Create a new node Node newNode = new Node(x); // If the Linked List is empty, make // the new node as the head and return if (head == null) { return newNode; } // Store the head reference in a temporary variable Node last = head; // Traverse till the last node while (last.next != null) { last = last.next; } // Change the next pointer of the last node // to point to the new node last.next = newNode; // Return the head of the list return head; } // This function prints the contents // of the linked list starting from the head static void printList(Node node) { while (node != null) { Console.Write(node.data); if (node.next != null) { Console.Write(" -> "); } node = node.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = insertAtEnd(head, 6); printList(head); } } // A linked list node class Node { constructor(x) { // Constructor to initialize a new node with data this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Given the head of a list and an int, appends // a new node at the end and returns the head. function insertAtEnd(head, x) { // Create a new node let newNode = new Node(x); // If the Linked List is empty, make // the new node as the head and return if (head === null) { return newNode; } // Store the head reference in a temporary variable let last = head; // Traverse till the last node while (last.next !== null) { last = last.next; } // Change the next pointer of the last node // to point to the new node last.next = newNode; // Return the head of the list return head; } // This function prints the contents // of the linked list starting from the head function printList(node) { while (node !== null) { process.stdout.write(node.data.toString()); if (node.next !== null) { process.stdout.write(" -> "); } node = node.next; } console.log(); } // Driver code function main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head = insertAtEnd(head, 6); printList(head); } main(); Output2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> 6 -> 1
Time Complexity: O(n) where n is the length of the linked list
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile