Insert a node in Linked List before a given node
Last Updated : 16 Sep, 2024
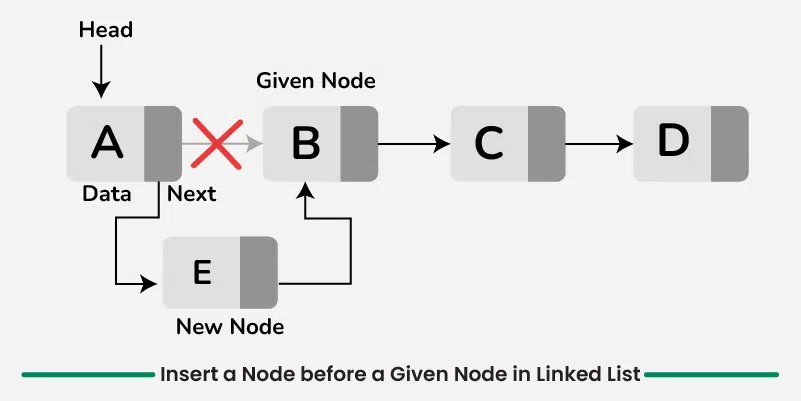
Given a linked list, the task is to insert a new node with a specified value into a linked list before a node with a given key.
Examples
Input: head: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 , newData = 6, key = 2
Output: 1 -> 6 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Explanation: After inserting node with value 6 before (key = 2) of the linked list, the resultant linked list will be: 1 -> 6 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
Input: head: 1 -> 3 -> 2, newData = 9, key = 1
Output: 9 -> 1 -> 3 -> 2
Explanation: After inserting node with value 9 before (key = 1) of the linked list, the resultant linked list will be: 9 -> 1 -> 3 -> 2
[Expected Approach - 1] Using Recursion- O(n) Time and O(n) Space:
The approach involves recursively traversing the linked list to insert a new node before the node with the specified key. The recursive function checks if the current node's data matches the key or not, if it matches it creates a new node with the given value and links this new node before the current node. If the current node does not match the key, the function makes a recursive call to process the next node in the list.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Implementation to insert a node before // a given key recursively #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Recursive function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key Node* insertBeforeKey(Node* head, int key, int newData) { // Base case: if the list is empty if (head == nullptr) { return nullptr; } // If the head's data matches the key, // insert new node if (head->data == key) { Node* new_node = new Node(newData); new_node->next = head; return new_node; } // Recursively call for the next node head->next = insertBeforeKey(head->next, key, newData); return head; } // Function to print the linked list void printList(Node* node) { Node* curr = node; while (curr != nullptr) { cout << curr->data << " "; curr = curr->next; } } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node* head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); return 0; } // C Implementation to insert a node before // a given key recursively #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* createNode(int x); // Recursive function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key struct Node* insertBeforeKey(struct Node* head, int key, int newData) { // Base case: if the list is empty if (head == NULL) { return NULL; } // If head's data matches the key, insert new node if (head->data == key) { struct Node* newNode = createNode(newData); newNode->next = head; return newNode; } // Recursively call insertBeforeKey for the next node head->next = insertBeforeKey(head->next, key, newData); return head; } void printList(struct Node* node) { struct Node* curr = node; while (curr != NULL) { printf("%d ", curr->data); curr = curr->next; } printf("\n"); } struct Node* createNode(int x) { struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = x; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 struct Node* head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); return 0; } // Java Implementation to insert a node before // a given key recursively class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } public class GfG { // Recursive function to insert a new node // with value newData before the node with the key static Node insertBeforeKey(Node head, int key, int newData) { // Base case: if the list is empty if (head == null) { return null; } // If head's data matches the key, insert new node if (head.data == key) { Node newNode = new Node(newData); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } // Recursively call insertBeforeKey for the next node head.next = insertBeforeKey(head.next, key, newData); return head; } static void printList(Node node) { Node curr = node; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + " "); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); } } # Python Implementation to insert a node before # a given key recursively class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Recursive function to insert a new node with value # newData before the node with the given key def insert_before_key(head, key, newData): # Base case: if the list is empty if head is None: return None # If head's data matches the key, insert new node if head.data == key: new_node = Node(newData) new_node.next = head return new_node # Recursively call insert_before_key for the next node head.next = insert_before_key(head.next, key, newData) return head def print_list(node): curr = node while curr is not None: print(curr.data, end=" ") curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a hard-coded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) newData = 6 key = 2 head = insert_before_key(head, key, newData) print_list(head)
// C# Implementation to insert a node before // a given key recursively using System; class Node { public int Data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Recursive function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key static Node InsertBeforeKey(Node head, int key, int newData) { // Base case: if the list is empty if (head == null) { return null; } // If head's data matches the key, insert new node if (head.Data == key) { Node newNode = new Node(newData); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } // Recursively call InsertBeforeKey for the next node head.next = InsertBeforeKey(head.next, key, newData); return head; } static void PrintList(Node node) { Node curr = node; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.Data + " "); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = InsertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); PrintList(head); } } // Javascript Implementation to insert a node before // a given key recursively class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Recursive function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key function insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData) { // Base case: if the list is empty if (head === null) { return null; } // If head's data matches the key, create new node if (head.data === key) { const newNode = new Node(newData); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } // Recursively call insertBeforeKey for the next node head.next = insertBeforeKey(head.next, key, newData); return head; } function printList(node) { let curr = node; let output = ""; while (curr !== null) { output += curr.data + " "; curr = curr.next; } console.log(output.trim()); } // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); let key = 2; let newData = 6; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the list.
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
[Expected Approach - 2] Using Iteration - O(n) Time and O(1) Space:
The approach involves iteratively traversing the linked list to insert a new node before the node with the specified key. If the key is at the head of the list, a new node with the given value is created and set as the new head, with its next pointer linking to the previous head. If the key is not at the head, traverse the list using prev and curr pointers. curr will be used to traverse the nodes one by one while prev tracks the node just before curr. When curr points to the node with the key, insert new node between prev and curr.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Implementation to insert a node before // a given key using iteration #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = nullptr; } }; // Iterative function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key Node* insertBeforeKey(Node* head, int key, int newData) { // If the list is empty if (head == nullptr) { return nullptr; } // Special case: if the key is at the head if (head->data == key) { Node* new_node = new Node(newData); new_node->next = head; return new_node; } // Initialize current and previous pointers Node* curr = head; Node* prev = nullptr; // Traverse the list to find the key while (curr != nullptr && curr->data != key) { prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } // If the key was found if (curr != nullptr) { Node* new_node = new Node(newData); prev->next = new_node; new_node->next = curr; } return head; } void printList(Node* node) { Node* curr = node; while (curr != nullptr) { cout << curr->data << " "; curr = curr->next; } cout << endl; } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node* head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); return 0; } // C Implementation to insert a node before // a given key using iteration #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* createNode(int x); // Iterative function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key struct Node* insertBeforeKey(struct Node* head, int key, int newData) { // Special case: if the key is at the head if (head == NULL) { return NULL; } if (head->data == key) { struct Node* newNode = createNode(newData); newNode->next = head; return newNode; } // Initialize current and previous pointers struct Node* curr = head; struct Node* prev = NULL; // Traverse the list to find the key while (curr != NULL && curr->data != key) { prev = curr; curr = curr->next; } // If the key was found if (curr != NULL) { struct Node* newNode = createNode(newData); prev->next = newNode; newNode->next = curr; } return head; } void printList(struct Node* node) { struct Node* curr = node; while (curr != NULL) { printf("%d ", curr->data); curr = curr->next; } printf("\n"); } struct Node* createNode(int x) { struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); new_node->data = x; new_node->next = NULL; return new_node; } int main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 struct Node* head = createNode(1); head->next = createNode(2); head->next->next = createNode(3); head->next->next->next = createNode(4); head->next->next->next->next = createNode(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); return 0; } // Java Implementation to insert a node before // a given key using iteration class Node { int data; Node next; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; } } public class GfG { // Iterative function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the key static Node insertBeforeKey(Node head, int key, int newData) { // Special case: if the key is at the head if (head == null) { return null; } if (head.data == key) { Node newNode = new Node(newData); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } // Initialize current and previous pointers Node curr = head; Node prev = null; // Traverse the list to find the key while (curr != null && curr.data != key) { prev = curr; curr = curr.next; } // If the key was found if (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(newData); prev.next = newNode; newNode.next = curr; } return head; } static void printList(Node node) { Node curr = node; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.data + " "); curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); } } # Python Implementation to insert a node before # a given key using iteration class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None # Iterative function to insert a new node with value # newData before the node with the given key def insert_before_key(head, key, newData): # Special case: if the key is at the head if head is None: return None # If the head's data matches the key, create # and insert new node as the new head if head.data == key: new_node = Node(newData) new_node.next = head return new_node # Initialize pointers prev = None curr = head # Traverse the list to find the key while curr is not None and curr.data != key: prev = curr curr = curr.next # If the key was found if curr is not None: new_node = Node(newData) prev.next = new_node new_node.next = curr return head def print_list(node): curr = node while curr is not None: print(curr.data, end=" ") curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Create a hard-coded linked list: # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) newData = 6 key = 2 head = insert_before_key(head, key, newData) print_list(head)
// C# Implementation to insert a node before // a given key using iteration using System; class Node { public int Data; public Node next; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = null; } } class GfG { // Iterative function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key static Node InsertBeforeKey(Node head, int key, int newData) { // Special case: if the key is at the head if (head == null) { return null; } // If the head's data matches the key, create // a new node and insert it as the new head if (head.Data == key) { Node newNode = new Node(newData); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } // Initialize pointers Node prev = null; Node curr = head; // Traverse the list to find the key while (curr != null && curr.Data != key) { prev = curr; curr = curr.next; } // If the key was found if (curr != null) { Node newNode = new Node(newData); prev.next = newNode; newNode.next = curr; } return head; } static void PrintList(Node node) { Node curr = node; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.Data + " "); curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main() { // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); int newData = 6; int key = 2; head = InsertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); PrintList(head); } } // Javascript Implementation to insert a node before // a given key using iteration class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.next = null; } } // Iterative function to insert a new node with value // newData before the node with the given key function insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData) { // Special case: if the key is at the head if (head === null) { return null; } // If the head's data matches the key, create // new node and insert it as the new head if (head.data === key) { const newNode = new Node(newData); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } // Initialize pointers let prev = null; let curr = head; // Traverse the list to find the key while (curr !== null && curr.data !== key) { prev = curr; curr = curr.next; } // If the key was found if (curr !== null) { const newNode = new Node(newData); prev.next = newNode; newNode.next = curr; } return head; } function printList(node) { let curr = node; let output = ""; while (curr !== null) { output += curr.data + " "; curr = curr.next; } console.log(output.trim()); } // Create a hard-coded linked list: // 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); let key = 2; let newData = 6; head = insertBeforeKey(head, key, newData); printList(head); Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile