Insert a node at a specific position in a linked list
Last Updated : 02 Sep, 2025
Given a head of singly linked list, a position pos, and val, Insert that data into a linked list at the given position.
Examples:
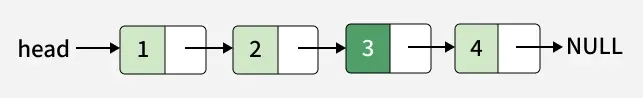
Input: val = 3, pos = 3
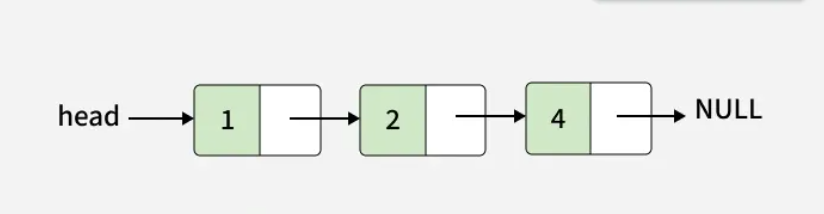
Output: 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
Explanation: Node inserted at position 3.
[Approach] Using Iterative Method - O(n) time and O(1) space:
The idea is simple: create a new node, then find the spot where it should be placed. Walk through the list until you reach the node just before that position. Link the new node’s next to the following node, and adjust the previous node’s next to point to the new node.
Step By Step Implementations:
- Initialize a variable , say curr points to head and allocate the memory to the new node with the given val.
- Traverse the Linked list using curr pointer upto position-1 nodes.
- If curr's next is not null , then next pointer of the new node points to the next of curr node.
- The next pointer of current node points to the new node.
- return the head of linked list.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; class Node { public: int val; Node *next; Node(int x) { val = x; next = nullptr; } }; Node *insertPos(Node *head, int pos, int val) { if (pos < 1) return head; // head will change if pos=1 if (pos == 1) { Node *newNode = new Node(val); newNode->next = head; return newNode; } Node *curr = head; // Traverse to the node that will be // present just before the new node for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1 && curr != nullptr; i++) { curr = curr->next; } // If position is greater than the // number of nodes if (curr == nullptr) return head; Node *newNode = new Node(val); // update the next pointers newNode->next = curr->next; curr->next = newNode; return head; } void printList(Node *head) { Node *curr = head; while (curr != nullptr) { cout << curr->val; if (curr->next != nullptr) { cout << " -> "; } curr = curr->next; } cout << endl; } int main() { // Creating the list 1->2->4 Node *head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(4); int val = 3, pos = 3; head = insertPos(head, pos, val); printList(head); return 0; } class Node { int val; Node next; Node(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node insertPos(Node head, int pos, int val) { if (pos < 1) return head; // head will change if pos=1 if (pos == 1) { Node newNode = new Node(val); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } Node curr = head; // Traverse to the node that will be // present just before the new node for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1 && curr != null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } // If position is greater than the // number of nodes if (curr == null) return head; Node newNode = new Node(val); // update the next pointers newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { System.out.print(curr.val); if (curr.next != null) { System.out.print(" -> "); } curr = curr.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating the list 1->2->4 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(4); int val = 3, pos = 3; head = insertPos(head, pos, val); printList(head); } } class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.val = x self.next = None def insertPos(head, pos, val): if pos < 1: return head # head will change if pos = 1 if pos == 1: newNode = Node(val) newNode.next = head return newNode curr = head # Traverse to the node just before the new node for i in range(1, pos - 1): if curr is None: return head curr = curr.next # If position is greater than number of nodes if curr is None: return head newNode = Node(val) # update the next pointers newNode.next = curr.next curr.next = newNode return head def printList(head): curr = head while curr: print(curr.val, end="") if curr.next: print(" -> ", end="") curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating the list 1->2->4 head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(4) val, pos = 3, 3 head = insertPos(head, pos, val) printList(head) using System; class Node { public int val; public Node next; public Node(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } class GfG { static Node insertPos(Node head, int pos, int val) { if (pos < 1) return head; // head will change if pos = 1 if (pos == 1) { Node newNode = new Node(val); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } Node curr = head; // Traverse to the node just before the new node for (int i = 1; i < pos - 1 && curr != null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } // If position is greater than number of nodes if (curr == null) return head; Node newNode2 = new Node(val); // update the next pointers newNode2.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode2; return head; } static void printList(Node head) { Node curr = head; while (curr != null) { Console.Write(curr.val); if (curr.next != null) { Console.Write(" -> "); } curr = curr.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Creating the list 1->2->4 Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(4); int val = 3, pos = 3; head = insertPos(head, pos, val); printList(head); } } class Node { constructor(x) { this.val = x; this.next = null; } } function insertPos(head, pos, val) { if (pos < 1) return head; // head will change if pos = 1 if (pos === 1) { let newNode = new Node(val); newNode.next = head; return newNode; } let curr = head; // Traverse to the node just before the new node for (let i = 1; i < pos - 1 && curr !== null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } // If position is greater than number of nodes if (curr === null) return head; let newNode = new Node(val); // update the next pointers newNode.next = curr.next; curr.next = newNode; return head; } function printList(head) { let curr = head; while (curr !== null) { process.stdout.write(curr.val.toString()); if (curr.next !== null) { process.stdout.write(" -> "); } curr = curr.next; } console.log(); } // Driver code // Creating the list 1->2->4 let head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(4); let val = 3, pos = 3; head = insertPos(head, pos, val); printList(head);
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile