Balanced Binary Tree or Not
Last Updated : 08 Oct, 2025
Given the root of a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced. A binary tree is considered height-balanced if the absolute difference in heights of the left and right subtrees is at most 1 for every node in the tree.
Examples:
Input:

Output: true
Explanation: The height difference between the left and right subtrees at all nodes is at most 1. Hence, the tree is balanced.
Input:
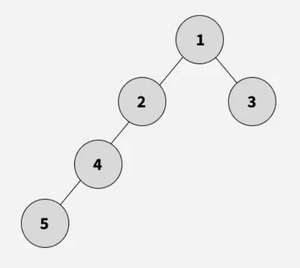
Output: false
Explanation: The height difference between the left and right subtrees at node 2 is 2, which exceeds 1. Hence, the tree is not balanced.
[Naive Approach] By Calculating Height For Each Node - O(n2) Time and O(h) Space
A simple approach is to compute the absolute difference between the heights of the left and right subtrees for each node of the tree using DFS traversal. If, for any node, this absolute difference becomes greater than one, then the entire tree is not height-balanced.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int d) { int data = d; left = right = NULL; } }; // Function to calculate the height of a tree int height(Node* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; // Height = 1 + max of left height and right heights return 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); } // Function to check if the binary tree with given root, is height-balanced bool isBalanced(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return true; // Get the height of left and right sub trees int lHeight = height(root->left); int rHeight = height(root->right); if (abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return false; // Recursively check the left and right subtrees return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); } int main() { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(20); root->right = new Node(30); root->left->left = new Node(40); root->left->right = new Node(60); cout << (isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> // Node structure typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; } Node; // Function to create a new node Node* newNode(int d) { Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); node->data = d; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node; } // Function to calculate the height of a tree int height(Node* node) { if (node == NULL) return 0; // Height = 1 + max of left height and right heights int lHeight = height(node->left); int rHeight = height(node->right); return 1 + (lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight : rHeight); } // Function to check if the binary tree with given root, is height-balanced int isBalanced(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return 1; // Get the height of left and right sub trees int lHeight = height(root->left); int rHeight = height(root->right); if (abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return 0; // Recursively check the left and right subtrees return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right); } int main() { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node* root = newNode(10); root->left = newNode(20); root->right = newNode(30); root->left->left = newNode(40); root->left->right = newNode(60); printf("%s\n", isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); return 0; } // Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; Node(int d) { int data = d; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } class GFG { // Function to calculate the height of a tree static int height(Node node) { if (node == null) return 0; // Height = 1 + max of left height and right heights return 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); } // Function to check if the binary tree with given root // is height-balanced static boolean isBalanced(Node root) { if (root == null) return true; // Get the height of left and right sub trees int lHeight = height(root.left); int rHeight = height(root.right); if (Math.abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return false; // Recursively check the left and right subtrees return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(60); System.out.println(isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); } } # Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, d): self.data = d self.left = None self.right = None # Function to calculate the height of a tree def height(node): if node is None: return 0 # Height = 1 + max of left height and right heights return 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)) # Function to check if the binary tree with given root # is height-balanced def isBalanced(root): if root is None: return True # Get the height of left and right sub trees lHeight = height(root.left) rHeight = height(root.right) if abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1: return False # Recursively check the left and right subtrees return isBalanced(root.left) and isBalanced(root.right) if __name__ == "__main__": # Representation of input BST: # 10 # / \ # 20 30 # / \ # 40 60 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(20) root.right = Node(30) root.left.left = Node(40) root.left.right = Node(60) print("true" if isBalanced(root) else "false") using System; // Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int d) { this.data = d; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } class GFG { // Function to calculate the height of a tree static int height(Node node) { if (node == null) return 0; // Height = 1 + max of left height and right heights return 1 + Math.Max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); } // Function to check if the binary tree // with given root, is height-balanced static bool isBalanced(Node root) { if (root == null) return true; // Get the height of left and right sub trees int lHeight = height(root.left); int rHeight = height(root.right); if (Math.Abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return false; // Recursively check the left and right subtrees return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); } static void Main() { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(60); Console.WriteLine(isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); } } // Node Structure class Node { constructor(d) { this.data = d; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function to calculate the height of a tree function height(node) { if (node === null) return 0; // Height = 1 + max of left height and right heights return 1 + Math.max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); } // Function to check if the binary tree with given root, is height-balanced function isBalanced(root) { if (root === null) return true; // Get the height of left and right sub trees const lHeight = height(root.left); const rHeight = height(root.right); if (Math.abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return false; // Recursively check the left and right subtrees return isBalanced(root.left) && isBalanced(root.right); } // Driver code // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 const root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(60); console.log(isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); [Expected Approach] Using Single Traversal - O(n) Time and O(h) Space
We can optimize by checking balance and calculating height in the same recursion. For each node, check its left and right subtrees. If both are balanced, return the subtree’s height; otherwise, return -1 to show it’s not balanced. This avoids extra height calculations.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node* left; Node* right; Node(int d) { int data = d; left = right = NULL; } }; // Function that returns the height of the tree if the tree is balanced // Otherwise it returns -1. int isBalancedRec(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; // Find Heights of left and right sub trees int lHeight = isBalancedRec(root->left); int rHeight = isBalancedRec(root->right); // If either the subtrees are unbalanced or the absolute difference // of their heights is greater than 1, return -1 if (lHeight == -1 || rHeight == -1 || abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return -1; return max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function to check if tree is height balanced bool isBalanced(Node *root) { return (isBalancedRec(root) > 0); } int main() { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(20); root->right = new Node(30); root->left->left = new Node(40); root->left->right = new Node(60); cout << (isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <math.h> // Node structure typedef struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; } Node; // Function to create a new node Node* newNode(int d) { Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); node->data = d; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node; } // Function that returns the height of the tree if the tree is balanced // Otherwise it returns -1. int isBalancedRec(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; // Find Heights of left and right sub trees int lHeight = isBalancedRec(root->left); int rHeight = isBalancedRec(root->right); // If either the subtrees are unbalanced or the absolute difference // of their heights is greater than 1, return -1 if (lHeight == -1 || rHeight == -1 || abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return -1; return (lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight : rHeight) + 1; } // Function to check if tree is height balanced int isBalanced(Node* root) { return isBalancedRec(root) > 0; } int main() { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node* root = newNode(10); root->left = newNode(20); root->right = newNode(30); root->left->left = newNode(40); root->left->right = newNode(60); printf("%s", isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); return 0; } // Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left; Node right; Node(int d) { this.data = d; left = right = null; } } class GFG { // Function that returns the height of the tree if the tree is balanced // Otherwise it returns -1. static int isBalancedRec(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; // Find Heights of left and right sub trees int lHeight = isBalancedRec(root.left); int rHeight = isBalancedRec(root.right); // If either the subtrees are unbalanced or the absolute difference // of their heights is greater than 1, return -1 if (lHeight == -1 || rHeight == -1 || Math.abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return -1; return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function to check if tree is height balanced static boolean isBalanced(Node root) { return isBalancedRec(root) > 0; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(60); System.out.println(isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); } } # Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, d): self.data = d self.left = None self.right = None # Function that returns the height of the tree if the tree is balanced # Otherwise it returns -1 def isBalancedRec(root): if root is None: return 0 # Find Heights of left and right sub trees lHeight = isBalancedRec(root.left) rHeight = isBalancedRec(root.right) # If either the subtrees are unbalanced or the absolute difference # of their heights is greater than 1, return -1 if lHeight == -1 or rHeight == -1 or abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1: return -1 return max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1 # Function to check if tree is height balanced def isBalanced(root): return isBalancedRec(root) > 0 if __name__ == "__main__": # Representation of input BST: # 10 # / \ # 20 30 # / \ # 40 60 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(20) root.right = Node(30) root.left.left = Node(40) root.left.right = Node(60) print("true" if isBalanced(root) else "false") using System; // Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left; public Node right; public Node(int d) { this.data = d; left = null; right = null; } } class GFG { // Function that returns the height of the tree if the tree is balanced // Otherwise it returns -1 static int isBalancedRec(Node root){ if (root == null) return 0; // Find Heights of left and right sub trees int lHeight = isBalancedRec(root.left); int rHeight = isBalancedRec(root.right); // If either the subtrees are unbalanced or the absolute difference // of their heights is greater than 1, return -1 if (lHeight == -1 || rHeight == -1 || Math.Abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return -1; return Math.Max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function to check if tree is height balanced static bool isBalanced(Node root) { return isBalancedRec(root) > 0; } static void Main() { // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(60); Console.WriteLine(isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false"); } } // Node Structure class Node { constructor(d) { this.data = d; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function that returns the height of the tree if the tree is balanced // Otherwise it returns -1 function isBalancedRec(root) { if (root === null) return 0; // Find Heights of left and right sub trees const lHeight = isBalancedRec(root.left); const rHeight = isBalancedRec(root.right); // If either the subtrees are unbalanced or the absolute difference // of their heights is greater than 1, return -1 if (lHeight === -1 || rHeight === -1 || Math.abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) return -1; return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Function to check if tree is height balanced function isBalanced(root) { return isBalancedRec(root) > 0; } // Driver code // Representation of input BST: // 10 // / \ // 20 30 // / \ // 40 60 const root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(20); root.right = new Node(30); root.left.left = new Node(40); root.left.right = new Node(60); console.log(isBalanced(root) ? "true" : "false");
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile