Minimum in a Binary Search Tree
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree. The task is to find the minimum valued element in this given BST.
Example:
Input:
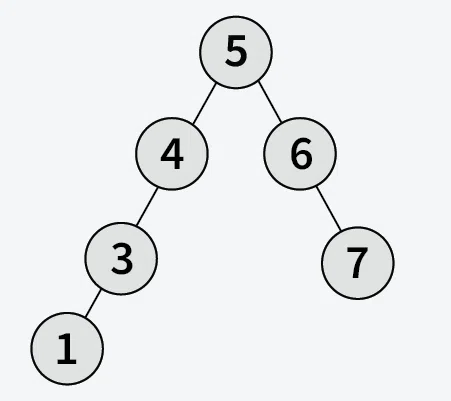
Output: 1
Explanation: The minimum element in the given BST is 1.
Input:
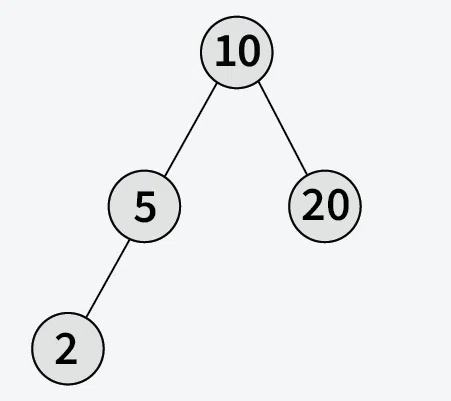
Output: 2
Explanation: The minimum element in the given BST is 2
[Naive Approach] Using Inorder Traversal - O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to use the property of BST which says inorder traversal of a binary search tree always returns the value of nodes in sorted order. So the 1st value in the sorted vector will be the minimum value which is the answer.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ code to find minimum value in BST // using inorder traversal #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = nullptr; } }; // Recursive function to solve and store elements // in a vector void inorder(Node* root, vector<int>& sortedInorder) { // Base Case if (root == nullptr) return; // Traverse left subtree inorder(root->left, sortedInorder); // Store the current node's data sortedInorder.push_back(root->data); // Traverse right subtree inorder(root->right, sortedInorder); } // Function to find the minimum value in BST int minValue(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return -1; } vector<int> sortedInorder; // Call the recursive inorder function inorder(root, sortedInorder); // Return the first element, which is the minimum return sortedInorder[0]; } int main() { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 Node* root = new Node(5); root->left = new Node(4); root->right = new Node(6); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->right->right = new Node(7); root->left->left->left = new Node(1); cout << minValue(root) << "\n"; return 0; } // C code to find minimum value in BST // using inorder traversal #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <limits.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; }; // Recursive function to traverse the tree // and store elements in a vector void inorder(struct Node* root, int *sortedInorder, int *index) { // Base Case if (root == NULL) return; // Traverse left subtree inorder(root->left, sortedInorder, index); // Store the current node's data sortedInorder[(*index)++] = root->data; // Traverse right subtree inorder(root->right, sortedInorder, index); } // Function to find the minimum value in a BST int minValue(struct Node* root) { if (root == NULL) { return -1; } // Create an array to hold inorder elements int sortedInorder[20000]; int index = 0; // Call the recursive inorder function inorder(root, sortedInorder, &index); // Return the first element, which is the minimum return sortedInorder[0]; } struct Node* createNode(int val) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = val; node->left = node->right = NULL; return node; } int main() { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 struct Node* root = createNode(5); root->left = createNode(4); root->right = createNode(6); root->left->left = createNode(3); root->right->right = createNode(7); root->left->left->left = createNode(1); printf("%d\n", minValue(root)); return 0; } // Java code to find minimum value in BST // using inorder traversal import java.util.ArrayList; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { static void inorder(Node root, ArrayList<Integer> sortedInorder) { // Base Case if (root == null) return; // Traverse left subtree inorder(root.left, sortedInorder); // Store the current node's data sortedInorder.add(root.data); // Traverse right subtree inorder(root.right, sortedInorder); } static int minValue(Node root) { if (root == null) { return -1; } // Create an ArrayList to hold inorder elements ArrayList<Integer> sortedInorder = new ArrayList<>(); // Call the recursive inorder function inorder(root, sortedInorder); // Return the first element, which is the minimum return sortedInorder.get(0); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(6); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.right.right = new Node(7); root.left.left.left = new Node(1); System.out.println(minValue(root)); } } # Python code to find minimum value in BST # using inorder traversal class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None def inorder(root, sorted_inorder): # Base Case if root is None: return # Traverse left subtree inorder(root.left, sorted_inorder) # Store the current node's data sorted_inorder.append(root.data) # Traverse right subtree inorder(root.right, sorted_inorder) def minValue(root): if root is None: return -1 # Using a list to hold inorder elements sorted_inorder = [] # Call the recursive inorder function inorder(root, sorted_inorder) # Return the first element, which is the minimum return sorted_inorder[0] if __name__ == "__main__": # Representation of input binary search tree # 5 # / \ # 4 6 # / \ # 3 7 # / # 1 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(4) root.right = Node(6) root.left.left = Node(3) root.right.right = Node(7) root.left.left.left = Node(1) print(minValue(root))
// C# code to find minimum value in BST // using inorder traversal using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { static void Inorder(Node root, List<int> sortedInorder) { // Base Case if (root == null) return; // Traverse left subtree Inorder(root.left, sortedInorder); // Store the current node's data sortedInorder.Add(root.data); // Traverse right subtree Inorder(root.right, sortedInorder); } static int MinValue(Node root) { if (root == null) { return -1; } // Create a list to hold inorder elements List<int> sortedInorder = new List<int>(); // Call the recursive inorder function Inorder(root, sortedInorder); // Return the first element, which is the minimum return sortedInorder[0]; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(6); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.right.right = new Node(7); root.left.left.left = new Node(1); Console.WriteLine(MinValue(root)); } } // JavaScript code to find minimum value in BST // using inorder traversal class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function inorder(root, sortedInorder) { // Base case if (root === null) return; // Traverse left subtree inorder(root.left, sortedInorder); // Store the current node's data sortedInorder.push(root.data); // Traverse right subtree inorder(root.right, sortedInorder); } function minValue(root) { if (root === null) { return -1; } // Create an array to hold inorder elements let sortedInorder = []; // Call the recursive inorder function inorder(root, sortedInorder); // Return the first element, which is the minimum return sortedInorder[0]; } // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(6); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.right.right = new Node(7); root.left.left.left = new Node(1); console.log(minValue(root)); Time Complexity: O(n), since we traversed through all the elements in a BST.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), we are storing all the n nodes in an array.
[Alternate Approach] Using Recursion- O(n) Time and O(n) Space
The idea is to just traverse the node from root to left recursively until left is NULL. The node whose left is NULL is the node with the minimum value. Please refer to Find the node with minimum value in a Binary Search Tree using recursion for implementation.
[Expected Approach] Traversing Only Left Edges - O(h) Time and O(1) Space
The idea is that in a Binary Search Tree (BST), the left child of a node is always smaller than the root. This ensures that the node whose left pointer is NULL must hold the minimum value in the tree. The leftmost node will always contain the smallest element.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ code to find minimum value in BST // using iteration #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = nullptr; } }; int minValue(Node* root) { // base case if (root == nullptr) { return -1; } Node* curr = root; // leftmost node is minimum so we move in BST till // left node is not nullptr while (curr->left != nullptr) { curr = curr->left; } // returning the data at the leftmost node return curr->data; } int main() { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 Node* root = new Node(5); root->left = new Node(4); root->right = new Node(6); root->left->left = new Node(3); root->right->right = new Node(7); root->left->left->left = new Node(1); cout << minValue(root) << "\n"; return 0; } // C code to find minimum value in BST // using iteration #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <limits.h> struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; }; // Function to find minimum value in BST int minValue(struct Node* root) { // base case if (root == NULL) { return -1; } struct Node* curr = root; // leftmost node is minimum, so move // till left is not NULL while (curr->left != NULL) { curr = curr->left; } // returning the data at the leftmost node return curr->data; } struct Node* createNode(int val) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = val; node->left = node->right = NULL; return node; } int main() { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 struct Node* root = createNode(5); root->left = createNode(4); root->right = createNode(6); root->left->left = createNode(3); root->right->right = createNode(7); root->left->left->left = createNode(1); printf("%d\n", minValue(root)); return 0; } // Java code to find minimum value in BST // using iteration class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } public class GfG { public static int minValue(Node root) { // base case if (root == null) { return -1; } Node curr = root; // leftmost node is minimum, so move till // left is not null while (curr.left != null) { curr = curr.left; } // returning the data at the leftmost node return curr.data; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(6); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.right.right = new Node(7); root.left.left.left = new Node(1); System.out.println(minValue(root)); } } # Python code to find minimum value in BST # using using iterationl class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None # Function to find the minimum value in BST def minValue(root): # base case if root is None: return -1 curr = root # leftmost node is minimum, so move # till left is not None while curr.left is not None: curr = curr.left # returning the data at the leftmost node return curr.data if __name__ == "__main__": # Representation of input binary search tree # 5 # / \ # 4 6 # / \ # 3 7 # / # 1 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(4) root.right = Node(6) root.left.left = Node(3) root.right.right = Node(7) root.left.left.left = Node(1) print(minValue(root))
// C# code to find minimum value in BST // using iteration using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = right = null; } } class GfG { static int minValue(Node root) { // base case if (root == null) { return -1; } Node curr = root; // leftmost node is minimum, so move // till left is not null while (curr.left != null) { curr = curr.left; } // returning the data at the leftmost node return curr.data; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(6); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.right.right = new Node(7); root.left.left.left = new Node(1); Console.WriteLine(minValue(root)); } } // Javascript code to find minimum value in BST // using iteration class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Function to find the minimum value in BST function minValue(root) { // base case if (root === null) { return -1; } let curr = root; // leftmost node is minimum, so move till // left is not null while (curr.left !== null) { curr = curr.left; } // returning the data at the leftmost node return curr.data; } // Representation of input binary search tree // 5 // / \ // 4 6 // / \ // 3 7 // / // 1 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(4); root.right = new Node(6); root.left.left = new Node(3); root.right.right = new Node(7); root.left.left.left = new Node(1); // Output the minimum value in the BST console.log(minValue(root)); Time Complexity: O(h), where h is the height of the BST. Worst case happens for left skewed trees, in that case complexity becomes O(n).
Auxiliary Space: O(1), we are not using any extra memory.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem