Maximum Depth or Height of a Binary Tree
Last Updated : 07 Oct, 2025
Given the root of a binary tree, find the maximum depth of the tree.
The maximum depth or height of the tree is the number of edges in the tree from the root to the deepest node.
Examples:
Input:

Output: 2
Explanation: The longest path from the root node to deepest node has 2 edges.
Input:
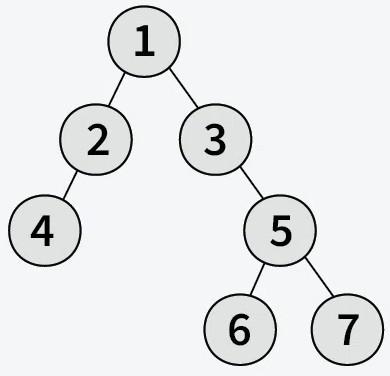
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest path from the root (node 1) to deepest leaf (node 6) has 3 edges.
[Approach 1] Using Recursion
The idea is to recursively compute the height of the left and right subtrees for each node. The height of the current node is then calculated by 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight). The recursion bottoms out when we reach to a null node, which contributes a height of 0.
C++ #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Node structure class Node { public: int data; Node *left; Node *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; int height(Node *root) { if (root == nullptr) return -1; // compute the height of left and right subtrees int lHeight = height(root->left); int rHeight = height(root->right); return max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } int main() { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node *root = new Node(12); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(18); root->left->left = new Node(5); root->left->right = new Node(11); cout << height(root); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Node structure struct Node { int data; struct Node* left; struct Node* right; }; int height(struct Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return -1; // compute the height of left and right subtrees int lHeight = height(root->left); int rHeight = height(root->right); return (lHeight > rHeight ? lHeight : rHeight) + 1; } struct Node* createNode(int val) { struct Node* node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->data = val; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node; } int main() { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 struct Node* root = createNode(12); root->left = createNode(8); root->right = createNode(18); root->left->left = createNode(5); root->left->right = createNode(11); printf("%d\n", height(root)); return 0; } // Node structure class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { static int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return -1; // compute the height of left and right subtrees int lHeight = height(root.left); int rHeight = height(root.right); return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node root = new Node(12); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(18); root.left.left = new Node(5); root.left.right = new Node(11); System.out.println(height(root)); } } # Node structure class Node: def __init__(self, val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None def height(root): if root is None: return -1 # compute the height of left and right subtrees lHeight = height(root.left) rHeight = height(root.right) return max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1 if __name__ == "__main__": # Representation of the input tree: # 12 # / \ # 8 18 # / \ # 5 11 root = Node(12) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(18) root.left.left = Node(5) root.left.right = Node(11) print(height(root))
using System; // Node structure class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { static int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return -1; // compute the height of left and right subtrees int lHeight = height(root.left); int rHeight = height(root.right); return Math.Max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node root = new Node(12); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(18); root.left.left = new Node(5); root.left.right = new Node(11); Console.WriteLine(height(root)); } } // Node structure class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function height(root) { if (root === null) { return -1; } // compute the height of left and right subtrees let lHeight = height(root.left); let rHeight = height(root.right); return Math.max(lHeight, rHeight) + 1; } // Driver Code // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 let root = new Node(12); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(18); root.left.left = new Node(5); root.left.right = new Node(11); console.log(height(root)); Time Complexity: O(n)
Space Complexity: O(n), Recursive stack space
[Approach 2] Level Order Traversal- O(n) Time and O(n) Space
In level order traversal (BFS), we process the tree level by level. At each step, we note the number of nodes in the current level, process exactly those nodes, and enqueue their children. After finishing each level, we increment the depth counter. By the time the queue is empty, the counter reflects the maximum depth or height of the tree.
C++ #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; // Node Structure class Node { public: int data; Node *left, *right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; int height(Node* root) { if (!root) return 0; // Initializing a queue to traverse // the tree level by level queue<Node*> q; q.push(root); int depth = 0; // Loop until the queue is empty while (!q.empty()) { int levelSize = q.size(); // Traverse all nodes at the current level for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) { Node* curr = q.front(); q.pop(); // enqueue their child nodes if (curr->left) q.push(curr->left); if (curr->right) q.push(curr->right); } // Increment depth after traversing each level depth++; } return depth - 1; } int main() { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node *root = new Node(12); root->left = new Node(8); root->right = new Node(18); root->left->left = new Node(5); root->left->right = new Node(11); cout << height(root); return 0; } #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Node Structure struct Node { int data; struct Node *left, *right; } // Function to create a new node Node* newNode(int val) { Node* node = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); node->data = val; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; return node; } // Queue structure struct Queue { Node** arr; int front, rear, size, capacity; } // Function to create a queue Queue* createQueue(int capacity) { Queue* q = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue)); q->capacity = capacity; q->front = 0; q->rear = 0; q->size = 0; q->arr = (Node**)malloc(capacity * sizeof(Node*)); return q; } int isEmpty(Queue* q) { return q->size == 0; } void enqueue(Queue* q, Node* node) { if (q->size == q->capacity) return; q->arr[q->rear] = node; q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % q->capacity; q->size++; } Node* dequeue(Queue* q) { if (isEmpty(q)) return NULL; Node* node = q->arr[q->front]; q->front = (q->front + 1) % q->capacity; q->size--; return node; } int height(Node* root) { if (!root) return 0; // Initializing a queue to traverse // the tree level by level Queue* q = createQueue(100); enqueue(q, root); int depth = 0; // Loop until the queue is empty while (!isEmpty(q)) { int levelSize = q->size; // Traverse all nodes at the current level for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) { Node* curr = dequeue(q); // enqueue their child nodes if (curr->left) enqueue(q, curr->left); if (curr->right) enqueue(q, curr->right); } // Increment depth after traversing each level depth++; } return depth - 1; } int main() { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node *root = newNode(12); root->left = newNode(8); root->right = newNode(18); root->left->left = newNode(5); root->left->right = newNode(11); printf("%d", height(root)); return 0; } import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // Node Structure class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { static int height(Node root) { if (root == null) return 0; // Initializing a queue to traverse // the tree level by level Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.add(root); int depth = 0; // Loop until the queue is empty while (!q.isEmpty()) { int levelSize = q.size(); // Traverse all nodes at the current level for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) { Node curr = q.poll(); if (curr.left != null) q.add(curr.left); if (curr.right != null) q.add(curr.right); } // Increment height after traversing each level depth++; } return depth - 1; } public static void main(String[] args) { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node root = new Node(12); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(18); root.left.left = new Node(5); root.left.right = new Node(11); System.out.println(height(root)); } } from collections import deque # Node Structure class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.left = None self.right = None def height(root): if root is None: return 0 # Initializing a queue to traverse # the tree level by level q = deque([root]) depth = 0 # Loop until the queue is empty while q: levelSize = len(q) # Traverse all nodes at the current level for _ in range(levelSize): curr = q.popleft() if curr.left: q.append(curr.left) if curr.right: q.append(curr.right) # Increment depth after traversing each level depth += 1 return depth - 1 if __name__ == "__main__": # Representation of the input tree: # 12 # / \ # 8 18 # / \ # 5 11 root = Node(12) root.left = Node(8) root.right = Node(18) root.left.left = Node(5) root.left.right = Node(11) print(height(root))
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Node Structure class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { static int height(Node root) { if (root == null) { return 0; } // Initializing a queue to traverse // the tree level by level Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); q.Enqueue(root); int depth = 0; // Loop until the queue is empty while (q.Count > 0) { int levelSize = q.Count; // Traverse all nodes at the current level for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) { Node curr = q.Dequeue(); if (curr.left != null) { q.Enqueue(curr.left); } if (curr.right != null) { q.Enqueue(curr.right); } } // Increment depth after traversing // a level depth++; } return depth - 1; } static void Main(string[] args) { // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 Node root = new Node(12); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(18); root.left.left = new Node(5); root.left.right = new Node(11); Console.WriteLine(height(root)); } } // Node Structure class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } function height(root) { if (root === null) { return 0; } // Initializing a queue to traverse // the tree level by level let queue = [root]; let depth = 0; // Loop until the queue is empty while (queue.length > 0) { let levelSize = queue.length; // Traverse all nodes at the current level for (let i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) { let curr = queue.shift(); if (curr.left) { queue.push(curr.left); } if (curr.right) { queue.push(curr.right); } } // Increment depth after traversing a level depth++; } return depth - 1; } //Driver Code // Representation of the input tree: // 12 // / \ // 8 18 // / \ // 5 11 let root = new Node(12); root.left = new Node(8); root.right = new Node(18); root.left.left = new Node(5); root.left.right = new Node(11); console.log(height(root));
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile