Eulerian path and circuit for undirected graph
Last Updated : 08 Jun, 2025
Given an undirected connected graph with v nodes, and e edges, with adjacency list adj. We need to write a function that returns 2 if the graph contains an eulerian circuit or cycle, else if the graph contains an eulerian path, returns 1, otherwise, returns 0.
A graph is said to be Eulerian if it contains an Eulerian Cycle, a cycle that visits every edge exactly once and starts and ends at the same vertex.
If a graph contains an Eulerian Path, a path that visits every edge exactly once but starts and ends at different vertices, it is called Semi-Eulerian.
Examples:
Input:
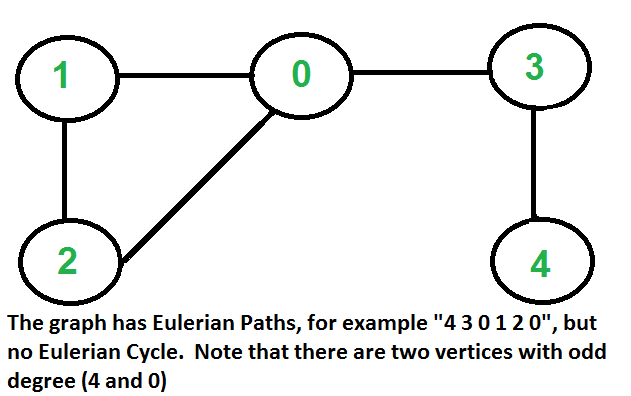
Output: 1
Input:
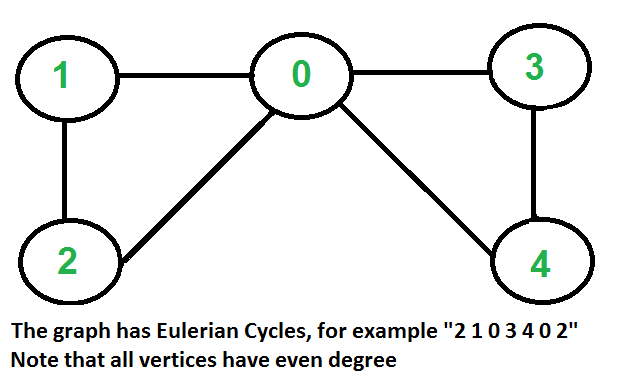
Output: 2
Input:
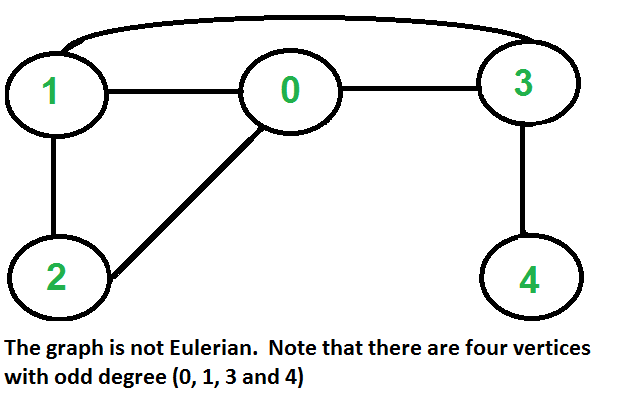
Output: 0
The problem can be framed as follows: "Is it possible to draw a graph without lifting your pencil from the paper and without retracing any edge?"
At first glance, this may seem similar to the Hamiltonian Path problem, which is NP-complete for general graphs. However, determining whether a graph has an Eulerian Path or Cycle is much more efficient: It can be solved in O(v + e) time.
Approach:
The idea is to use some key properties of undirected graphs that help determine whether they are Eulerian (i.e., contain an Eulerian Path or Cycle) or not.
Eulerian Cycle
A graph has an Eulerian Cycle if and only if the below two conditions are true
- All vertices with non-zero degree are part of a single connected component. (We ignore isolated vertices— those with zero degree — as they do not affect the cycle.)
- Every vertex in the graph has an even degree.
Eulerian Path
A graph has an Eulerian Path if and only if the below two conditions are true
- All vertices with non-zero degree must belong to the same connected component. (Same as Eulerian Cycle)
- Exactly Zero or Two Vertices with Odd Degree:
- If zero vertices have odd degree → Eulerian Cycle exists (which is also a path).
- If two vertices have odd degree → Eulerian Path exists (but not a cycle).
- If one vertex has odd degree → Not possible in an undirected graph. (Because the sum of all degrees in an undirected graph is always even.)
Note: A graph with no edges is trivially Eulerian. There are no edges to traverse, so by definition, it satisfies both Eulerian Path and Cycle conditions.
How Does This Work?
- In an Eulerian Path, whenever we enter a vertex (except start and end), we must also leave it. So all intermediate vertices must have even degree.
- In an Eulerian Cycle, since we start and end at the same vertex, every vertex must have even degree. This ensures that every entry into a vertex can be paired with an exit.
Steps to implement the above idea:
- Create an adjacency list to represent the graph and initialize a visited array for DFS traversal.
- Perform DFS starting from the first vertex having non-zero degree to check graph connectivity.
- After DFS, ensure all non-zero degree vertices were visited to confirm the graph is connected.
- Count the number of vertices with odd degree to classify the graph as Eulerian or not.
- If all degrees are even, the graph has an Eulerian Circuit; if exactly two are odd, it's a Path.
- If more than two vertices have odd degree or graph isn't connected, it's not Eulerian.
- Return 2 for Circuit, 1 for Path, and 0 when graph fails Eulerian conditions.
C++ // C++ program to check whether a graph is // Eulerian Path, Eulerian Circuit, or neither #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // DFS to check connectivity, excluding zero-degree vertices void dfs(int node, vector<int> adj[], vector<bool> &visited) { visited[node] = true; for (int neighbor : adj[node]) { if (!visited[neighbor]) { dfs(neighbor, adj, visited); } } } // Function to check Eulerian Path or Circuit int isEulerCircuit(int v, vector<int> adj[]) { vector<bool> visited(v, false); // Find first vertex with non-zero degree int start = -1; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].size() > 0) { start = i; break; } } // No edges: graph is trivially Eulerian if (start == -1) { return 2; } // DFS from the first non-zero degree vertex dfs(start, adj, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].size() > 0 && !visited[i]) { return 0; // Not connected } } // Count vertices with odd degree int odd = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].size() % 2 != 0) { odd++; } } // Apply Eulerian rules if (odd == 0) { return 2; } else if (odd == 2) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } // Driver code int main() { int v = 5; vector<int> adj[5] = {{1, 2, 3}, {0, 2}, {1, 0}, {0, 4}, {3}}; cout << isEulerCircuit(v, adj); return 0; } // Java program to check whether a graph is // Eulerian Path, Eulerian Circuit, or neither import java.util.*; class GfG { // DFS to check connectivity, excluding zero-degree vertices static void dfs(int node, List<Integer>[] adj, boolean[] visited) { visited[node] = true; for (int neighbor : adj[node]) { if (!visited[neighbor]) { dfs(neighbor, adj, visited); } } } // Function to check Eulerian Path or Circuit static int isEulerCircuit(int v, List<Integer>[] adj) { boolean[] visited = new boolean[v]; // Find first vertex with non-zero degree int start = -1; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].size() > 0) { start = i; break; } } // No edges: graph is trivially Eulerian if (start == -1) { return 2; } // DFS from the first non-zero degree vertex dfs(start, adj, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].size() > 0 && !visited[i]) { return 0; // Not connected } } // Count vertices with odd degree int odd = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].size() % 2 != 0) { odd++; } } // Apply Eulerian rules if (odd == 0) { return 2; } else if (odd == 2) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int v = 5; List<Integer>[] adj = new ArrayList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { adj[i] = new ArrayList<>(); } adj[0].addAll(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3)); adj[1].addAll(Arrays.asList(0, 2)); adj[2].addAll(Arrays.asList(1, 0)); adj[3].addAll(Arrays.asList(0, 4)); adj[4].addAll(Arrays.asList(3)); System.out.println(isEulerCircuit(v, adj)); } } # Python program to check whether a graph is # Eulerian Path, Eulerian Circuit, or neither # DFS to check connectivity, excluding zero-degree vertices def dfs(node, adj, visited): visited[node] = True for neighbor in adj[node]: if not visited[neighbor]: dfs(neighbor, adj, visited) # Function to check Eulerian Path or Circuit def isEulerCircuit(v, adj): visited = [False] * v # Find first vertex with non-zero degree start = -1 for i in range(v): if len(adj[i]) > 0: start = i break # No edges: graph is trivially Eulerian if start == -1: return 2 # DFS from the first non-zero degree vertex dfs(start, adj, visited) # Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected for i in range(v): if len(adj[i]) > 0 and not visited[i]: return 0 # Not connected # Count vertices with odd degree odd = 0 for i in range(v): if len(adj[i]) % 2 != 0: odd += 1 # Apply Eulerian rules if odd == 0: return 2 elif odd == 2: return 1 else: return 0 if __name__ == "__main__": v = 5 adj = [ [1, 2, 3], [0, 2], [1, 0], [0, 4], [3] ] print(isEulerCircuit(v, adj))
// C# program to check whether a graph is // Eulerian Path, Eulerian Circuit, or neither using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // DFS to check connectivity, excluding zero-degree vertices static void dfs(int node, List<int>[] adj, bool[] visited) { visited[node] = true; foreach (int neighbor in adj[node]) { if (!visited[neighbor]) { dfs(neighbor, adj, visited); } } } // Function to check Eulerian Path or Circuit static int isEulerCircuit(int v, List<int>[] adj) { bool[] visited = new bool[v]; // Find first vertex with non-zero degree int start = -1; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].Count > 0) { start = i; break; } } // No edges: graph is trivially Eulerian if (start == -1) { return 2; } // DFS from the first non-zero degree vertex dfs(start, adj, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].Count > 0 && !visited[i]) { return 0; // Not connected } } // Count vertices with odd degree int odd = 0; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].Count % 2 != 0) { odd++; } } // Apply Eulerian rules if (odd == 0) { return 2; } else if (odd == 2) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } static void Main() { int v = 5; List<int>[] adj = new List<int>[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) { adj[i] = new List<int>(); } adj[0].AddRange(new int[] {1, 2, 3}); adj[1].AddRange(new int[] {0, 2}); adj[2].AddRange(new int[] {1, 0}); adj[3].AddRange(new int[] {0, 4}); adj[4].AddRange(new int[] {3}); Console.WriteLine(isEulerCircuit(v, adj)); } } // JavaScript program to check whether a graph is // Eulerian Path, Eulerian Circuit, or neither // DFS to check connectivity, excluding zero-degree vertices function dfs(node, adj, visited) { visited[node] = true; for (let neighbor of adj[node]) { if (!visited[neighbor]) { dfs(neighbor, adj, visited); } } } // Function to check Eulerian Path or Circuit function isEulerCircuit(v, adj) { let visited = new Array(v).fill(false); // Find first vertex with non-zero degree let start = -1; for (let i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].length > 0) { start = i; break; } } // No edges: graph is trivially Eulerian if (start === -1) { return 2; } // DFS from the first non-zero degree vertex dfs(start, adj, visited); // Check if all non-zero degree vertices are connected for (let i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].length > 0 && !visited[i]) { return 0; // Not connected } } // Count vertices with odd degree let odd = 0; for (let i = 0; i < v; i++) { if (adj[i].length % 2 !== 0) { odd++; } } // Apply Eulerian rules if (odd === 0) { return 2; } else if (odd === 2) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } // Driver Code let v = 5; let adj = [ [1, 2, 3], [0, 2], [1, 0], [0, 4], [3] ]; console.log(isEulerCircuit(v, adj)); Time Complexity: O(v + e), DFS traverses all vertices and edges to check connectivity and degree.
Space Complexity: O(v + e), Space used for visited array and adjacency list to represent graph.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile