Detect Cycle in a Directed Graph using BFS
Last Updated : 28 Jul, 2022
Given a directed graph, check whether the graph contains a cycle or not. Your function should return true if the given graph contains at least one cycle, else return false. For example, the following graph contains two cycles 0->1->2->3->0 and 2->4->2, so your function must return true.
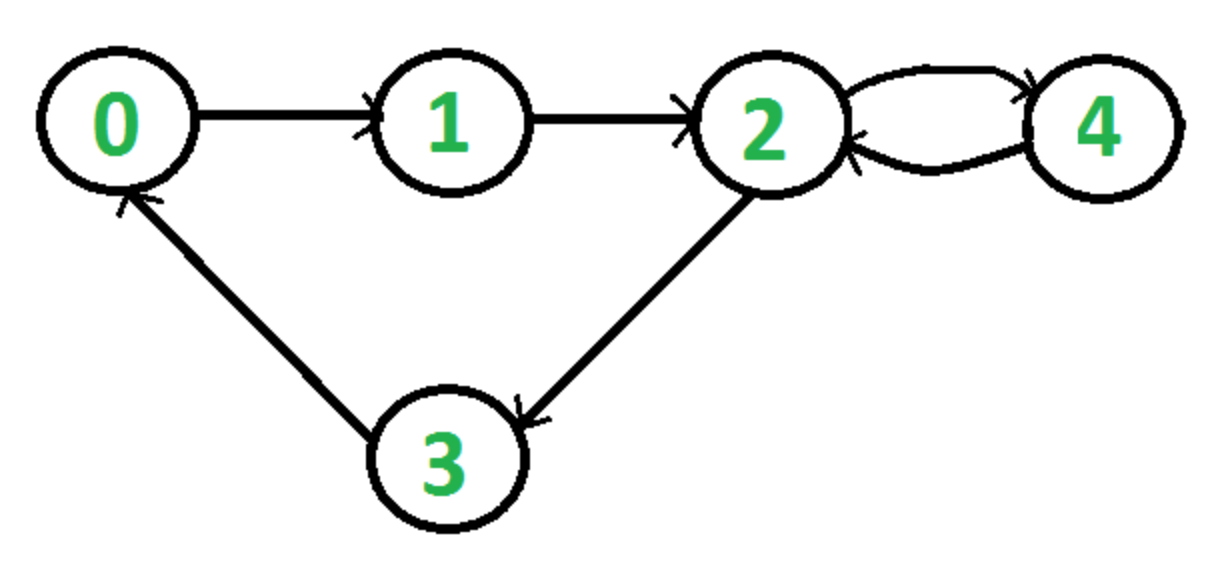
We have discussed a DFS based solution to detect cycle in a directed graph. In this post, BFS based solution is discussed.
The idea is to simply use Kahn's algorithm for Topological Sorting
Steps involved in detecting cycle in a directed graph using BFS.
Step-1: Compute in-degree (number of incoming edges) for each of the vertex present in the graph and initialize the count of visited nodes as 0.
Step-2: Pick all the vertices with in-degree as 0 and add them into a queue (Enqueue operation)
Step-3: Remove a vertex from the queue (Dequeue operation) and then.
- Increment count of visited nodes by 1.
- Decrease in-degree by 1 for all its neighboring nodes.
- If in-degree of a neighboring nodes is reduced to zero, then add it to the queue.
Step 4: Repeat Step 3 until the queue is empty.
Step 5: If count of visited nodes is not equal to the number of nodes in the graph has cycle, otherwise not.
How to find in-degree of each node?
There are 2 ways to calculate in-degree of every vertex:
Take an in-degree array which will keep track of
1) Traverse the array of edges and simply increase the counter of the destination node by 1.
for each node in Nodes indegree[node] = 0; for each edge(src,dest) in Edges indegree[dest]++
Time Complexity: O(V+E)
2) Traverse the list for every node and then increment the in-degree of all the nodes connected to it by 1.
for each node in Nodes If (list[node].size()!=0) then for each dest in list indegree[dest]++;
Time Complexity: The outer for loop will be executed V number of times and the inner for loop will be executed E number of times, Thus overall time complexity is O(V+E).
The overall time complexity of the algorithm is O(V+E)
C++ // A C++ program to check if there is a cycle in // directed graph using BFS. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Class to represent a graph class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices' // Pointer to an array containing adjacency list list<int>* adj; public: Graph(int V); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge(int u, int v); // Returns true if there is a cycle in the graph // else false. bool isCycle(); }; Graph::Graph(int V) { this->V = V; adj = new list<int>[V]; } void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v) { adj[u].push_back(v); } // This function returns true if there is a cycle // in directed graph, else returns false. bool Graph::isCycle() { // Create a vector to store indegrees of all // vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0. vector<int> in_degree(V, 0); // Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees of // vertices. This step takes O(V+E) time for (int u = 0; u < V; u++) { for (auto v : adj[u]) in_degree[v]++; } // Create an queue and enqueue all vertices with // indegree 0 queue<int> q; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) if (in_degree[i] == 0) q.push(i); // Initialize count of visited vertices // 1 For src Node int cnt = 1; // Create a vector to store result (A topological // ordering of the vertices) vector<int> top_order; // One by one dequeue vertices from queue and enqueue // adjacents if indegree of adjacent becomes 0 while (!q.empty()) { // Extract front of queue (or perform dequeue) // and add it to topological order int u = q.front(); q.pop(); top_order.push_back(u); // Iterate through all its neighbouring nodes // of dequeued node u and decrease their in-degree // by 1 list<int>::iterator itr; for (itr = adj[u].begin(); itr != adj[u].end(); itr++) // If in-degree becomes zero, add it to queue if (--in_degree[*itr] == 0) { q.push(*itr); //while we are pushing elements to the queue we will incrementing the cnt cnt++; } } // Check if there was a cycle if (cnt != V) return true; else return false; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(1, 2); g.addEdge(2, 0); g.addEdge(3, 4); g.addEdge(4, 5); if (g.isCycle()) cout << "Yes"; else cout << "No"; return 0; } // Java program to check if there is a cycle in // directed graph using BFS. import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Class to represent a graph static class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices' // Pointer to an array containing adjacency list Vector<Integer>[] adj; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Graph(int V) { // Constructor this.V = V; this.adj = new Vector[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) adj[i] = new Vector<>(); } // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge(int u, int v) { adj[u].add(v); } // Returns true if there is a cycle in the graph // else false. // This function returns true if there is a cycle // in directed graph, else returns false. boolean isCycle() { // Create a vector to store indegrees of all // vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0. int[] in_degree = new int[this.V]; Arrays.fill(in_degree, 0); // Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees of // vertices. This step takes O(V+E) time for (int u = 0; u < V; u++) { for (int v : adj[u]) in_degree[v]++; } // Create an queue and enqueue all vertices with // indegree 0 Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>(); for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) if (in_degree[i] == 0) q.add(i); // Initialize count of visited vertices int cnt = 0; // Create a vector to store result (A topological // ordering of the vertices) Vector<Integer> top_order = new Vector<>(); // One by one dequeue vertices from queue and enqueue // adjacents if indegree of adjacent becomes 0 while (!q.isEmpty()) { // Extract front of queue (or perform dequeue) // and add it to topological order int u = q.poll(); top_order.add(u); // Iterate through all its neighbouring nodes // of dequeued node u and decrease their in-degree // by 1 for (int itr : adj[u]) if (--in_degree[itr] == 0) q.add(itr); cnt++; } // Check if there was a cycle if (cnt != this.V) return true; else return false; } } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g = new Graph(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(1, 2); g.addEdge(2, 0); g.addEdge(3, 4); g.addEdge(4, 5); if (g.isCycle()) System.out.println("Yes"); else System.out.println("No"); } } // This code is contributed by // sanjeev2552 # A Python3 program to check if there is a cycle in # directed graph using BFS. import math import sys from collections import defaultdict # Class to represent a graph class Graph: def __init__(self,vertices): self.graph=defaultdict(list) self.V=vertices # No. of vertices' # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self,u,v): self.graph[u].append(v) # This function returns true if there is a cycle # in directed graph, else returns false. def isCycleExist(n,graph): # Create a vector to store indegrees of all # vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0. in_degree=[0]*n # Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees of # vertices. This step takes O(V+E) time for i in range(n): for j in graph[i]: in_degree[j]+=1 # Create an queue and enqueue all vertices with # indegree 0 queue=[] for i in range(len(in_degree)): if in_degree[i]==0: queue.append(i) # Initialize count of visited vertices cnt=0 # One by one dequeue vertices from queue and enqueue # adjacents if indegree of adjacent becomes 0 while(queue): # Extract front of queue (or perform dequeue) # and add it to topological order nu=queue.pop(0) # Iterate through all its neighbouring nodes # of dequeued node u and decrease their in-degree # by 1 for v in graph[nu]: in_degree[v]-=1 # If in-degree becomes zero, add it to queue if in_degree[v]==0: queue.append(v) cnt+=1 # Check if there was a cycle if cnt==n: return False else: return True # Driver program to test above functions if __name__=='__main__': # Create a graph given in the above diagram g=Graph(6) g.addEdge(0,1) g.addEdge(1,2) g.addEdge(2,0) g.addEdge(3,4) g.addEdge(4,5) if isCycleExist(g.V,g.graph): print("Yes") else: print("No") # This Code is Contributed by Vikash Kumar 37 // C# program to check if there is a cycle in // directed graph using BFS. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG{ // Class to represent a graph public class Graph { // No. of vertices' public int V; // Pointer to an array containing // adjacency list public List<int>[] adj; public Graph(int V) { // Constructor this.V = V; this.adj = new List<int>[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) adj[i] = new List<int>(); } // Function to add an edge to graph public void addEdge(int u, int v) { adj[u].Add(v); } // Returns true if there is a cycle in the // graph else false. // This function returns true if there is // a cycle in directed graph, else returns // false. public bool isCycle() { // Create a vector to store indegrees of all // vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0. int[] in_degree = new int[this.V]; // Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees // of vertices. This step takes O(V+E) time for(int u = 0; u < V; u++) { foreach(int v in adj[u]) in_degree[v]++; } // Create an queue and enqueue all // vertices with indegree 0 Queue<int> q = new Queue<int>(); for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) if (in_degree[i] == 0) q.Enqueue(i); // Initialize count of visited vertices int cnt = 0; // Create a vector to store result // (A topological ordering of the // vertices) List<int> top_order = new List<int>(); // One by one dequeue vertices from // queue and enqueue adjacents if // indegree of adjacent becomes 0 while (q.Count != 0) { // Extract front of queue (or perform // dequeue) and add it to topological // order int u = q.Peek(); q.Dequeue(); top_order.Add(u); // Iterate through all its neighbouring // nodes of dequeued node u and decrease // their in-degree by 1 foreach(int itr in adj[u]) if (--in_degree[itr] == 0) q.Enqueue(itr); cnt++; } // Check if there was a cycle if (cnt != this.V) return true; else return false; } } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g = new Graph(6); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(1, 2); g.addEdge(2, 0); g.addEdge(3, 4); g.addEdge(4, 5); if (g.isCycle()) Console.WriteLine("Yes"); else Console.WriteLine("No"); } } // This code is contributed by Princi Singh <script> // JavaScript program to check if there is a cycle in // directed graph using BFS. // Class to represent a graph // No. of vertices' var V = 0; // Pointer to an array containing // adjacency list var adj ; function initialize(v) { // Constructor V = v; adj = Array.from(Array(V), ()=>Array(V)); } // Function to add an edge to graph function addEdge(u, v) { adj[u].push(v); } // Returns true if there is a cycle in the // graph else false. // This function returns true if there is // a cycle in directed graph, else returns // false. function isCycle() { // Create a vector to store indegrees of all // vertices. Initialize all indegrees as 0. var in_degree = Array(V).fill(0); // Traverse adjacency lists to fill indegrees // of vertices. This step takes O(V+E) time for(var u = 0; u < V; u++) { for(var v of adj[u]) in_degree[v]++; } // Create an queue and enqueue all // vertices with indegree 0 var q = []; for(var i = 0; i < V; i++) if (in_degree[i] == 0) q.push(i); // Initialize count of visited vertices var cnt = 0; // Create a vector to store result // (A topological ordering of the // vertices) var top_order = []; // One by one dequeue vertices from // queue and enqueue adjacents if // indegree of adjacent becomes 0 while (q.length != 0) { // Extract front of queue (or perform // dequeue) and add it to topological // order var u = q[0]; q.shift(); top_order.push(u); // Iterate through all its neighbouring // nodes of dequeued node u and decrease // their in-degree by 1 for(var itr of adj[u]) if (--in_degree[itr] == 0) q.push(itr); cnt++; } // Check if there was a cycle if (cnt != V) return true; else return false; } // Create a graph given in the above diagram initialize(6) addEdge(0, 1); addEdge(1, 2); addEdge(2, 0); addEdge(3, 4); addEdge(4, 5); if (isCycle()) document.write("Yes"); else document.write("No"); </script> Time Complexity: O(V+E)
Auxiliary Space: O(V)
Similar Reads
Breadth First Search or BFS for a Graph Given a undirected graph represented by an adjacency list adj, where each adj[i] represents the list of vertices connected to vertex i. Perform a Breadth First Search (BFS) traversal starting from vertex 0, visiting vertices from left to right according to the adjacency list, and return a list conta
15+ min read
BFS in different language
BFS for Disconnected Graph In the previous post, BFS only with a particular vertex is performed i.e. it is assumed that all vertices are reachable from the starting vertex. But in the case of a disconnected graph or any vertex that is unreachable from all vertex, the previous implementation will not give the desired output, s
14 min read
Applications, Advantages and Disadvantages of Breadth First Search (BFS) We have earlier discussed Breadth First Traversal Algorithm for Graphs. Here in this article, we will see the applications, advantages, and disadvantages of the Breadth First Search. Applications of Breadth First Search: 1. Shortest Path and Minimum Spanning Tree for unweighted graph: In an unweight
4 min read
Breadth First Traversal ( BFS ) on a 2D array Given a matrix of size M x N consisting of integers, the task is to print the matrix elements using Breadth-First Search traversal. Examples: Input: grid[][] = {{1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16}}Output: 1 2 5 3 6 9 4 7 10 13 8 11 14 12 15 16 Input: grid[][] = {{-1, 0, 0,
9 min read
0-1 BFS (Shortest Path in a Binary Weight Graph) Given an undirected graph where every edge has a weight as either 0 or 1. The task is to find the shortest path from the source vertex to all other vertices in the graph.Example: Input: Source Vertex = 0 and below graph Having vertices like (u, v, w): edges: [[0,1,0], [0, 7, 1], [1,2,1], [1, 7, 1],
10 min read
Variations of BFS implementations
Easy problems on BFS
Find if there is a path between two vertices in a directed graphGiven a Directed Graph and two vertices src and dest, check whether there is a path from src to dest.Example: Consider the following Graph: adj[][] = [ [], [0, 2], [0, 3], [], [2] ]Input : src = 1, dest = 3Output: YesExplanation: There is a path from 1 to 3, 1 -> 2 -> 3Input : src = 0, dest =
11 min read
Find if there is a path between two vertices in an undirected graphGiven an undirected graph with N vertices and E edges and two vertices (U, V) from the graph, the task is to detect if a path exists between these two vertices. Print "Yes" if a path exists and "No" otherwise. Examples: U = 1, V = 2 Output: No Explanation: There is no edge between the two points and
15+ min read
Print all the levels with odd and even number of nodes in it | Set-2Given an N-ary tree, print all the levels with odd and even number of nodes in it. Examples: For example consider the following tree 1 - Level 1 / \ 2 3 - Level 2 / \ \ 4 5 6 - Level 3 / \ / 7 8 9 - Level 4 The levels with odd number of nodes are: 1 3 4 The levels with even number of nodes are: 2 No
12 min read
Finding the path from one vertex to rest using BFSGiven an adjacency list representation of a directed graph, the task is to find the path from source to every other node in the graph using BFS. Examples: Input: Output: 0 <- 2 1 <- 0 <- 2 2 3 <- 1 <- 0 <- 2 4 <- 5 <- 2 5 <- 2 6 <- 2 Approach: In the images shown below:
14 min read
Find all reachable nodes from every node present in a given setGiven an undirected graph and a set of vertices, find all reachable nodes from every vertex present in the given set.Consider below undirected graph with 2 disconnected components.  arr[] = {1 , 2 , 5}Reachable nodes from 1 are 1, 2, 3, 4Reachable nodes from 2 are 1, 2, 3, 4Reachable nodes from 5 ar
12 min read
Program to print all the non-reachable nodes | Using BFSGiven an undirected graph and a set of vertices, we have to print all the non-reachable nodes from the given head node using a breadth-first search. For example: Consider below undirected graph with two disconnected components: In this graph, if we consider 0 as a head node, then the node 0, 1 and 2
8 min read
Check whether a given graph is Bipartite or notGiven a graph with V vertices numbered from 0 to V-1 and a list of edges, determine whether the graph is bipartite or not.Note: A bipartite graph is a type of graph where the set of vertices can be divided into two disjoint sets, say U and V, such that every edge connects a vertex in U to a vertex i
8 min read
Print all paths from a given source to a destination using BFSGiven a directed graph, a source vertex ‘src’ and a destination vertex ‘dst’, print all paths from given ‘src’ to ‘dst’. Please note that in the cases, we have cycles in the graph, we need not to consider paths have cycles as in case of cycles, there can by infinitely many by doing multiple iteratio
9 min read
Minimum steps to reach target by a Knight | Set 1Given a square chessboard of n x n size, the position of the Knight and the position of a target are given. We need to find out the minimum steps a Knight will take to reach the target position.Examples: Input: KnightknightPosition: (1, 3) , targetPosition: (5, 0)Output: 3Explanation: In above diagr
9 min read
Intermediate problems on BFS
Traversal of a Graph in lexicographical order using BFSC++ // C++ program to implement // the above approach #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to traverse the graph in // lexicographical order using BFS void LexiBFS(map<char, set<char> >& G, char S, map<char, bool>& vis) { // Stores nodes of the gr
8 min read
Detect cycle in an undirected graph using BFSGiven an undirected graph, the task is to determine if cycle is present in it or not.Examples:Input: V = 5, edges[][] = [[0, 1], [0, 2], [0, 3], [1, 2], [3, 4]]Undirected Graph with 5 NodeOutput: trueExplanation: The diagram clearly shows a cycle 0 → 2 → 1 → 0.Input: V = 4, edges[][] = [[0, 1], [1,
6 min read
Detect Cycle in a Directed Graph using BFSGiven a directed graph, check whether the graph contains a cycle or not. Your function should return true if the given graph contains at least one cycle, else return false. For example, the following graph contains two cycles 0->1->2->3->0 and 2->4->2, so your function must return
11 min read
Minimum number of edges between two vertices of a GraphYou are given an undirected graph G(V, E) with N vertices and M edges. We need to find the minimum number of edges between a given pair of vertices (u, v). Examples: Input: For given graph G. Find minimum number of edges between (1, 5). Output: 2Explanation: (1, 2) and (2, 5) are the only edges resu
8 min read
Word Ladder - Shortest Chain To Reach Target WordGiven an array of strings arr[], and two different strings start and target, representing two words. The task is to find the length of the smallest chain from string start to target, such that only one character of the adjacent words differs and each word exists in arr[].Note: Print 0 if it is not p
15 min read
Print the lexicographically smallest BFS of the graph starting from 1Given a connected graph with N vertices and M edges. The task is to print the lexicographically smallest BFS traversal of the graph starting from 1. Note: The vertices are numbered from 1 to N.Examples: Input: N = 5, M = 5 Edges: 1 4 3 4 5 4 3 2 1 5 Output: 1 4 3 2 5 Start from 1, go to 4, then to 3
7 min read
Shortest path in an unweighted graphGiven an unweighted, undirected graph of V nodes and E edges, a source node S, and a destination node D, we need to find the shortest path from node S to node D in the graph. Input: V = 8, E = 10, S = 0, D = 7, edges[][] = {{0, 1}, {1, 2}, {0, 3}, {3, 4}, {4, 7}, {3, 7}, {6, 7}, {4, 5}, {4, 6}, {5,
11 min read
Number of shortest paths in an unweighted and directed graphGiven an unweighted directed graph, can be cyclic or acyclic. Print the number of shortest paths from a given vertex to each of the vertices. For example consider the below graph. There is one shortest path vertex 0 to vertex 0 (from each vertex there is a single shortest path to itself), one shorte
11 min read
Distance of nearest cell having 1 in a binary matrixGiven a binary grid of n*m. Find the distance of the nearest 1 in the grid for each cell.The distance is calculated as |i1 - i2| + |j1 - j2|, where i1, j1 are the row number and column number of the current cell, and i2, j2 are the row number and column number of the nearest cell having value 1. Th
15+ min read
Hard Problems on BFS
Islands in a graph using BFSGiven an n x m grid of 'W' (Water) and 'L' (Land), the task is to count the number of islands. An island is a group of adjacent 'L' cells connected horizontally, vertically, or diagonally, and it is surrounded by water or the grid boundary. The goal is to determine how many distinct islands exist in
15+ min read
Print all shortest paths between given source and destination in an undirected graphGiven an undirected and unweighted graph and two nodes as source and destination, the task is to print all the paths of the shortest length between the given source and destination.Examples: Input: source = 0, destination = 5 Output: 0 -> 1 -> 3 -> 50 -> 2 -> 3 -> 50 -> 1 ->
13 min read
Count Number of Ways to Reach Destination in a Maze using BFSGiven a maze of dimensions n x m represented by the matrix mat, where mat[i][j] = -1 represents a blocked cell and mat[i][j] = 0 represents an unblocked cell, the task is to count the number of ways to reach the bottom-right cell starting from the top-left cell by moving right (i, j+1) or down (i+1,
8 min read
Coin Change | BFS ApproachGiven an integer X and an array arr[] of length N consisting of positive integers, the task is to pick minimum number of integers from the array such that they sum up to N. Any number can be chosen infinite number of times. If no answer exists then print -1.Examples: Input: X = 7, arr[] = {3, 5, 4}
6 min read
Water Jug problem using BFSGiven two empty jugs of m and n litres respectively. The jugs don't have markings to allow measuring smaller quantities. You have to use the jugs to measure d litres of water. The task is to find the minimum number of operations to be performed to obtain d litres of water in one of the jugs. In case
12 min read
Word Ladder - Set 2 ( Bi-directional BFS )Given a dictionary, and two words start and target (both of the same length). Find length of the smallest chain from start to target if it exists, such that adjacent words in the chain only differ by one character and each word in the chain is a valid word i.e., it exists in the dictionary. It may b
15+ min read
Implementing Water Supply Problem using Breadth First SearchGiven N cities that are connected using N-1 roads. Between Cities [i, i+1], there exists an edge for all i from 1 to N-1.The task is to set up a connection for water supply. Set the water supply in one city and water gets transported from it to other cities using road transport. Certain cities are b
10 min read
Minimum Cost Path in a directed graph via given set of intermediate nodesGiven a weighted, directed graph G, an array V[] consisting of vertices, the task is to find the Minimum Cost Path passing through all the vertices of the set V, from a given source S to a destination D. Examples: Input: V = {7}, S = 0, D = 6 Output: 11 Explanation: Minimum path 0->7->5->6.
10 min read
Shortest path in a Binary MazeGiven an M x N matrix where each element can either be 0 or 1. We need to find the shortest path between a given source cell to a destination cell. The path can only be created out of a cell if its value is 1.Note: You can move into an adjacent cell in one of the four directions, Up, Down, Left, and
15+ min read
Minimum cost to traverse from one index to another in the StringGiven a string S of length N consisting of lower case character, the task is to find the minimum cost to reach from index i to index j. At any index k, the cost to jump to the index k+1 and k-1(without going out of bounds) is 1. Additionally, the cost to jump to any index m such that S[m] = S[k] is
10 min read