Clone linked list with next and random pointer using Recursion
Last Updated : 28 Dec, 2024
Given a linked list of size n where each node has two links: next pointer pointing to the next node and random pointer to any random node in the list. The task is to create a clone of this linked list.
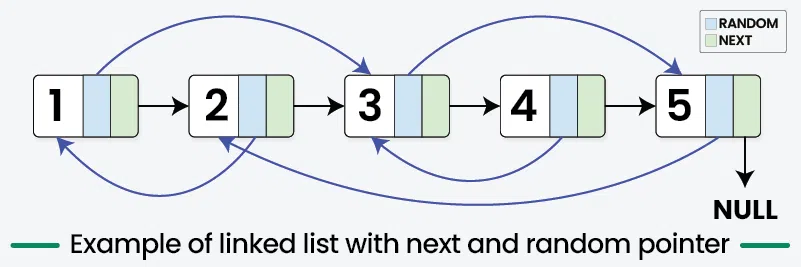
Approach :
The idea is to create a new node corresponding to each node in the original linked list and store the new nodes in a hash table. While traversing the original linked list we also use recursion to update the next and random pointers of new nodes corresponding to every original node.
Steps to clone a linked list with next and random pointer:
- Create a hash table, say mp to store each original node to its corresponding cloned node.
- Recursive Cloning Function:
- If the current node (head) is nullptr, return nullptr.
- If the node is already present in the hash table (mp), return the cloned node from the hash table.
- Create a new node (clonedNode) with the same data as the current node and store it in the hash table (mp[head] = clonedNode).
- Recursively clone the next and random pointers of the current node:
- Update the next pointer of clonedNode by calling the recursive function on head->next.
- Update the random pointer of clonedNode by calling the recursive function on head->random.
- After cloning, return the Cloned List Head.
C++ // C++ code to Clone a linked list with next // and random pointer using Hashing and Recursion #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; Node *next; Node *random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = random = NULL; } }; // Helper function to clone the list Node *cloneHelper(Node*head, unordered_map<Node*, Node*> &mp) { if (head == nullptr) { return nullptr; } // If the node is already cloned, return the cloned node if (mp.find(head) != mp.end()) { return mp[head]; } // Create a new node with the same data Node *clonedNode = new Node(head->data); mp[head] = clonedNode; // Recursively clone the next and random pointers clonedNode->next = cloneHelper(head->next, mp); clonedNode->random = cloneHelper(head->random, mp); return clonedNode; } // Function to clone the linked list Node *cloneLinkedList(Node *head) { unordered_map<Node *, Node *> mp; return cloneHelper(head, mp); } void printList(Node *head) { while (head != nullptr) { cout << head->data << "("; if (head->random) cout << head->random->data << ")"; else cout << "null" << ")"; if (head->next != nullptr) cout << " -> "; head = head->next; } cout << endl; } int main() { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node *head = new Node(1); head->next = new Node(2); head->next->next = new Node(3); head->next->next->next = new Node(4); head->next->next->next->next = new Node(5); head->random = head->next->next; head->next->random = head; head->next->next->random = head->next->next->next->next; head->next->next->next->random = head->next->next; head->next->next->next->next->random = head->next; Node *clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); printList(clonedList); return 0; } // Java code to Clone a linked list with next // and random pointer using Hashing and Recursion import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; class Node { int data; Node next; Node random; Node(int x) { data = x; next = null; random = null; } } class GfG { // Helper function to recursively clone nodes static Node cloneHelper(Node node,Map<Node, Node> mp) { if (node == null) { return null; } // If the node is already cloned, // return the cloned // node if (mp.containsKey(node)) { return mp.get(node); } // Create a new node with the same data Node newNode = new Node(node.data); mp.put(node,newNode); // Recursively clone the next and random pointers newNode.next = cloneHelper(node.next, mp); newNode.random = cloneHelper(node.random, mp); return newNode; } // Function to clone the linked list static Node cloneLinkedList(Node head) { Map<Node, Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); return cloneHelper(head, mp); } static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + "("); if (head.random != null) System.out.print(head.random.data + ")"); else System.out.print("null" + ")"); if (head.next != null) System.out.print(" -> "); head = head.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; Node clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); printList(clonedList); } } # Python code to Clone a linked list with next # and random pointer using Hashing and Recursion class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.next = None self.random = None def cloneLinkedList(head): # Helper function to recursively clone nodes def cloneHelper(node, mp): if node is None: return None if node in mp: return mp[node] # Create a new node newNode = Node(node.data) mp[node] = newNode # Recursively clone the next and # random pointers newNode.next = cloneHelper(node.next, mp) newNode.random = cloneHelper(node.random, mp) return newNode # Map to store original nodes # to cloned nodes mp = {} return cloneHelper(head, mp) def printList(head): curr = head while curr is not None: print(f'{curr.data}(', end='') if curr.random: print(f'{curr.random.data})', end='') else: print('null)', end='') if curr.next is not None: print(' -> ', end='') curr = curr.next print() if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating a linked list with random pointer head = Node(1) head.next = Node(2) head.next.next = Node(3) head.next.next.next = Node(4) head.next.next.next.next = Node(5) head.random = head.next.next head.next.random = head head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head) printList(clonedList) // C# code to Clone a linked list with next // and random pointer using Hashing and Recursion using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int Data; public Node next; public Node random; public Node(int x) { Data = x; next = null; random = null; } } class GfG { // Function to clone the linked list static Node CloneLinkedList(Node head) { // Dictionary to store the mapping of original nodes // to new nodes Dictionary<Node, Node> mp = new Dictionary<Node, Node>(); return CloneHelper(head, mp); } // Recursive helper function to clone the linked list static Node CloneHelper(Node node, Dictionary<Node, Node> mp) { // Base case: if the node is null, return null if (node == null) { return null; } // If the node has already been cloned, return the // cloned node if (mp.ContainsKey(node)) { return mp[node]; } // Create a new node for the current node Node newNode = new Node(node.Data); mp[node] = newNode; // Recursively clone the next and random pointers newNode.next = CloneHelper(node.next, mp); newNode.random = CloneHelper(node.random, mp); return newNode; } static void PrintList(Node head) { while (head != null) { Console.Write(head.Data + "("); if (head.random != null) Console.Write(head.random.Data); else Console.Write("null"); Console.Write(")"); if (head.next != null) Console.Write(" -> "); head = head.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { // Creating a linked list with random pointer Node head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; Node clonedList = CloneLinkedList(head); PrintList(clonedList); } } // Javascript code to Clone a linked list with next // and random pointer using Hashing and Recursion class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; this.random = null; } } // Recursive function to clone the linked list function cloneLinkedList(head) { const mp = new Map(); // Recursive helper function function cloneHelper(node) { if (node === null) { return null; } // If the node is already cloned, // return the cloned // node if (mp.has(node)) { return mp.get(node); } // Create a new node for the current node const newNode = new Node(node.data); mp.set(node, newNode); // Recursively clone the next and random pointers newNode.next = cloneHelper(node.next); newNode.random = cloneHelper(node.random); return newNode; } // Start the cloning process return cloneHelper(head); } function printList(head) { let result = ""; while (head !== null) { result += head.data + "("; result += head.random ? head.random.data : "null"; result += ")"; if (head.next !== null) { result += " -> "; } head = head.next; } console.log(result); } // Creating a linked list with // random pointer const head = new Node(1); head.next = new Node(2); head.next.next = new Node(3); head.next.next.next = new Node(4); head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); head.random = head.next.next; head.next.random = head; head.next.next.random = head.next.next.next.next; head.next.next.next.random = head.next.next; head.next.next.next.next.random = head.next; const clonedList = cloneLinkedList(head); printList(clonedList); Output1(3) -> 2(1) -> 3(5) -> 4(3) -> 5(2)
Time complexity : O(n) , where n is the number of nodes in linked list.
Auxiliary space : O(3n) , extra O(n) space as we are using a hash table to store the new nodes as well for recursion stack space.
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile