Binary Tree to Binary Search Tree Conversion
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Given a Binary Tree, the task is to convert it to a Binary Search Tree. The conversion must be done in such a way that keeps the original structure of the Binary Tree.
Examples
Input:
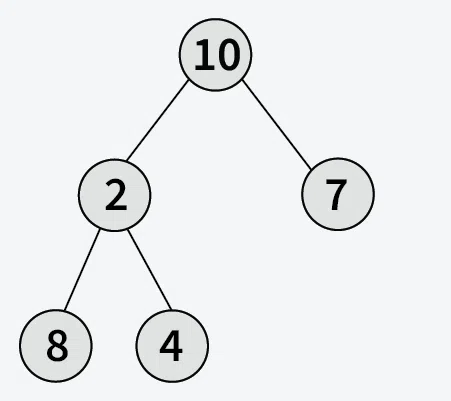
Output:
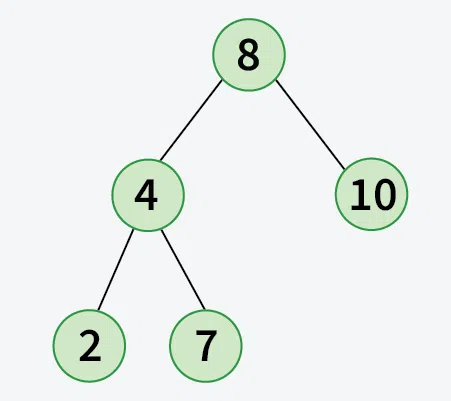
Explanation: The above Binary tree is converted to Binary Search tree by keeping the original structure of Binary Tree.
Approach:
The idea to recursively traverse the binary tree and store the nodes in an array. Sort the array, and perform in-order traversal of the tree and update the value of each node to the corresponding value in tree.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Program to convert binary // tree to binary search tree. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; class Node { public: int data; Node* left, *right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = nullptr; right = nullptr; } }; // Inorder traversal to store the nodes in a vector void inorder(Node* root, vector<int>& nodes) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } inorder(root->left, nodes); nodes.push_back(root->data); inorder(root->right, nodes); } // Inorder traversal to convert tree // to BST. void constructBST(Node* root, vector<int> nodes, int& index) { if (root == nullptr) return; constructBST(root->left, nodes, index); // Update root value root->data = nodes[index++]; constructBST(root->right, nodes, index); } // Function to convert a binary tree to a binary search tree Node* binaryTreeToBST(Node* root) { vector<int> nodes; inorder(root, nodes); // sort the nodes sort(nodes.begin(), nodes.end()); int index = 0; constructBST(root, nodes, index); return root; } // Function to print the inorder traversal of a binary tree void printInorder(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) { return; } printInorder(root->left); cout << root->data << " "; printInorder(root->right); } int main() { // Creating the tree // 10 // / \ // 2 7 // / \ // 8 4 Node* root = new Node(10); root->left = new Node(2); root->right = new Node(7); root->left->left = new Node(8); root->left->right = new Node(4); Node* ans = binaryTreeToBST(root); printInorder(ans); return 0; } // Java Program to convert binary // tree to binary search tree. import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collections; class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // Inorder traversal to store the nodes in a vector static void inorder(Node root, ArrayList<Integer> nodes) { if (root == null) { return; } inorder(root.left, nodes); nodes.add(root.data); inorder(root.right, nodes); } // Inorder traversal to convert tree to BST. static void constructBST(Node root, ArrayList<Integer> nodes, int[] index) { if (root == null) return; constructBST(root.left, nodes, index); // Update root value root.data = nodes.get(index[0]); index[0]++; constructBST(root.right, nodes, index); } // Function to convert a binary tree to a binary search tree static Node binaryTreeToBST(Node root) { ArrayList<Integer> nodes = new ArrayList<>(); inorder(root, nodes); // sort the nodes Collections.sort(nodes); int[] index = {0}; constructBST(root, nodes, index); return root; } // Function to print the inorder traversal of a binary tree static void printInorder(Node root) { if (root == null) { return; } printInorder(root.left); System.out.print(root.data + " "); printInorder(root.right); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating the tree // 10 // / \ // 2 7 // / \ // 8 4 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(7); root.left.left = new Node(8); root.left.right = new Node(4); Node ans = binaryTreeToBST(root); printInorder(ans); } } # Python Program to convert binary # tree to binary search tree. class Node: def __init__(self, x): self.data = x self.left = None self.right = None # Inorder traversal to store the nodes in a vector def inorder(root, nodes): if root is None: return inorder(root.left, nodes) nodes.append(root.data) inorder(root.right, nodes) # Inorder traversal to convert tree to BST. def constructBst(root, nodes, index): if root is None: return constructBst(root.left, nodes, index) # Update root value root.data = nodes[index[0]] index[0] += 1 constructBst(root.right, nodes, index) # Function to convert a binary tree to a binary search tree def binaryTreeToBst(root): nodes = [] inorder(root, nodes) # sort the nodes nodes.sort() index = [0] constructBst(root, nodes, index) return root # Function to print the inorder traversal of a binary tree def printInorder(root): if root is None: return printInorder(root.left) print(root.data, end=" ") printInorder(root.right) if __name__ == "__main__": # Creating the tree # 10 # / \ # 2 7 # / \ # 8 4 root = Node(10) root.left = Node(2) root.right = Node(7) root.left.left = Node(8) root.left.right = Node(4) ans = binaryTreeToBst(root) printInorder(ans)
// C# Program to convert binary // tree to binary search tree. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node(int x) { data = x; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // Inorder traversal to store the nodes in a list static void Inorder(Node root, List<int> nodes) { if (root == null) { return; } Inorder(root.left, nodes); nodes.Add(root.data); Inorder(root.right, nodes); } // Inorder traversal to convert tree to BST. static void ConstructBST(Node root, List<int> nodes, ref int index) { if (root == null) return; ConstructBST(root.left, nodes, ref index); // Update root value root.data = nodes[index]; index++; ConstructBST(root.right, nodes, ref index); } // Function to convert a binary tree to a binary search tree static Node BinaryTreeToBST(Node root) { List<int> nodes = new List<int>(); Inorder(root, nodes); // sort the nodes nodes.Sort(); int index = 0; ConstructBST(root, nodes, ref index); return root; } // Function to print the inorder traversal of a binary tree static void PrintInorder(Node root) { if (root == null) { return; } PrintInorder(root.left); Console.Write(root.data + " "); PrintInorder(root.right); } static void Main() { // Creating the tree // 10 // / \ // 2 7 // / \ // 8 4 Node root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(7); root.left.left = new Node(8); root.left.right = new Node(4); Node ans = BinaryTreeToBST(root); PrintInorder(ans); } } // JavaScript Program to convert binary // tree to binary search tree. class Node { constructor(x) { this.data = x; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // Inorder traversal to store the nodes in a vector function inorderTrav(root, nodes) { if (root === null) { return; } inorderTrav(root.left, nodes); nodes.push(root.data); inorderTrav(root.right, nodes); } // Inorder traversal to convert tree to BST. function constructBST(root, nodes, index) { if (root === null) return; constructBST(root.left, nodes, index); // Update root value root.data = nodes[index[0]]; index[0]++; constructBST(root.right, nodes, index); } // Function to convert a binary tree to a binary search tree function binaryTreeToBST(root) { let nodes = []; inorderTrav(root, nodes); // sort the nodes nodes.sort((a, b) => a - b); let index = [0]; constructBST(root, nodes, index); return root; } // Function to print the inorder traversal of a binary tree function printInorder(root) { if (root === null) { return; } printInorder(root.left); console.log(root.data); printInorder(root.right); } // Creating the tree // 10 // / \ // 2 7 // / \ // 8 4 let root = new Node(10); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(7); root.left.left = new Node(8); root.left.right = new Node(4); let ans = binaryTreeToBST(root); printInorder(ans); Time Complexity: O(nlogn), for sorting the array.
Auxiliary Space: O(n), for storing nodes in an array.
Related article:
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem
My Profile