C++ Program for Topological Sorting
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
Topological sorting for Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a linear ordering of vertices such that for every directed edge uv, vertex u comes before v in the ordering. Topological Sorting for a graph is not possible if the graph is not a DAG. For example, a topological sorting of the following graph is "5 4 2 3 1 0". There can be more than one topological sorting for a graph. For example, another topological sorting of the following graph is "4 5 2 3 1 0". The first vertex in topological sorting is always a vertex with in-degree as 0 (a vertex with no in-coming edges).
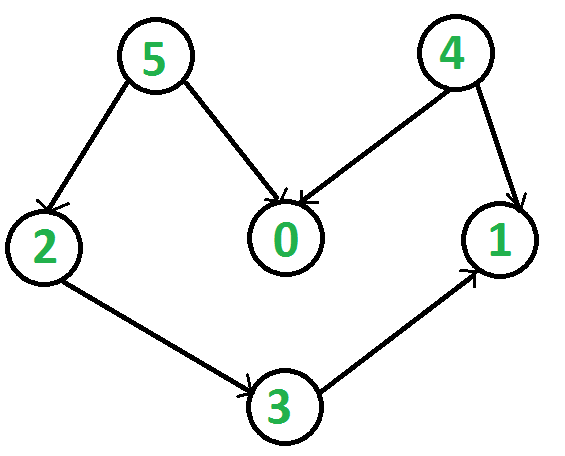
CPP // A C++ program to print topological sorting of a DAG #include <iostream> #include <list> #include <stack> using namespace std; // Class to represent a graph class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices' // Pointer to an array containing adjacency listsList list<int>* adj; // A function used by topologicalSort void topologicalSortUtil(int v, bool visited[], stack<int>& Stack); public: Graph(int V); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge(int v, int w); // prints a Topological Sort of the complete graph void topologicalSort(); }; Graph::Graph(int V) { this->V = V; adj = new list<int>[V]; } void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v’s list. } // A recursive function used by topologicalSort void Graph::topologicalSortUtil(int v, bool visited[], stack<int>& Stack) { // Mark the current node as visited. visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex list<int>::iterator i; for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i) if (!visited[*i]) topologicalSortUtil(*i, visited, Stack); // Push current vertex to stack which stores result Stack.push(v); } // The function to do Topological Sort. It uses recursive // topologicalSortUtil() void Graph::topologicalSort() { stack<int> Stack; // Mark all the vertices as not visited bool* visited = new bool[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) visited[i] = false; // Call the recursive helper function to store Topological // Sort starting from all vertices one by one for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) if (visited[i] == false) topologicalSortUtil(i, visited, Stack); // Print contents of stack while (Stack.empty() == false) { cout << Stack.top() << " "; Stack.pop(); } } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g(6); g.addEdge(5, 2); g.addEdge(5, 0); g.addEdge(4, 0); g.addEdge(4, 1); g.addEdge(2, 3); g.addEdge(3, 1); cout << "Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph: "; g.topologicalSort(); return 0; } OutputFollowing is a Topological Sort of the given graph: 5 4 2 3 1 0
Time Complexity: O(V+E). The above algorithm is simply DFS with an extra stack. So time complexity is the same as DFS
Auxiliary space: O(V). The extra space is needed for the stack
Please refer complete article on Topological Sorting for more details!
Explore
C++ Basics
Core Concepts
OOP in C++
Standard Template Library(STL)
Practice & Problems
My Profile