C++ Implementation Double-Ended Queue
Last Updated : 23 Jul, 2025
A Double-Ended Queue (Deque) is an abstract data structure that generalizes a queue, for which elements can be added to or removed from either the front (head) or back (tail). It is also often called a head-tail linked list. In this article, we will learn how to implement a Deque in C++ along with its basic operations.
A Deque (pronounced "deck") is a linear collection of elements that supports insertion and deletion at both ends. The name "deque" is short for "double-ended queue". It can be thought of as a combination of a stack and a queue that allows insertion and deletion of elements from both ends.

Properties of Deques
- Elements can be added to both the front and rear ends of the queue.
- Elements can be removed from both the front and rear ends of the queue.
- Deques support both LIFO (Last In First Out) and FIFO (First In First Out) operations.
- Random access is generally not allowed.
- Deques can be implemented using either arrays or linked lists.
Implementation of Double Ended Queue in C++
A Deque can be implemented using either an array or a doubly linked list. For this implementation, we'll use a doubly linked list to allow for efficient insertions and deletions at both ends.
Representation of Double Ended Queue in C++
The following diagram represents the structure of deque in C++:
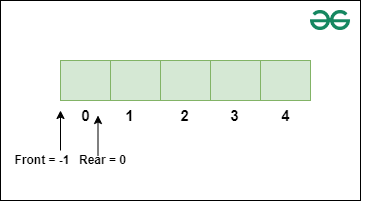 Deque
DequeTo represent a Deque in C++, we'll implement a class Deque that contains the required definition: a structure to represent each node and member functions to provide basic functionality. We have used templates to keep the deque generic so that it can support multiple data types.
template <typename T>
class Deque {
private:
struct Node {
T data;
Node* prev;
Node* next;
};
Node* front;
Node* rear;
int size;
Here:
- data: stores the value in the node.
- prev and next: store pointers to the previous and next nodes.
- front and rear: store pointers to the front and rear of the deque.
- size: stores the current number of elements in the deque.
Basic Operations of Double Ended Queue in C++
Following are some of the basic operations of a Deque that are required to manipulate its elements:
Operation | Description | Time Complexity | Space Complexity |
|---|
Insertion at front | Inserts an element at the front of the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
Insertion at rear | Inserts an element at the rear of the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
Deletion at front | Removes an element from the front of the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
Deletion at rear | Removes an element from the rear of the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
get_front | Returns the element at the front of the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
get_rear | Returns the element at the rear of the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
is_empty | Checks if the deque is empty or not | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
get_size | Returns the number of elements in the deque | O(1) | O(1) |
|---|
Implementation of Insertion at Front in Deque in C++
.png)
- Create a new node with the given value.
- If the deque is empty, set both front and rear to the new node.
- Otherwise, set the new node's next to the current front, set the current front's prev to the new node, and update front to the new node.
- Increment the size.
Implementation of Insertion at Rear in Deque in C++
.png)
- Create a new node with the given value.
- If the deque is empty, set both front and rear to the new node.
- Otherwise, set the new node's prev to the current rear, set the current rear's next to the new node, and update rear to the new node.
- Increment the size.
Implementation of Deletion at Front in Deque in C++
- If the deque is empty, throw an exception or return.
- Store the current front node.
- Update front to the next node.
- If front becomes null (deque is now empty), set rear to null as well.
- Otherwise, set the new front's prev to null.
- Delete the stored node and decrement the size.
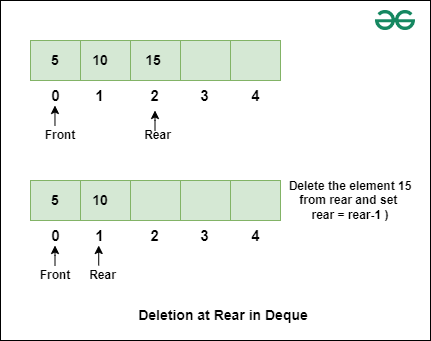
Implementation of Deletion at Rear in Deque in C++
- If the deque is empty, throw an exception or return.
- Store the current rear node.
- Update rear to the previous node.
- If rear becomes null (deque is now empty), set front to null as well.
- Otherwise, set the new rear's next to null.
- Delete the stored node and decrement the size.
Implementation of get_front and get_rear Functions
- If the deque is empty, throw an exception.
- Return the data of the front (or rear) node.
Implementation of is_empty and get_size Functions
- is_empty: Return true if size is 0, false otherwise.
- get_size: Return the size.
C++ Program to Implement Double Ended Queue
The following program demonstrates the implementation of a Double Ended Queue in C++.
C++ // C++ Program to Implement Double Ended Queue #include <iostream> #include <stdexcept> using namespace std; // Template class for a doubly linked list based Deque template <typename T> class Deque { private: // Node structure representing each element in the Deque struct Node { // Data held by the node T data; // Pointer to the previous node Node* prev; // Pointer to the next node Node* next; // Constructor to initialize a Node with a given // value Node(T value) : data(value) , prev(nullptr) , next(nullptr) { } }; // Pointer to the front of the Deque Node* front; // Pointer to the rear of the Deque Node* rear; // Number of elements in the Deque int size; public: // Constructor to initialize an empty Deque Deque() : front(nullptr) , rear(nullptr) , size(0) { } // Destructor to clean up memory by removing all // elements ~Deque() { while (!is_empty()) { pop_front(); } } // Function to add an element to the front of the Deque void push_front(T value) { // Create a new node Node* new_node = new Node(value); // If Deque is empty, both front and rear point to // the new node if (is_empty()) { front = rear = new_node; } else { // Link the new node to the current front new_node->next = front; // Link the current front to the new node front->prev = new_node; // Update front to the new node front = new_node; } // Increment the size of the Deque size++; } // Function to add an element to the back of the Deque void push_back(T value) { Node* new_node = new Node(value); // Create a new node if (is_empty()) { // If Deque is empty, both front and rear point // to the new node front = rear = new_node; } else { // Link the new node to the current rear new_node->prev = rear; // Link the current rear to the new node rear->next = new_node; // Update rear to the new node rear = new_node; } // Increment the size of the Deque size++; } // Function to remove an element from the front of the // Deque void pop_front() { if (is_empty()) { // Throw an error if Deque is empty throw runtime_error("Deque is empty"); } // Temporarily hold the front node Node* temp = front; // Move front to the next node front = front->next; if (front == nullptr) { // If Deque is now empty, set rear to null rear = nullptr; } else { // Otherwise, unlink the old front node front->prev = nullptr; } // Free the memory of the old front node delete temp; // Decrement the size of the Deque size--; } // Function to remove an element from the back of the // Deque void pop_back() { if (is_empty()) { // Throw an error if Deque is empty throw runtime_error("Deque is empty"); } // Temporarily hold the rear node Node* temp = rear; // Move rear to the previous node rear = rear->prev; if (rear == nullptr) { // If Deque is now empty, set front to null front = nullptr; } else { // Otherwise, unlink the old rear node rear->next = nullptr; } // Free the memory of the old rear node delete temp; // Decrement the size of the Deque size--; } // Function to get the element at the front of the Deque T get_front() { if (is_empty()) { // Throw an error if Deque is empty throw runtime_error("Deque is empty"); } // Return the data of the front node return front->data; } // Function to get the element at the rear of the Deque T get_rear() { if (is_empty()) { // Throw an error if Deque is empty throw runtime_error("Deque is empty"); } // Return the data of the rear node return rear->data; } // Function to check if the Deque is empty bool is_empty() { // Deque is empty if size is 0 return size == 0; } // Function to get the number of elements in the Deque int get_size() { // Return the current size of the Deque return size; } // Function to display the elements of the Deque void display() { // Start from the front node Node* current = front; while (current != nullptr) { // Print the data of the current node cout << current->data << " "; // Move to the next node current = current->next; } cout << endl; } }; int main() { // Create a Deque of integers Deque<int> deque; // Push elements to the front and back deque.push_front(10); deque.push_back(20); deque.push_front(5); deque.push_back(30); // Display the Deque after pushes cout << "Deque after pushes: "; deque.display(); // Get and display the front and rear elements cout << "Front element: " << deque.get_front() << endl; cout << "Rear element: " << deque.get_rear() << endl; // Pop elements from the front and back deque.pop_front(); deque.pop_back(); // Display the Deque after pops cout << "Deque after pops: "; deque.display(); // Display the size of the Deque cout << "Size of deque: " << deque.get_size() << endl; return 0; } OutputDeque after pushes: 5 10 20 30 Front element: 5 Rear element: 30 Deque after pops: 10 20 Size of deque: 2
Applications of Deque
Following are some of the common applications of deque:
- Deque is used to efficiently check if a string is a palindrome by comparing characters from both ends simultaneously.
- Deque is used to implement undo/redo operations in text editors and other applications by maintaining a history of actions.
- Deque is used to implement forward and backward navigation in web browsers, allowing efficient movement through browsing history.
- Deque is used in round-robin scheduling algorithms, where tasks can be added or removed from either end of the queue.
- Deque is used to solve sliding window maximum/minimum problems efficiently in algorithmic challenges and data processing.
- Deque is used in certain graph traversal algorithms, such as breadth-first search variations that require bidirectional exploration.
Explore
C++ Basics
Core Concepts
OOP in C++
Standard Template Library(STL)
Practice & Problems
My Profile