File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
Last Updated : 16 Oct, 2025
File transfer protocol (FTP) is an Internet tool provided by TCP/IP. It helps to transfer files from one computer to another by providing access to directories or folders on remote computers and allows software, data and text files to be transferred between different kinds of computers.
- It encourages the direct use of remote computers.
- It shields users from system variations (operating system, directory structures, file structures, etc.)
- It promotes the sharing of files and other types of data.
Note: The end-user in the connection is known as localhost and the server which provides data is known as the remote host.
Applications of FTP
- Business File Sharing: Used by large enterprises to share files between employees across locations.
- Backup & Recovery: IT companies use FTP to maintain disaster recovery backup sites.
- Financial Sector: For secure transmission of sensitive documents between institutions and regulatory authorities.
- Collaboration: Employees use FTP to share files and project data with co-workers.
FTP Client and Server Model
FTP follows a client-server architecture.
- FTP Client: A program that runs on the user’s computer, enabling communication with an FTP server. It provides commands to connect, browse and transfer files.
- FTP Server: A system that hosts the files and directories, waiting for requests from clients.
Commands
- get the filename(retrieve the file from the directories get server)
- mget filename(retrieve multiple files from the server )
- ls(lists files available in the current directory of the server)
Note: Many modern operating systems have built-in FTP programs, making file transfer easier without needing to memorize commands.
Types of FTP Connections
FTP connections are of two types:
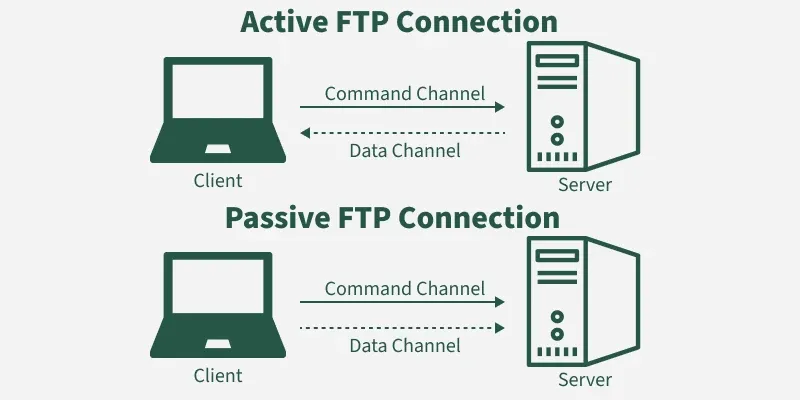 FTP Connections
FTP Connections1. Active FTP connection
- In an Active FTP connection, the client establishes the command channel and the server establishes the data channel.
- When the client requests the data over the connection the server initiates the transfer of the data to the client.
- It is not the default connection because it may cause problems if there is a firewall in between the client and the server.
2. Passive FTP connection
- n a Passive FTP connection, the client establishes both the data channel as well as the command channel.
- When the client requests the data over the connection, the server sends a random port number to the client, as soon as the client receives this port number it establishes the data channel.
- It is the default connection, as it works better even if the client is protected by the firewall.
Anonymous FTP
Some servers provide anonymous FTP, where files are available for public access without authentication.
- The username is set to anonymous.
- The password is typically the user’s email address.
- Access is limited: users can download files but not browse directories or make modifications.
How FTP works?
When an FTP connection is established, two parallel channels are created:
- Command Channel: Used for transmitting commands (like login, navigation and file requests). Operates over Port 21.
- Data Channel: Used for transferring the actual data/files. Operates over Port 20.
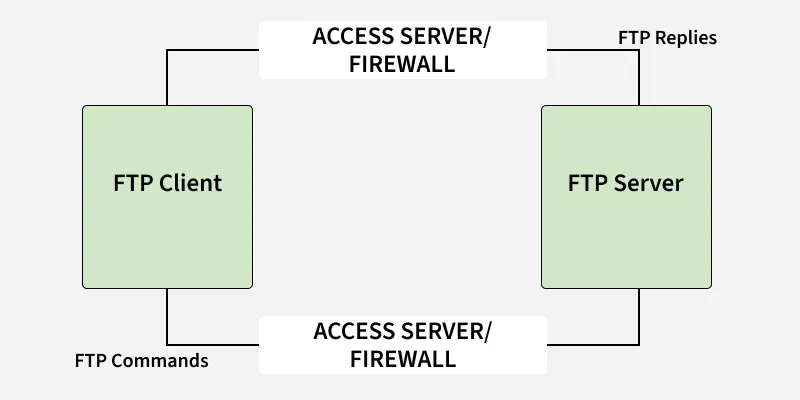 How FTP Works?
How FTP Works?Detail Steps of FTP
- Client contacts the server on Port 21.
- Authentication is performed (username/password or anonymous login).
- The client browses directories using commands.
- When a file transfer is requested, the server opens a new data connection to the client.
- After transferring a file, the data connection closes (but the control connection remains open).
- The process repeats for additional file transfers.
Note: FTP uses the NVT ASCII character set for communication over the control channel, similar to TELNET and SMTP.
Transmission Mode
FTP supports three transmission modes:
- Stream Mode: (Default) Data is sent as a continuous stream of bytes. TCP handles fragmentation. Connection closes automatically at the end of transmission.
- Block Mode: Data is sent in blocks, each with a 3-byte header describing the block. Useful for structured data.
- Compressed Mode: Large files are compressed before transfer to save bandwidth and speed up transmission.
FTP Commands
| Command | Meaning |
|---|
cd | Change working directory on the remote host. |
close | Close the FTP connection. |
quit | Exit the FTP session. |
pwd | Show current working directory on remote host. |
dir/ls | List files in the current directory. |
help | Display list of client FTP commands. |
remotehelp | Display list of server FTP commands. |
type | Specify file type (ASCII/Binary). |
struct | Specify file structure. |
Why FTP?
While other protocols like HTTP can also transfer files, FTP provides a more specialized, reliable and standardized way to handle file exchanges between heterogeneous systems.
FTP supports transferring:
- ASCII files (default, character-based).
- EBCDIC files (for mainframes).
- Binary (image) files (default for non-text files like executables, images, etc.).
Note: It ensures compatibility between different operating systems, file structures and character sets.
Explore
Basics of Computer
Application Software
System Software
Networks & Internet Protocols
Programming Languages
My Profile