A computer bus is a communication system used to transfer data between components within a computer or between different computers. It plays an important role in minimizing the number of connections needed by centralizing communication over shared pathways.
- It consists of physical connections like wires, circuits, or cables.
- Components like the CPU, memory, and input/output (I/O) devices are connected through a bus.
- It simplifies data transfer and improves efficiency.
Types Of Buses
There are three main types of buses in a computer system, which are discussed below:
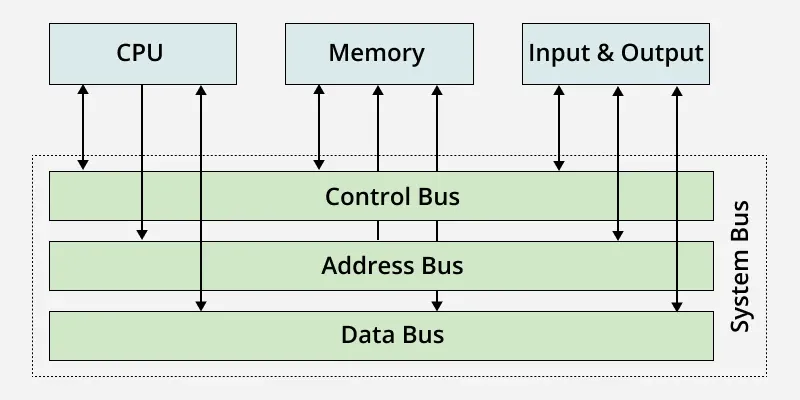
1. Address Bus
A collection of wires used to identify particular location in main memory is called Address Bus. Or in other words, the information used to describe the memory locations travels along the address bus.
- The address bus transports memory addresses which the processor wants to access in order to read or write data..
- The address bus is unidirectional.
- The size of address bus determines how many unique memory locations can be addressed.
Example:
- A system with 4-bit address bus can address 24 = 16 Bytes of memory.
- A system with 16-bit address bus can address 216 = 64 KB of memory
- A system with 20-bit address bus can address 220 = 1 MB of memory.
2. Data Bus
A collection of wires through which data is transmitted from one part of a computer to another is called Data Bus. It can be thought of as a highway on which data travels within a computer.
- The main objective of data bus is transfer of the data between microprocessor to input/ output devices or memory.
- The data bus transfers instructions coming from or going to the processor.
- The data bus is bidirectional because the data can flow in either direction from CPU to memory(or input/output device) or from memory to the CPU.
- The size (width) of bus determines how much data can be transmitted at one time.
Example:
- A 16-bit bus can transmit 16 bits of data at a time.
- 32-bit bus can transmit 32 bits at a time.
3. Control Bus
The connections that carry control information between the CPU and other devices within the computer is called Control Bus. The control bus transports orders and synchronization signal coming from the control unit and travelling to all other hardware components
- The main objective of control bus is all signals controller carried from processor to other hardware device.
- The Control bus is bidirectional because the data can flow in either direction from CPU to memory(or input/output device) or from memory to the CPU.
- It also transmits response signals from the hardware.
Comparison Between System Buses
The below table shows the comparison between the three buses as below :
| Buses | Purpose & Key Role |
|---|---|
| Address Bus (Unidirectional) | Carries memory addresses; Identifies where data should go |
| Data Bus (Bidirectional) | Carries actual data, moves data between components |
Control Bus(Bidirectional) | Carries control and sync signals, coordinates CPU and device actions |
