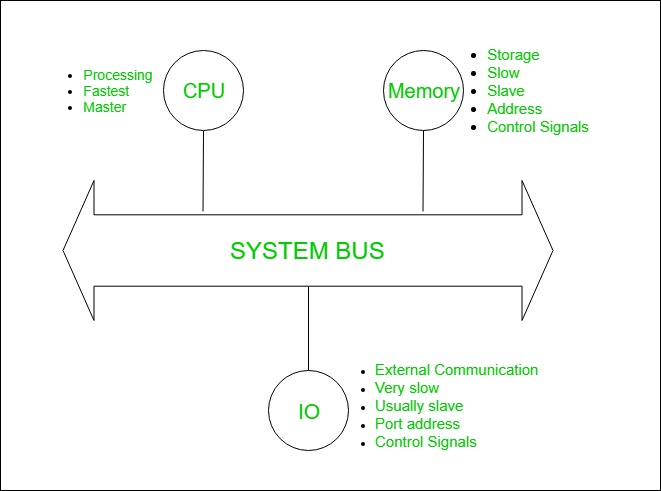
System bus design refers to the architecture and layout of communication pathways that transfer data, addresses, and control signals among core components like the CPU, memory, and I/O devices. It acts as a shared communication channel — like a highway — enabling efficient data exchange and influencing overall system performance.
- A system bus consists of parallel conductors (wires, PCB tracks, or chip-level trails), where each wire carries one bit; the total number of wires determines the data word size (e.g., 8-bit, 16-bit, etc.).
- It is a shared transmission medium, meaning only one device can transmit data at a time.
Categories of System Buses
System bus contains 3 categories of lines used to provide the communication between the CPU, memory and IO.
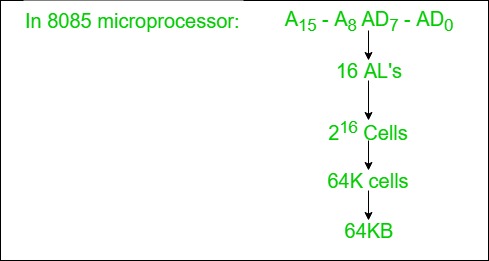
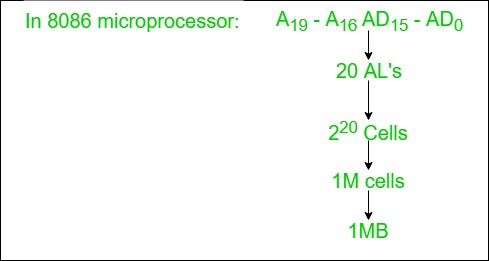
1. Address Lines
The address lines carry addresses from the CPU to memory and I/O devices and are unidirectional.
- They transmit signals only from the CPU to memory or I/O.
- The width of the address lines determines the maximum capacity of the main memory.
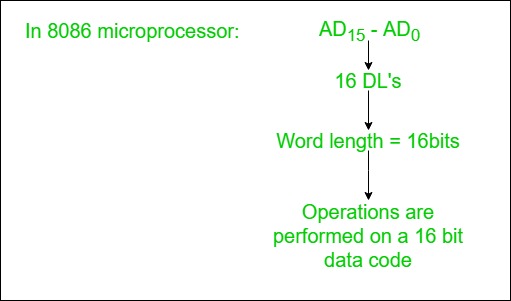
 2. Data Lines
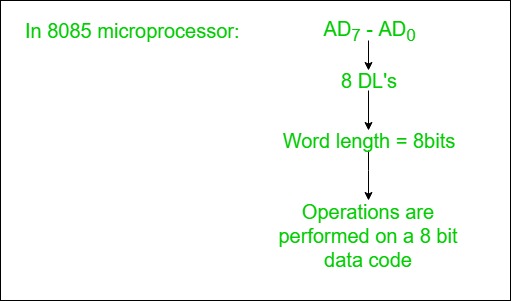
2. Data Lines
The data lines carry binary data between the CPU, memory, and I/O devices and are bidirectional.
- They transmit data both to and from the CPU, memory, and I/O.
- The width of the data lines determines the CPU’s word length, which affects the CPU’s performance.
 3. Control Lines
3. Control Lines
Control lines carry control and timing signals between the CPU, memory, and I/O devices.
- Control signals indicate the type of operation, such as Memory Read, Memory Write, I/O Read, or I/O Write, ensuring components know what action to perform.
- Timing signals synchronize memory and I/O operations with the CPU clock to coordinate data transfers and prevent errors.
- Typical control lines include Memory Read/Write, I/O Read/Write, Bus Request/Grant, Interrupt Request, and Clock signals.
- Control signals also manage bus arbitration, allowing multiple devices to communicate efficiently without conflicts.
- Without control signals, the system would lack coordination, causing data corruption, timing issues, and malfunction.