Presentation Layer Services
Last Updated : 15 Oct, 2025
The Presentation Layer is the 6th layer in the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. It acts as the translator between the Application layer (Layer 7) and the lower layers of the OSI model. Its main purpose is to ensure that the data sent from the sender’s system can be understood by the receiver’s system, regardless of differences in encoding, encryption or compression.
Note: This is why the presentation layer is often referred to as the Translation Layer. In short, the presentation layer plays a vital supporting role in the OSI model, bridging the gap between application-level data and lower-level transmission mechanisms.
Core Services Offered by the Presentation Layer
The presentation layer provides several essential services that prepare, secure and optimize data for transmission across networks. These include:
1. Data Translation
Different systems may use different encoding formats for data representation. The presentation layer translates data into a format that the receiving system can interpret correctly.
Character coding systems:
- ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange)
- EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code)
Example: If the sender’s system uses ASCII and the receiver only supports EBCDIC, the presentation layer converts ASCII-encoded data into EBCDIC.
2. Data Compression
Data compression reduces the size of transmitted data, optimizing bandwidth usage and improving transmission speed. The presentation layer compresses data at the sender’s side and decompresses it at the receiver’s end.
Types of compression:
 Types of Data Compression
Types of Data Compression- Lossless compression: Ensures no data is lost. The decompressed data is identical to the original (e.g., ZIP files for text).
- Lossy compression: Sacrifices some data accuracy for higher compression efficiency (e.g., JPEG for images).
3. Data Encryption and Decryption
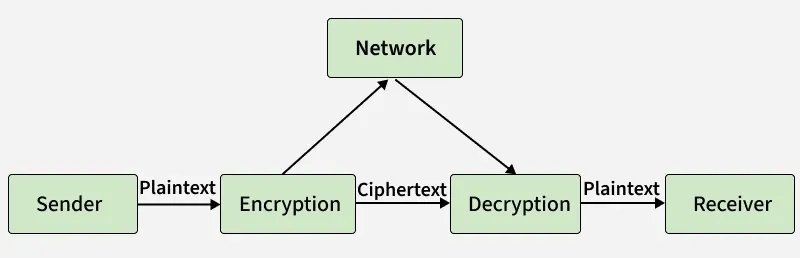
To maintain data security, the presentation layer provides encryption before transmission and decryption upon reception.
 Data Encryption and Decryption
Data Encryption and Decryption
- Encryption: Converts plaintext into ciphertext, making it unreadable to unauthorized users.
- Decryption: Converts ciphertext back into plaintext at the receiver’s side.
Example: Protocols like SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) are used to secure sensitive data such as passwords and banking details.
4. Syntax and Semantics Management
The presentation layer ensures that data is both correctly structured (syntax) and meaningful (semantics) for the receiving system.
- Syntax management: Validates the structure or format of the transmitted data.
- Semantics management: Ensures that the meaning of the transmitted data remains intact.
Example: Conversion between structured formats like XML and JSON so that applications can correctly interpret shared information.
Limitations of the Presentation Layer
Despite its importance, the presentation layer has certain limitations:
- Limited error handling: Relies on the Transport Layer for error detection and correction.
- Protocol dependency: Communication may fail if incompatible protocols or unsupported formats are used.
- Processing overhead: Extra workload due to encryption, compression and translation.
- No direct communication control: Depends on lower layers for physical data transfer.
- Protocol constraints: Effectiveness is limited to supported standards like SSL/TLS, MIME, etc.
Read more about articles Lossless vs Lossy Compression. and Data Encryption and Decryption.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice
My Profile