Congestion Control in Computer Networks
Last Updated : 03 Oct, 2025
In computer networks, congestion occurs when too much data is sent through the network at the same time, causing delays, packet loss, or even network collapse. This is similar to a traffic jam on a highway - when too many cars try to move at once, everything slows down.
Congestion control is the set of techniques and mechanisms used to prevent, detect, and manage congestion. Its main goal is to maintain smooth data flow, fair bandwidth allocation, and efficient utilization of network resources, ensuring a stable and reliable network performance.
Effects of Congestion Control
- Improved Network Stability: Prevents overload and keeps the network running smoothly.
- Reduced Latency and Packet Loss: Ensures data is delivered faster with fewer retransmissions.
- Enhanced Throughput: Maximizes the volume of data successfully transferred in a given time.
- Fairness in Resource Allocation: Distributes bandwidth evenly so no user monopolizes resources.
- Better User Experience: Provides faster access to websites, applications, and services.
- Prevention of Congestion Collapse: Avoids severe breakdowns where the network becomes nearly unusable.
Congestion Control Algorithms
1. Leaky Bucket Algorithm
The leaky bucket algorithm controls the flow of packets by sending them out at a constant, fixed rate, regardless of incoming burst traffic. Packets are placed into a bucket (queue), and if the bucket overflows, excess packets are discarded. This ensures smooth traffic but wastes bandwidth during idle times.
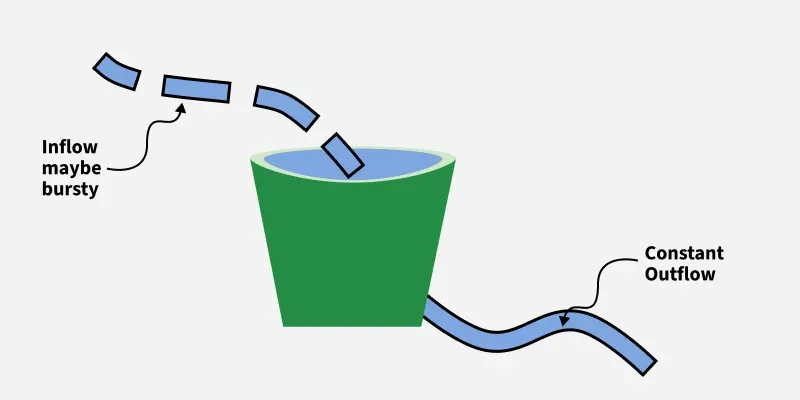 Leaky Bucket
Leaky BucketSteps:
- Packets arrive -> placed into the bucket.
- Bucket leaks (transmits) at a constant rate.
- Bursty traffic is smoothed into uniform traffic.
Limitation: Too rigid, wastes available bandwidth if traffic is bursty.
2. Token Bucket Algorithm
The token bucket algorithm allows more flexibility by generating tokens at a fixed rate. A packet can only be transmitted if a token is available, and each packet consumes one token. If enough tokens accumulate, burst traffic can be sent quickly, making it better for handling variable traffic patterns without unnecessary drops.
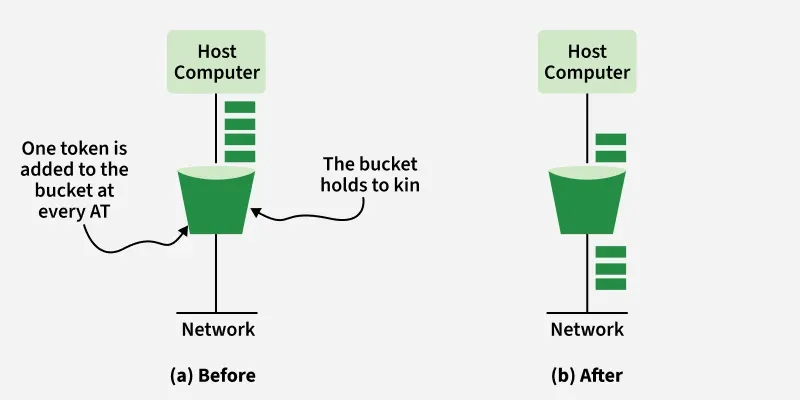 Token Bucket
Token BucketSteps:
- Tokens are added to the bucket at regular intervals.
- Each token permits sending one packet.
- If tokens exist -> packets can be transmitted immediately.
- If no tokens -> packets must wait.
Advantage: Handles bursty traffic efficiently without unnecessary data loss.
Leaky Bucket vs Token Bucket
| Parameter | Leaky Bucket | Token Bucket |
|---|
| Output | Fixed, constant rate | Variable, allows bursts |
|---|
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible |
|---|
| Packet Loss | Possible during bursts | Avoids loss if tokens available |
|---|
Need of Token Bucket: The leaky bucket algorithm enforces output pattern at the average rate, no matter how bursty the traffic is. So in order to deal with the bursty traffic we need a flexible algorithm so that the data is not lost.
Advantages of Congestion Control
- Ensures stable and reliable operation of networks.
- Reduces delays and retransmissions.
- Minimizes data loss.
- Optimizes resource utilization.
- Scales well with growing networks.
- Adapts to changing traffic conditions.
Disadvantages of Congestion Control
- Adds complexity to network design.
- May introduce overhead in processing.
- Can be sensitive to network conditions.
- May struggle with resource prioritization in critical scenarios.
- Effectiveness depends on modern infrastructure.
Explore
Computer Network Basics
Physical Layer
Data Link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer & Presentation Layer
Application Layer
Advanced Topics
Practice
My Profile