Rotate an Array - Clockwise or Right
Last Updated : 30 Oct, 2024
Rotations in the array is defined as the process of rearranging the elements in an array by shifting each element to a new position. This is mostly done by rotating the elements of the array clockwise or counterclockwise.
Types of Rotations in Array
1. Right Rotation (or Clockwise)
Here, The array elements are shifted towards the right.
2. Left Rotation (Or Counter Clockwise)
Here, The array elements are shifted towards the left.

In this article, we will discuss about right rotation of the array. You can refer to Left rotate an array by d positions to know about the left rotation of the array.
How to implement rotations in an array?
There are several ways to implement array rotations. Some of the approaches are mentioned below. Here we are considering right rotation. The movements will be just the opposite for left rotation.
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, d = 2
Output: {5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 4}
Explanation: After first right rotation, arr[] becomes {6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and after the second rotation, arr[] becomes {5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 4}
Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3}, d = 4
Output: {3, 1, 2}
Explanation: The array is rotated as follows:
- After first left rotation, arr[] = {3, 1, 2}
- After second left rotation, arr[] = {2, 3, 1}
- After third left rotation, arr[] = {1, 2, 3}
- After fourth left rotation, arr[] = {3, 1, 2}
At each iteration, shift the elements by one position to the right in a circular fashion (the last element becomes the first). Perform this operation d times to rotate the elements to the right by d positions.
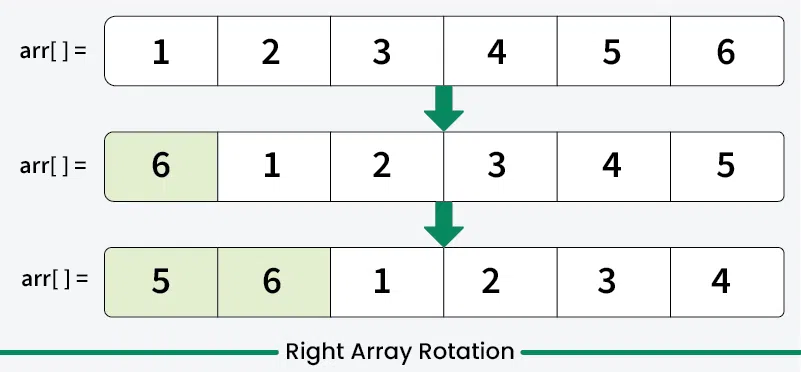
Illustration:
Let us take arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, d = 2.
First Step:
=> Rotate to right by one position.
=> arr[] = {6, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Second Step:
=> Rotate again to right by one position
=> arr[] = {5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 4}
Rotation is done 2 times.
So the array becomes arr[] = {5, 6, 1, 2, 3, 4}
C++ // C++ Program to right rotate the array by d positions // by rotating one element at a time #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to right rotate array by d positions void rotateArr(vector<int>& arr, int d) { int n = arr.size(); // Repeat the rotation d times for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) { // Right rotate the array by one position int last = arr[n - 1]; for (int j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) { arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; } arr[0] = last; } } int main() { vector<int> arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; return 0; } // C Program to right rotate the array by d positions // by rotating one element at a time #include <stdio.h> // Function to right rotate array by d positions void rotateArr(int arr[], int n, int d) { // Repeat the rotation d times for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) { // Right rotate the array by one position int last = arr[n - 1]; for (int j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) { arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; } arr[0] = last; } } int main() { int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, n, d); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); return 0; } // Java Program to right rotate the array by d positions // by rotating one element at a time import java.util.Arrays; class GfG { // Function to right rotate array by d positions static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.length; // Repeat the rotation d times for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) { // Right rotate the array by one position int last = arr[n - 1]; for (int j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) { arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; } arr[0] = last; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } } # Python Program to right rotate the array by d positions # by rotating one element at a time # Function to right rotate array by d positions def rotateArr(arr, d): n = len(arr) # Repeat the rotation d times for _ in range(d): # Right rotate the array by one position last = arr[n - 1] for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1): arr[i] = arr[i - 1] arr[0] = last if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] d = 2 rotateArr(arr, d) # Print the rotated array for i in range(len(arr)): print(arr[i], end=" ")
// C# Program to right rotate the array by d positions // by rotating one element at a time using System; class GfG { // Function to right rotate array by d positions static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.Length; // Repeat the rotation d times for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) { // Right rotate the array by one position int last = arr[n - 1]; for (int j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; arr[0] = last; } } static void Main() { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); } } // JavaScript Program to right rotate the array by d positions // by rotating one element at a time // Function to right rotate array by d positions function rotateArr(arr, d) { let n = arr.length; // Repeat the rotation d times for (let i = 0; i < d; i++) { // Right rotate the array by one position let last = arr[n - 1]; for (let j = n - 1; j > 0; j--) arr[j] = arr[j - 1]; arr[0] = last; } } let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; let d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); console.log(arr.join(' ')); Time Complexity: O(n * d)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
The idea is to use a temporary array of size n, where n is the length of the original array. If we right rotate the array by d positions, the last d elements will be in the beginning and the first (n - d) elements will be at the end.
- Copy the last d elements of the original array into the first d positions of the temporary array
- Then copy the first n - d elements of the original array to the end of temporary array.
- Finally, copy all the elements of temporary array back into the original array.
Illustration for Right Rotation by 2 positions:
Below is the implementation of the above approach
C++ // C++ Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using temporary array #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to rotate vector void rotateArr(vector<int>& arr, int d) { int n = arr.size(); // Handle case when d > n d %= n; // Storing rotated version of array vector<int> temp(n); // Copy last d elements to the front of temp for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) temp[i] = arr[n - d + i]; // Copy the first n - d elements to the back of temp for (int i = 0; i < n - d; i++) temp[i + d] = arr[i]; // Copying the elements of temp in arr // to get the final rotated vector for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = temp[i]; } int main() { vector<int> arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated vector for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; return 0; } // C Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using temporary array #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Function to rotate array by d positions using a temporary array void rotateArr(int arr[], int n, int d) { // Handle case when d > n d %= n; // Storing rotated version of array int temp[n]; // Copy last d elements to the front of temp for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) temp[i] = arr[n - d + i]; // Copy the first n - d elements to the back of temp for (int i = 0; i < n - d; i++) temp[i + d] = arr[i]; // Copying the elements of temp in arr to get the // final rotated array for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = temp[i]; } int main() { int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, n, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); return 0; } // Java Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using temporary array import java.util.Arrays; class GfG { // Function to rotate array by d positions using a temporary array static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.length; // Handle case when d > n d %= n; // Storing rotated version of array int[] temp = new int[n]; // Copy last d elements to the front of temp for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) temp[i] = arr[n - d + i]; // Copy the first n - d elements to the back of temp for (int i = 0; i < n - d; i++) temp[i + d] = arr[i]; // Copying the elements of temp in arr to get the // final rotated array for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = temp[i]; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } # Python Program to right rotate the array by d positions # using temporary array def rotateArr(arr, d): n = len(arr) # Handle case when d > n d %= n # Storing rotated version of array temp = [0] * n # Copy last d elements to the front of temp for i in range(d): temp[i] = arr[n - d + i] # Copy the first n - d elements to the back of temp for i in range(n - d): temp[i + d] = arr[i] # Copying the elements of temp in arr # to get the final rotated array for i in range(n): arr[i] = temp[i] if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] d = 2 rotateArr(arr, d) # Print the rotated array print(' '.join(map(str, arr))) // C# Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using temporary array using System; class GfG { // Function to rotate array static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.Length; // Handle case when d > n d %= n; // Storing rotated version of array int[] temp = new int[n]; // Copy last d elements to the front of temp for (int i = 0; i < d; i++) temp[i] = arr[n - d + i]; // Copy the first n - d elements to the back of temp for (int i = 0; i < n - d; i++) temp[i + d] = arr[i]; // Copying the elements of temp in arr // to get the final rotated array for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) arr[i] = temp[i]; } static void Main() { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); Console.WriteLine(); } } // JavaScript Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using temporary array // Function to rotate array function rotateArr(arr, d) { let n = arr.length; // Handle case when d > n d %= n; // Storing rotated version of array let temp = new Array(n); // Copy last d elements to the front of temp for (let i = 0; i < d; i++) { temp[i] = arr[n - d + i]; } // Copy the first n - d elements to the back of temp for (let i = 0; i < n - d; i++) { temp[i + d] = arr[i]; } // Copying the elements of temp in arr // to get the final rotated array for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { arr[i] = temp[i]; } } let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; let d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array console.log(arr.join(' ')); Time complexity: O(n), where n is the size of input array arr[].
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
3. Juggling Algorithm
The idea behind Juggling Algorithm is that instead of moving one by one, we can use the concept of cycles. Each cycle is independent and represents a group of elements that will shift among themselves during the rotation. If the starting index of a cycle is i, then the next elements will be present at indices (i + d) % n, (i + 2d) % n, (i + 3d) % n ... and so on till we reach back to index i.
So for any index i, we know that element at index i will move to index (i + d) % n. Now, we can simply rotate all elements in the same cycle without interfering with any other cycle.
Working of the above algorithm:
Below is the implementation of the algorithm:
C++ // C++ Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using Juggling Algorithm #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to rotate vector void rotateArr(vector<int> &arr, int d) { int n = arr.size(); // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Calculate the number of cycles in the rotation int cycles = __gcd(n, d); // Process each cycle for (int i = 0; i < cycles; i++) { // Start index of current cycle int currIdx = i; int currEle = arr[currIdx]; // Rotate elements till we reach the start of cycle do { int nextIdx = (currIdx + d) % n; int nextEle = arr[nextIdx]; // Update the element at next index with the current element arr[nextIdx] = currEle; // Update the current element to next element currEle = nextEle; // Move to the next index currIdx = nextIdx; } while (currIdx != i); } } int main() { vector<int> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated vector for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; return 0; } // C Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using Juggling Algorithm #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Function to rotate array void rotateArr(int *arr, int n, int d) { // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Calculate the number of cycles in the rotation int cycles = gcd(n, d); // Process each cycle for (int i = 0; i < cycles; i++) { // Start index of current cycle int currIdx = i; int currEle = arr[currIdx]; // Rotate elements till we reach the start of cycle do { int nextIdx = (currIdx + d) % n; int nextEle = arr[nextIdx]; // Update the element at next index with the current element arr[nextIdx] = currEle; // Update the current element to next element currEle = nextEle; // Move to the next index currIdx = nextIdx; } while (currIdx != i); } } // function to compute GCD int gcd(int a, int b) { while (b) { int temp = b; b = a % b; a = temp; } return a; } int main() { int arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, n, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); return 0; } // Java Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using Juggling Algorithm import java.util.Arrays; class GfG { // Function to rotate array static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.length; // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Calculate the number of cycles in the rotation int cycles = gcd(n, d); // Process each cycle for (int i = 0; i < cycles; i++) { // Start index of current cycle int currIdx = i; int currEle = arr[currIdx]; // Rotate elements till we reach the start of cycle do { int nextIdx = (currIdx + d) % n; int nextEle = arr[nextIdx]; // Update the element at next index with the current element arr[nextIdx] = currEle; // Update the current element to next element currEle = nextEle; // Move to the next index currIdx = nextIdx; } while (currIdx != i); } } // function to compute GCD public static int gcd(int a, int b) { while (b != 0) { int temp = b; b = a % b; a = temp; } return a; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } # Java Program to right rotate the array by d positions # using Juggling Algorithm from math import gcd # Function to rotate list def rotateArr(arr, d): n = len(arr) # Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n # Calculate the number of cycles in the rotation cycles = gcd(n, d) # Process each cycle for i in range(cycles): # Start index of current cycle currIdx = i currEle = arr[currIdx] # Rotate elements till we reach the start of cycle while True: nextIdx = (currIdx + d) % n nextEle = arr[nextIdx] # Update the element at next index with the current element arr[nextIdx] = currEle # Update the current element to next element currEle = nextEle # Move to the next index currIdx = nextIdx if currIdx == i: break if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] d = 2 rotateArr(arr, d) # Print the rotated list for i in range(len(arr)): print(arr[i], end=" ")
// C# Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using Juggling Algorithm using System; class GfG { // Function to rotate array static void RotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.Length; // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Calculate the number of cycles in the rotation int cycles = Gcd(n, d); // Process each cycle for (int i = 0; i < cycles; i++) { // Start index of current cycle int currIdx = i; int currEle = arr[currIdx]; // Rotate elements till we reach the start of cycle do { int nextIdx = (currIdx + d) % n; int nextEle = arr[nextIdx]; // Update the element at next index with the current element arr[nextIdx] = currEle; // Update the current element to next element currEle = nextEle; // Move to the next index currIdx = nextIdx; } while (currIdx != i); } } // function to compute GCD static int Gcd(int a, int b) { while (b != 0) { int temp = b; b = a % b; a = temp; } return a; } static void Main(string[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; RotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); } } // JavaScript Program to right rotate the array by d positions // using Juggling Algorithm // Function to rotate array function rotateArr(arr, d) { const n = arr.length; // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Calculate the number of cycles in the rotation const cycles = gcd(n, d); // Process each cycle for (let i = 0; i < cycles; i++) { // Start index of current cycle let currIdx = i; let currEle = arr[currIdx]; // Rotate elements till we reach the start of cycle do { let nextIdx = (currIdx + d) % n; let nextEle = arr[nextIdx]; // Update the element at next index with the current element arr[nextIdx] = currEle; // Update the current element to next element currEle = nextEle; // Move to the next index currIdx = nextIdx; } while (currIdx !== i); } } // function to compute GCD function gcd(a, b) { while (b !== 0) { const temp = b; b = a % b; a = temp; } return a; } const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; const d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); // Print the rotated array console.log(arr.join(" ")); The idea is based on the observation that if we right rotate the array by d positions, the last d elements will be in the front and first (n - d) elements will be at the end.
- First reverse all the elements of the array.
- Then reverse first d elements.
- Finally, reverse last (n - d) elements to get the final rotated array.
Illustration:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++ // C++ Code to right rotate an array using Reversal Algorithm #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to rotate an array by d elements to the right void rotateArr(vector<int>& arr, int d) { int n = arr.size(); // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Reverse the entire array reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end()); // Reverse the first d elements reverse(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + d); // Reverse the remaining n-d elements reverse(arr.begin() + d, arr.end()); } int main() { vector<int> arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; return 0; } // C Code to right rotate an array using Reversal Algorithm #include <stdio.h> // Function to reverse a portion of the array from start to end void reverse(int arr[], int start, int end) { while (start < end) { int temp = arr[start]; arr[start] = arr[end]; arr[end] = temp; start++; end--; } } // Function to rotate an array by d elements to the right void rotateArr(int arr[], int n, int d) { // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Reverse the entire array reverse(arr, 0, n - 1); // Reverse the first d elements reverse(arr, 0, d - 1); // Reverse the remaining n-d elements reverse(arr, d, n - 1); } int main() { int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, n, d); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) printf("%d ", arr[i]); return 0; } // Java Code to right rotate an array using Reversal Algorithm import java.util.*; class GfG { // Function to rotate an array by d elements to the right static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.length; // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Reverse the entire array reverse(arr, 0, n - 1); // Reverse the first d elements reverse(arr, 0, d - 1); // Reverse the remaining n-d elements reverse(arr, d, n - 1); } // function to reverse a portion of the array static void reverse(int[] arr, int start, int end) { while (start < end) { int temp = arr[start]; arr[start] = arr[end]; arr[end] = temp; start++; end--; } } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); } } # Python Code to right rotate an array using Reversal Algorithm # Function to rotate an array by d elements to the right def rotateArr(arr, d): n = len(arr) # Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n # Reverse the entire array arr.reverse() # Reverse the first d elements arr[:d] = reversed(arr[:d]) # Reverse the remaining n-d elements arr[d:] = reversed(arr[d:]) if __name__ == "__main__": arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] d = 2 rotateArr(arr, d) for i in range(len(arr)): print(arr[i], end=" ")
// C# Code to right rotate an array using Reversal Algorithm using System; class GfG { // Function to rotate an array by d elements to the right static void rotateArr(int[] arr, int d) { int n = arr.Length; // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Reverse the entire array Array.Reverse(arr); // Reverse the first d elements Array.Reverse(arr, 0, d); // Reverse the remaining n-d elements Array.Reverse(arr, d, n - d); } static void Main() { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); } } // JavaScript Code to right rotate an array using Reversal Algorithm // Function to rotate an array by d elements to the right function rotateArr(arr, d) { let n = arr.length; // Handle the case where d > size of array d %= n; // Reverse the entire array arr.reverse(); // Reverse the first d elements reverse(arr, 0, d - 1); // Reverse the remaining n-d elements reverse(arr, d, n - 1); } // function to reverse a portion of the array function reverse(arr, start, end) { while (start < end) { let temp = arr[start]; arr[start] = arr[end]; arr[end] = temp; start++; end--; } } let arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; let d = 2; rotateArr(arr, d); console.log(arr.join(" ")); Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Similar Reads
Rotate an Array by d - Counterclockwise or Left Given an array of integers arr[] of size n, the task is to rotate the array elements to the left by d positions.Examples:Input: arr[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}, d = 2Output: {3, 4, 5, 6, 1, 2}Explanation: After first left rotation, arr[] becomes {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1} and after the second rotation, arr[] bec
15+ min read
Rotate Matrix Clockwise by 1 Given a square matrix, the task is to rotate its elements clockwise by one step.Examples:Input 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9Output: 4 1 27 5 3 8 9 6Input: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1213 14 15 16 Output: 5 1 2 3 9 10 6 4 13 11 7 8 14 15 16 12The idea is to use nested loops to move elements in four directions (right
9 min read
Rotate a Matrix k Times Clockwise Given a matrix of order m*n and a value k, the task is to rotate each ring of the matrix clockwise by k.Examples:Input :k = 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16Output: 13 9 5 114 10 6 215 11 7 316 12 8 4Input : k = 2 1 2 3 410 11 12 5 9 8 7 6Output: 9 10 1 2 8 11 12 3 7 6 5 4Naive Solution - O(k
15+ min read
Rotate an Image 90 Degree Counterclockwise Given an image represented by m x n matrix, rotate the image by 90 degrees in counterclockwise direction. Please note the dimensions of the result matrix are going to n x m for an m x n input matrix.Input: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Output: 4 8 12 16 3 7 11 15 2 6 10 14 1 5 9 13Input: 1
6 min read
Rotate Matrix Counterclockwise by 1 Given a square matrix, the task is to rotate its elements counterclockwise by one step.Examples:Input 1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9Output: 2 3 61 5 94 7 8Input: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 1213 14 15 16 Output: 2 3 4 81 7 11 12 5 6 10 169 13 14 15 The idea is to use nested loops to move elements in four directions (
8 min read
Mth element after K Right Rotations of an Array Given non-negative integers K, M, and an array arr[ ] consisting of N elements, the task is to find the Mth element of the array after K right rotations. Examples: Input: arr[] = {3, 4, 5, 23}, K = 2, M = 1 Output: 5 Explanation: The array after first right rotation a1[ ] = {23, 3, 4, 5} The array a
11 min read