Simple Banking System in C#
Last Updated : 29 Sep, 2025
The Simple Banking System is a console application that demonstrates fundamental C# concepts including Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), methods, arrays and string manipulation. This project allows users to create accounts, deposit money, withdraw money, check balances and view account details.
How the System Works
The banking system manages multiple customer accounts with basic operations:
- Account Creation: Create new bank accounts with customer details
- Deposit: Add money to an existing account
- Withdraw: Remove money from an account (with balance validation)
- Balance Inquiry: Check current account balance
- Account Details: View complete account information
- Account Listing: Display all existing accounts
The system uses arrays to store account data and demonstrates core OOP principles through a BankAccount class.
Algorithm
- Define BankAccount class with properties and methods
- Initialize arrays to store multiple accounts
- Display menu system and get user input
- Process user operations based on choice
- Repeat until user exits
Step 1: Class Definition and Properties
C# using System; namespace SimpleBankingSystem { // BankAccount class demonstrating OOP concepts public class BankAccount { // Private fields (Encapsulation) private int accountNumber; private string accountHolderName; private double balance; private string accountType; // Constructor public BankAccount(int accNum, string name, double initialBalance, string type) { accountNumber = accNum; accountHolderName = name; balance = initialBalance; accountType = type; } // Public properties (Encapsulation) public int AccountNumber { get { return accountNumber; } } public string AccountHolderName { get { return accountHolderName; } set { accountHolderName = value; } } public double Balance { get { return balance; } } public string AccountType { get { return accountType; } } } } Explanation
Namespace: Groups related classes together and prevents naming conflicts.
Class Definition: The BankAccount class represents a real-world bank account using OOP principles.
Private Fields: Data members are kept private to ensure encapsulation - external code cannot directly access or modify them.
- accountNumber: Unique identifier for each account
- accountHolderName: Customer's name as a string
- balance: Current account balance as double for decimal values
- accountType: Type of account (Savings/Checking)
Constructor: Special method that initializes new objects with required data when creating an account.
Properties: Provide controlled access to private fields:
- get accessor retrieves the value
- set accessor allows modification (only for AccountHolderName)
- Read-only properties (AccountNumber, Balance, AccountType) only have get accessors
Step 2: Account Methods (Deposit and Withdraw)
C# // Method to deposit money public void Deposit(double amount) { if (amount > 0) { balance += amount; Console.WriteLine($"Successfully deposited ${amount:F2}"); Console.WriteLine($"New balance: ${balance:F2}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Deposit amount must be positive!"); } } // Method to withdraw money public bool Withdraw(double amount) { if (amount <= 0) { Console.WriteLine("Withdrawal amount must be positive!"); return false; } else if (amount > balance) { Console.WriteLine("Insufficient funds!"); Console.WriteLine($"Current balance: ${balance:F2}"); return false; } else { balance -= amount; Console.WriteLine($"Successfully withdrew ${amount:F2}"); Console.WriteLine($"New balance: ${balance:F2}"); return true; } } // Method to display account details public void DisplayAccountDetails() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- Account Details ---"); Console.WriteLine($"Account Number: {accountNumber}"); Console.WriteLine($"Account Holder: {accountHolderName}"); Console.WriteLine($"Account Type: {accountType}"); Console.WriteLine($"Current Balance: ${balance:F2}"); Console.WriteLine("------------------------"); } Explanation
Deposit Method:
- Takes double amount parameter
- Validates input (must be positive)
- Updates balance and displays confirmation
- Uses string interpolation ($"") and format specifier (:F2) for currency display
Withdraw Method:
- Returns bool to indicate success/failure
- Multiple validation checks using if-else statements
- Checks for positive amount and sufficient funds
- Updates balance only if all validations pass
DisplayAccountDetails Method:
- void return type (no return value)
- Uses formatted console output for clean display
- Demonstrates string formatting and layout techniques
Step 3: Main Program Structure and Arrays
C# class Program { // Array to store bank accounts static BankAccount[] accounts = new BankAccount[100]; static int accountCount = 0; static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("================================="); Console.WriteLine(" Welcome to Simple Bank System "); Console.WriteLine("================================="); // Main program loop while (true) { DisplayMenu(); int choice = GetUserChoice(); switch (choice) { case 1: CreateAccount(); break; case 2: DepositMoney(); break; case 3: WithdrawMoney(); break; case 4: CheckBalance(); break; case 5: ViewAccountDetails(); break; case 6: ListAllAccounts(); break; case 7: Console.WriteLine("Thank you for using Simple Bank System!"); return; default: Console.WriteLine("Invalid choice! Please try again."); break; } Console.WriteLine("\nPress any key to continue..."); Console.ReadKey(); Console.Clear(); } } } Explanation
Static Array:
- BankAccount[] accounts stores up to 100 account objects
- static keyword allows access without creating Program instance
- accountCount tracks how many accounts are currently stored
Main Method:
- Entry point of the program
- Contains infinite loop (while(true)) for continuous operation
- Uses switch statement for menu navigation
- Console.ReadKey() pauses execution
- Console.Clear() clears screen for better user experience
Program Flow:
- Display welcome message
- Show menu and get user choice
- Execute corresponding method based on choice
- Repeat until user chooses to exit
C# // Method to display menu static void DisplayMenu() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- Bank Menu ---"); Console.WriteLine("1. Create Account"); Console.WriteLine("2. Deposit Money"); Console.WriteLine("3. Withdraw Money"); Console.WriteLine("4. Check Balance"); Console.WriteLine("5. View Account Details"); Console.WriteLine("6. List All Accounts"); Console.WriteLine("7. Exit"); Console.Write("Enter your choice (1-7): "); } // Method to get user choice with validation static int GetUserChoice() { string input = Console.ReadLine(); if (int.TryParse(input, out int choice)) { return choice; } return -1; // Invalid input } // Method to find account by account number static BankAccount FindAccount(int accountNumber) { for (int i = 0; i < accountCount; i++) { if (accounts[i].AccountNumber == accountNumber) { return accounts[i]; } } return null; } Explanation
DisplayMenu Method:
- static method accessible without object instance
- Uses Console.WriteLine() for menu options
- Console.Write() for input prompt (no newline)
GetUserChoice Method:
- Demonstrates input validation using int.TryParse()
- Returns -1 for invalid input (error handling)
- Converts string input to integer safely
FindAccount Method:
- Linear search through accounts array
- Uses for loop to iterate through stored accounts
- Returns BankAccount object if found, null if not found
- Demonstrates array traversal and object comparison
Step 5: Account Creation and String Validation
C# // Method to create new account static void CreateAccount() { if (accountCount >= accounts.Length) { Console.WriteLine("Maximum number of accounts reached!"); return; } Console.WriteLine("\n--- Create New Account ---"); Console.Write("Enter account holder name: "); string name = Console.ReadLine(); // Validate name input if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(name)) { Console.WriteLine("Invalid name! Account creation failed."); return; } Console.Write("Enter account type (Savings/Checking): "); string type = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("Enter initial deposit amount: $"); string balanceInput = Console.ReadLine(); if (double.TryParse(balanceInput, out double initialBalance) && initialBalance >= 0) { // Generate account number int accountNumber = 1000 + accountCount + 1; // Create new account object BankAccount newAccount = new BankAccount(accountNumber, name, initialBalance, type); // Add to array accounts[accountCount] = newAccount; accountCount++; Console.WriteLine($"\nAccount created successfully!"); Console.WriteLine($"Account Number: {accountNumber}"); Console.WriteLine($"Account Holder: {name}"); Console.WriteLine($"Initial Balance: ${initialBalance:F2}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid amount! Account creation failed."); } } Explanation
Array Bounds Checking:
- Prevents array overflow by checking accountCount >= accounts.Length
- Graceful error handling with informative messages
String Validation:
- string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace() checks for empty or whitespace-only input
- Ensures data integrity before account creation
Account Number Generation:
- Starts from 1001 (1000 + accountCount + 1)
- Provides unique identifiers for each account
Object Creation and Storage:
- Uses constructor to create new BankAccount object
- Stores object in array and increments counter
- Demonstrates object instantiation and array manipulation
Input Validation:
- double.TryParse() safely converts string to double
- Additional check for non-negative balance
- Multiple validation layers ensure data integrity
Step 6: Transaction Methods (Deposit/Withdraw/Balance Check)
C# // Method to deposit money static void DepositMoney() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- Deposit Money ---"); Console.Write("Enter account number: "); if (int.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out int accountNumber)) { BankAccount account = FindAccount(accountNumber); if (account != null) { Console.Write("Enter deposit amount: $"); if (double.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out double amount)) { account.Deposit(amount); } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid amount entered!"); } } else { Console.WriteLine("Account not found!"); } } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid account number!"); } } // Method to withdraw money static void WithdrawMoney() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- Withdraw Money ---"); Console.Write("Enter account number: "); if (int.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out int accountNumber)) { BankAccount account = FindAccount(accountNumber); if (account != null) { Console.Write("Enter withdrawal amount: $"); if (double.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out double amount)) { account.Withdraw(amount); } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid amount entered!"); } } else { Console.WriteLine("Account not found!"); } } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid account number!"); } } // Method to check balance static void CheckBalance() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- Check Balance ---"); Console.Write("Enter account number: "); if (int.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out int accountNumber)) { BankAccount account = FindAccount(accountNumber); if (account != null) { Console.WriteLine($"Current Balance: ${account.Balance:F2}"); } else { Console.WriteLine("Account not found!"); } } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid account number!"); } } ExplanationCommon Pattern in Transaction Methods:
- Display section header
- Get account number with validation
- Find account using FindAccount() method
- Perform operation if account exists
- Handle errors gracefully
Method Reusability:
- FindAccount() is reused across multiple methods
- Reduces code duplication and improves maintainability
Error Handling:
- Multiple validation layers (input parsing, account existence, amount validation)
- Informative error messages for user guidance
Object Method Calls:
- account.Deposit(amount) and account.Withdraw(amount) demonstrate method invocation
- Accessing object properties with account.Balance
Step 7: Account Management and Display Methods
C# // Method to view account details static void ViewAccountDetails() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- View Account Details ---"); Console.Write("Enter account number: "); if (int.TryParse(Console.ReadLine(), out int accountNumber)) { BankAccount account = FindAccount(accountNumber); if (account != null) { account.DisplayAccountDetails(); } else { Console.WriteLine("Account not found!"); } } else { Console.WriteLine("Invalid account number!"); } } // Method to list all accounts static void ListAllAccounts() { Console.WriteLine("\n--- All Accounts ---"); if (accountCount == 0) { Console.WriteLine("No accounts found!"); return; } Console.WriteLine($"{"Account#",-10} {"Name",-20} {"Type",-10} {"Balance",-10}"); Console.WriteLine(new string('-', 50)); for (int i = 0; i < accountCount; i++) { BankAccount account = accounts[i]; Console.WriteLine($"{account.AccountNumber,-10} {account.AccountHolderName,-20} {account.AccountType,-10} ${account.Balance,-10:F2}"); } } Explanation
ViewAccountDetails Method:
- Follows same validation pattern as other transaction methods
- Calls object's DisplayAccountDetails() method for formatted output
ListAllAccounts Method:
- Checks if any accounts exist before displaying
- Uses formatted string output for tabular display
- {"Account#",-10} creates left-aligned column with width 10
- new string('-', 50) creates separator line
- for loop iterates through all stored accounts
String Formatting:
- Negative numbers in format specifiers (-10) create left alignment
- :F2 formats currency with 2 decimal places
- Creates professional-looking tabular output
Outputs
1. Creating an Account
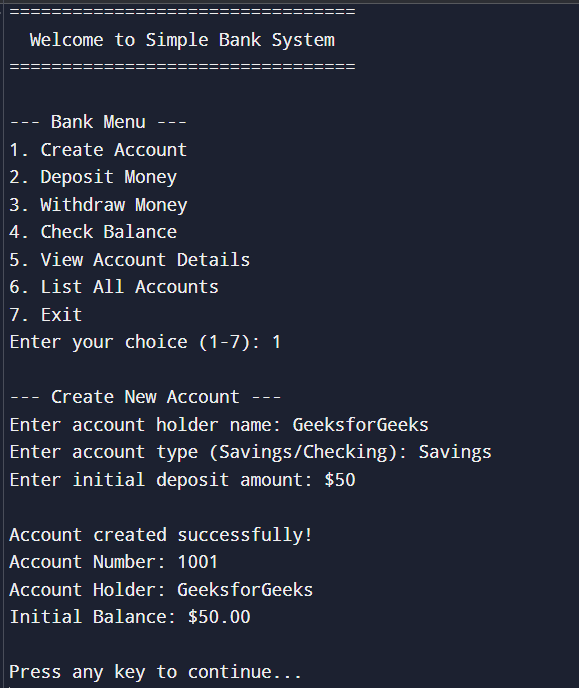 Creating an Account
Creating an Account2. Depositing money in Account
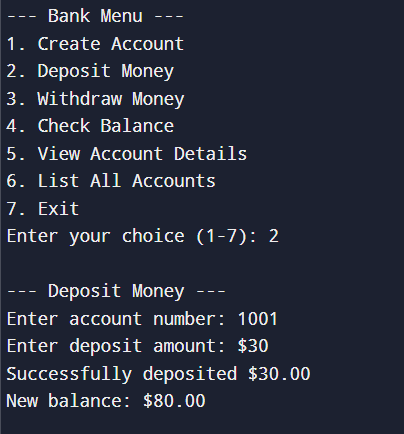 Depositing money
Depositing money3. Withdrawing Money
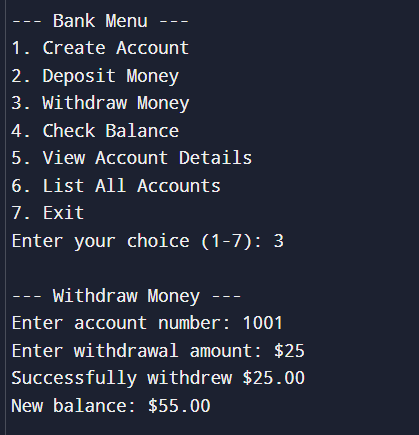 Withdrawing money
Withdrawing money4. Check Balance
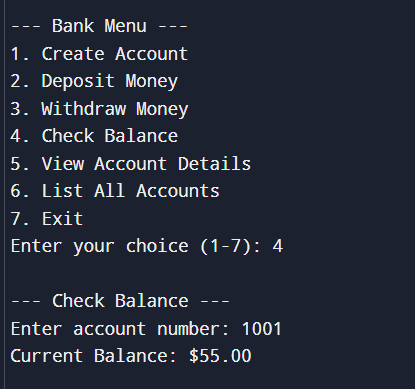 Checking balance
Checking balance5. Check Account details
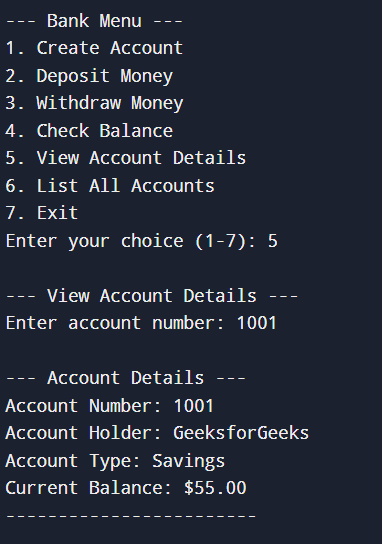 Checking account details
Checking account details6. List all accounts
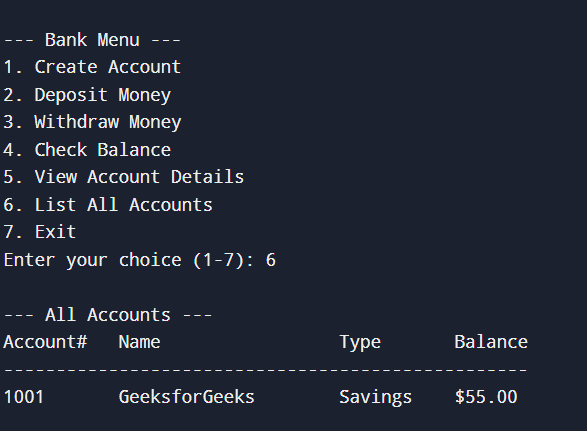 List all accounts
List all accounts
Explore
Introduction
Fundamentals
Control Statements
OOP Concepts
Methods
Arrays
ArrayList
String
Tuple
Indexers
My Profile