Backup Database in MS SQL Server
Last Updated : 20 Sep, 2024
Creating regular backups of your database is crucial for ensuring data integrity and recovery in case of system failures or accidental data loss. In Microsoft SQL Server, we can create full database backups using either SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) or Transact-SQL (T-SQL).
In this guide, we will learn an overview of the methods for performing full backups, highlight the necessary permissions and prerequisites, and explain how to handle backups using both SSMS and T-SQL.
Prerequisites
To Create a Full Database Backup, the below methods could be used:
Restriction:
Backups created on a newer version of SQL Server cannot be restored in previous versions of SQL Server.
Facts to know:
- When the database size increases, full database backups require more time and more storage space to complete.
- The sp_spaceused system stored procedure could be used to estimate the size of a full database backup.
- An entry is added for every successful backup in the SQL Server error logs and in the system event log.
Permissions:
- BACKUP DATABASE permissions to members of the sysadmin server role and the db_owner and db_backupoperator to database roles.
- The account under which the SQL Server service runs must have write permissions to the backup device, so the SQL Server service must be able to read and write to the device.
Backup Database in MS SQL Server Using SQL Server Management Studio
- In Object Explorer, connect to the desired instance of the Microsoft SQL Server Database Engine, expand the server instance.
- Expand Databases box and select a user database or select a system database.
- Right-click the database that need to backup, click on Tasks, and then click Back Up.
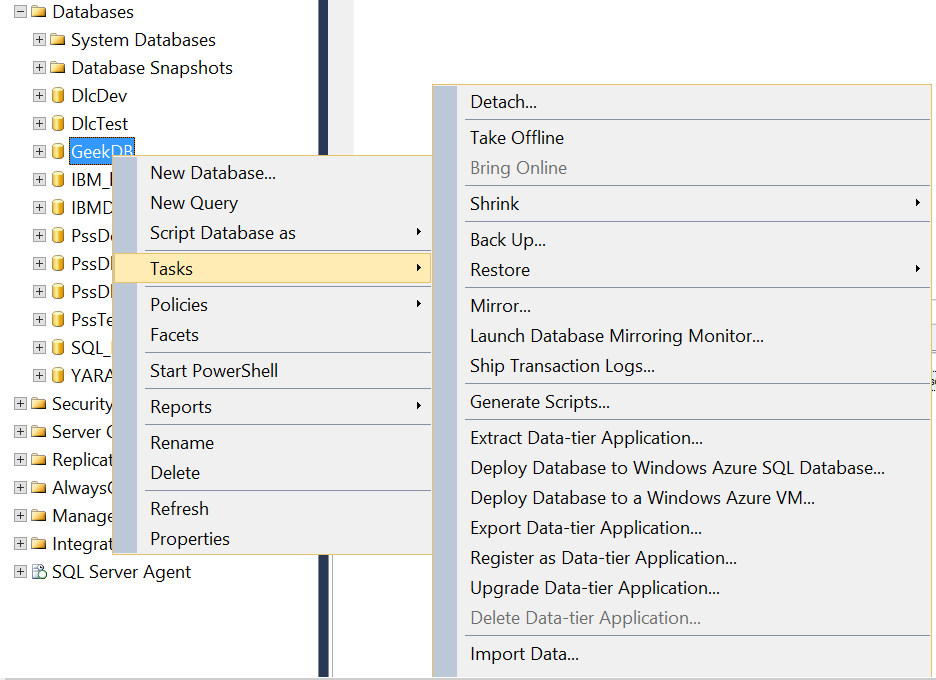
- In the Back-Up Database dialog box, the database that you selected appears in the drop-down list.
- In the Backup type drop-down list, select the backup type - the default is Full.
- Under Backup component, select Database.
- Review the default location for the backup file, in the Destination section.
- To remove a backup destination, click on it and Remove.
- To backup to a new device, change the selection using the Add and select destination.
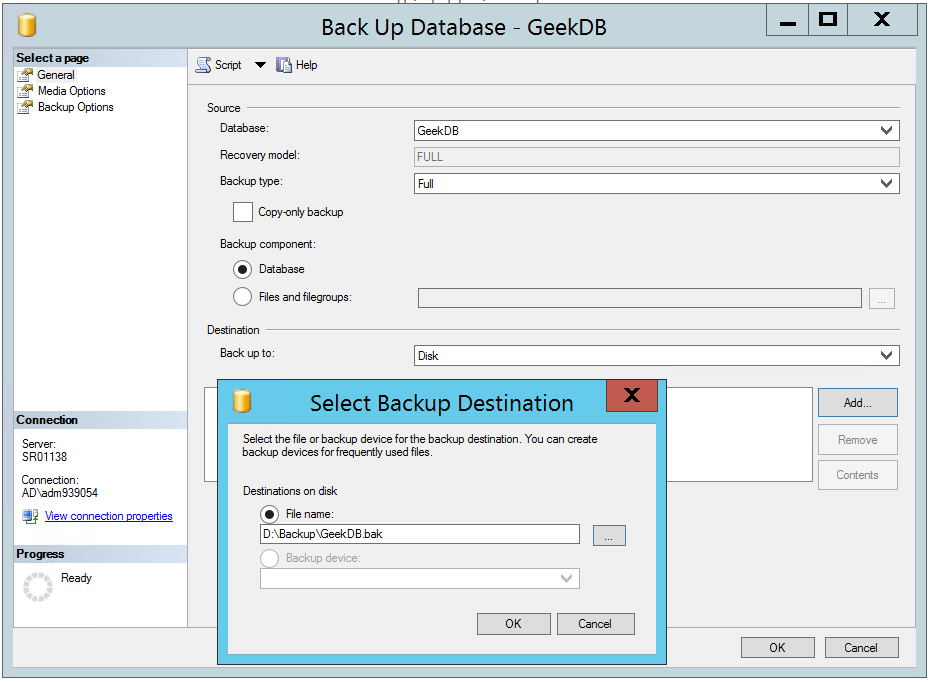
- Review the other available settings under the Media Options and Backup Options pages.

- Click OK to start the backup. Click OK to close the SQL Server Management Studio dialog box once the backup completed successfully.

Backup Database in MS SQL Server Using Transact-SQL:
- Connect to the Database Engine.
- Open New Query.
Syntax:
BACKUP DATABASE databasename TO backup_device [][WITH with_options[]];
Where,
- databasename: It is the database that need to be backed up.
- backup_device [DISK | TAPE]: It declares a list of backup devices from 1 to 64 to be used for the backup operation.
- WITH with_options [] : defines one or more options mentioned below:
- COMPRESSION | NO_COMPRESSION:It defines whether backup compression is performed on this backup or not.
- DESCRIPTION:It could have a maximum of 255 characters and describes the backup set.
- NAME: It could have a maximum of 128 characters and describes the name of the backup set.
- FORMAT [MEDIANAME] [MEDIADESCRIPTION]: It could be used while using media for the first time or to overwrite all existing data.
Example 1: Back up Database to a Disk Device
Let's write a SQL query performs a full backup of the GeekDB database and saves it to a specified disk location.
USE GeekDB;
GO
BACKUP DATABASE GeekDB
TO DISK = 'D:\Backup\GeekDB.bak'
WITH FORMAT,
MEDIANAME = 'GeekDBBackup',
NAME = 'Full Backup of GeekDB';
GO
Explanation:
- This query operates on the
GeekDB database, creating a full backup stored on the disk at D:\Backup\GeekDB.bak.
- The
WITH FORMAT option ensures that the backup file is initialized and any existing backup on the disk is overwritten.
- The
MEDIANAME specifies a label for the backup media, while the NAME provides a descriptive name for the backup set.
Example 2: Back up to a Tape Device
Let's write a SQL query provided performs a full backup of the GeekDB database to a specified tape location.
USE GeekDB;
GO
BACKUP DATABASE GeekDB
TO TAPE = '\\.\TapeLocation'
WITH NOINIT,
NAME = 'Full Backup of GeekDB';
GO
Explanation:
- The query executes in the
GeekDB database and creates a full backup of it, saving the backup to the tape drive located at \\.\TapeLocation.
- The
WITH NOINIT option ensures that the backup is appended to the existing backups on the tape rather than overwriting them, while the NAME parameter provides a label for this backup set.
Conclusion
Regular full database backups are essential for maintaining the health and recoverability of your SQL Server databases. Whether using SQL Server Management Studio for a graphical interface or Transact-SQL for scripting and automation, it's vital to ensure that backups are performed correctly and stored securely. Remember that backups created in newer SQL Server versions may not be restored in older versions, and proper permissions must be set for both the SQL Server service account and the database roles involved.
Similar Reads
SQL Interview Questions Are you preparing for a SQL interview? SQL is a standard database language used for accessing and manipulating data in databases. It stands for Structured Query Language and was developed by IBM in the 1970's, SQL allows us to create, read, update, and delete data with simple yet effective commands.
15+ min read
SQL Tutorial Structured Query Language (SQL) is the standard language used to interact with relational databases. Whether you want to create, delete, update or read data, SQL provides the structure and commands to perform these operations. SQL is widely supported across various database systems like MySQL, Oracl
8 min read
SQL Commands | DDL, DQL, DML, DCL and TCL Commands SQL commands are crucial for managing databases effectively. These commands are divided into categories such as Data Definition Language (DDL), Data Manipulation Language (DML), Data Control Language (DCL), Data Query Language (DQL), and Transaction Control Language (TCL). In this article, we will e
7 min read
SQL Joins (Inner, Left, Right and Full Join) SQL joins are fundamental tools for combining data from multiple tables in relational databases. Joins allow efficient data retrieval, which is essential for generating meaningful observations and solving complex business queries. Understanding SQL join types, such as INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN, RIGHT JO
5 min read
Normal Forms in DBMS In the world of database management, Normal Forms are important for ensuring that data is structured logically, reducing redundancy, and maintaining data integrity. When working with databases, especially relational databases, it is critical to follow normalization techniques that help to eliminate
7 min read
SQL Query Interview Questions SQL or Structured Query Language, is the standard language for managing and manipulating relational databases such as MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL. It serves as a powerful tool for efficiently handling data whether retrieving specific data points, performing complex analysis, or modifying database
15+ min read
CTE in SQL In SQL, a Common Table Expression (CTE) is an essential tool for simplifying complex queries and making them more readable. By defining temporary result sets that can be referenced multiple times, a CTE in SQL allows developers to break down complicated logic into manageable parts. CTEs help with hi
6 min read
Top 60 DBMS Interview Questions with Answers for 2025 A Database Management System (DBMS) is the backbone of modern data storage and management. Understanding DBMS concepts is critical for anyone looking to work with databases. Whether you're preparing for your first job in database management or advancing in your career, being well-prepared for a DBMS
15+ min read
Window Functions in SQL SQL window functions are essential for advanced data analysis and database management. It is a type of function that allows us to perform calculations across a specific set of rows related to the current row. These calculations happen within a defined window of data and they are particularly useful
6 min read
SQL | WITH Clause SQL queries can sometimes be complex, especially when you need to deal with multiple nested subqueries, aggregations, and joins. This is where the SQL WITH clause also known as Common Table Expressions (CTEs) comes in to make life easier. The WITH Clause is a powerful tool that simplifies complex SQ
6 min read