atrm command in Linux with examples
Last Updated : 04 Apr, 2019
atrm command is used to remove the specified jobs. To remove a job, its job number is passed in the command. A user can only delete jobs that belong to him. Only superuser can delete any job even if that belongs to another user.
Syntax: atrm [-V] job [job...]
Options: - -V : Used to print the version number
atrm -V

- job : Job number of the job which is to be deleted. To see the list of the pending jobs use following:
 Example 1: Deleting job number 22.
Example 1: Deleting job number 22. atrm 22
 Example 2: Deleting multiple jobs in single atrm command:
Example 2: Deleting multiple jobs in single atrm command: atrm 21 26

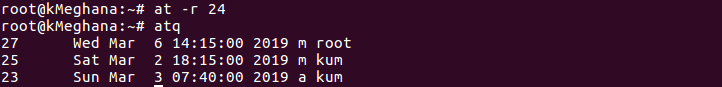
Alternative command for atrm: Syntax: at -r Job
Example 1: Deleting single job:
at -r 24
 Example 2:
Example 2: Deleting multiple jobs:
at -r 25 27

const rawVideoDataMap = null; // Convert it into a JS Map const videoDataMap = new Map(Object.entries(rawVideoDataMap)); document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function () { let currentlySelectedTile = document.getElementById("video-info-container-title"); let firstVideoH2; let firstSelectedVideo var videoPlayer = document.getElementById('video-iframe-container'); if (!videoPlayer) return; var videoIframe = videoPlayer.querySelector('iframe'); if (!videoIframe) return; // Safely inject PHP data as JSON into JavaScript var resp = null; function postToIframeWhenReady(iframe, data, maxAttempts = 20, intervalTime = 100) { let attempts = 0; const interval = setInterval(() => { if (iframe && iframe.contentWindow) { try { iframe.contentWindow.postMessage(data, '*'); clearInterval(interval); } catch (err) { console.warn("❌ Failed to postMessage, retrying..."); } } if (++attempts >= maxAttempts) { console.warn("⚠️ postMessage failed: iframe not ready after multiple attempts."); clearInterval(interval); } }, intervalTime); } // Call the function right after iframe is confirmed to exist videoIframe.onload = function () { postToIframeWhenReady(videoIframe, { resp: resp, inView: false }); }; const playlistContainer = document.getElementById("video-playlist-container"); if(playlistContainer) { firstSelectedVideo = playlistContainer.querySelectorAll('.playlist-video-tile')[0]; if(firstSelectedVideo) { firstVideoH2 = firstSelectedVideo.querySelector('h2'); firstVideoH2.style.setProperty('color', 'var(--discussion-button-color)', 'important'); } } function changeCurrentPlayingVideoTitle(tile, autoplayed = true) { const playlistVideoTileHeading = tile.querySelector('h2'); if (playlistVideoTileHeading) { if(!autoplayed && firstVideoH2.innerText !== playlistVideoTileHeading.innerText) { firstVideoH2.style.setProperty('color', '#EC4E20', 'important'); } if(autoplayed) { let siblingElement = tile.previousElementSibling; const siblingElementH2 = siblingElement.querySelector('h2'); siblingElementH2.style.setProperty('color', '#EC4E20', 'important'); firstVideoH2 = playlistVideoTileHeading; } playlistVideoTileHeading.style.setProperty('color', 'var(--discussion-button-color)', 'important'); if (currentlySelectedTile) { currentlySelectedTile.innerText = playlistVideoTileHeading.innerText; } } } // Inject the video data map as a JS object window.addEventListener('message', function (event) { if (event.data.type === 'AUTOPLAYED_NEXT_VIDEO' && event.data.autoplayPlaylistEnabled) { // Changing the current video index on autoplaying the next video from playlist const allVideoTiles = Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('.playlist-video-tile')); changeCurrentPlayingVideoTitle(allVideoTiles[event.data.currentVideoIndex]); } }); if(playlistContainer) { playlistContainer.addEventListener('click', (event) => { const tile = event.target.closest('.playlist-video-tile'); // Find the index of the clicked tile const allTiles = Array.from(playlistContainer.querySelectorAll('.playlist-video-tile')); const currentIndex = allTiles.findIndex((el) => el === tile); if (tile) { const videoId = tile.getAttribute('data-video-id'); const videoData = videoDataMap.get(videoId); videoIframe.contentWindow.postMessage({ playlist: [videoData], inView: true, clickedVideoFromPlaylist: true, currentIndex: currentIndex }, '*'); // handleVideoTitle([videoData]); changeCurrentPlayingVideoTitle(tile, false); firstVideoH2 = tile.querySelector('h2'); } }); } });
Similar Reads
How to Create and Use Alias Command in Linux Imagine you're lost in a maze of complicated Linux commands. You stumble upon a secret doorway marked "Alias," and inside you find shortcuts to all your favorite commands! That's what creating aliases is like. You get to make your own mini-commands for the long ones you use all the time, making thin
6 min read
amixer command in Linux with Examples amixer is a command-line mixer for ALSA(Advanced Linux Sound Architecture) sound-card driver . amixer can support multiple soundcards. amixer with no arguments will display the current mixer settings for the default soundcard as well as the device. This is a good way to see a list of the simple mixe
2 min read
aplay command in Linux with examples aplay is a command-line audio player for ALSA(Advanced Linux Sound Architecture) sound card drivers. It supports several file formats and multiple soundcards with multiple devices. It is basically used to play audio on command-line interface. aplay is much the same as arecord only it plays instead o
2 min read
aplaymidi Command in Linux with Examples aplaymidi command in Linux is used to play standard MIDI(Musical Instrument Digital Interface) files, by sending the content of a MIDI file to an ALSA(Advanced Linux Sound Architecture) MIDI port, sound renderer like timidity or a hardware MIDI device is required to play MIDI files. Syntaxaplaymidi
3 min read
apropos command in Linux with Examples Linux/Unix comes with a huge number of commands and thus it become quite difficult sometimes to remember each and every command. apropos command becomes useful in such cases. apropos command helps the user when they don't remember the exact command but knows a few keywords related to the command tha
3 min read
apt command in linux with examples apt provides a high-level Command Line Interface (CLI) for the APT package management system, offering a user-friendly interface intended for interactive use. It simplifies common tasks like installation, upgrades, and removal, with better defaults than more specialized tools like apt-get and apt-ca
5 min read
apt-get command in Linux with Examples The command-line tool `apt-get` is the most popular package management tool used in our Debian-based Linux operating system. This article provides an overview of `apt-get` and its basic syntax. It will include the most commonly used commands, their syntax, description, and examples. It also gives an
15+ min read
aptitude command in Linux with examples The aptitude command in Linux provides a user-friendly interface to interact with the machine's package manager. It functions similarly to a control panel, like in Windows, allowing you to install, upgrade, and remove packages. The command can be used in either a visual interface or directly via the
4 min read
ar command in Linux with examples The 'ar' command in Linux is a versatile tool used for creating, modifying, and extracting files from archives. An archive is essentially a collection of files bundled together in a specific structure, making it easy to manage multiple files as a single entity. Each file within the archive is referr
5 min read
arch command in Linux with examples The arch command is a simple yet powerful utility in Linux used to display the architecture of the system's hardware. By running this command, users can quickly determine the type of processor their system is running on, such as i386, x86_64, or arm. Knowing the architecture is crucial for installin
2 min read